typeof
typeof 操作符返回一个字符串,表示未经计算的操作数的类型。(MDN)
typeof 可以用来检测一个值的类型。
1. 表现
在 ES6 之前,typeof 在浏览器的表现是这样的:
| 类型 | 结果 |
|---|---|
| Boolean | “boolean” |
| String | “string” |
| Number | “Number” |
| Function | “function” |
| undefined | “undefined” |
| null | “object” |
| 数组 | “object” |
| 任意对象 | “object” |
typeof 233; // 输出:"number"
typeof '嘎?'; // 输出:"string"
typeof true; // 输出:"boolean"
typeof undefined; // 输出:"undefined"
var fn1 = function() {};
function fn2() {};
typeof fn1; // 输出:"function"
typeof fn2; // 输出:"function"
typeof null; // 输出:"object"
typeof []; // 输出:"object";
typeof ['9', '9', '6']; // 输出:"object";
typeof {}; // 输出:"object"
2. 为什么检查 null 的类型返回 object
这是一个历史遗留问题,JavaScript 从出现开始都是这个表现。
typeof null; // 输出:"object"
原因是 null 表示为一个空指针,其内部表示类型的标签和对象相同,所以会被设别为 object。
有提案表示想要修复这个问题,使表现如下:
typeof null; // 输出:"null"
但这个提案被拒绝了。
3. 为什么检查数组类型返回 object
数组的本质是个对象,从数组的原型上观察就可以发现。
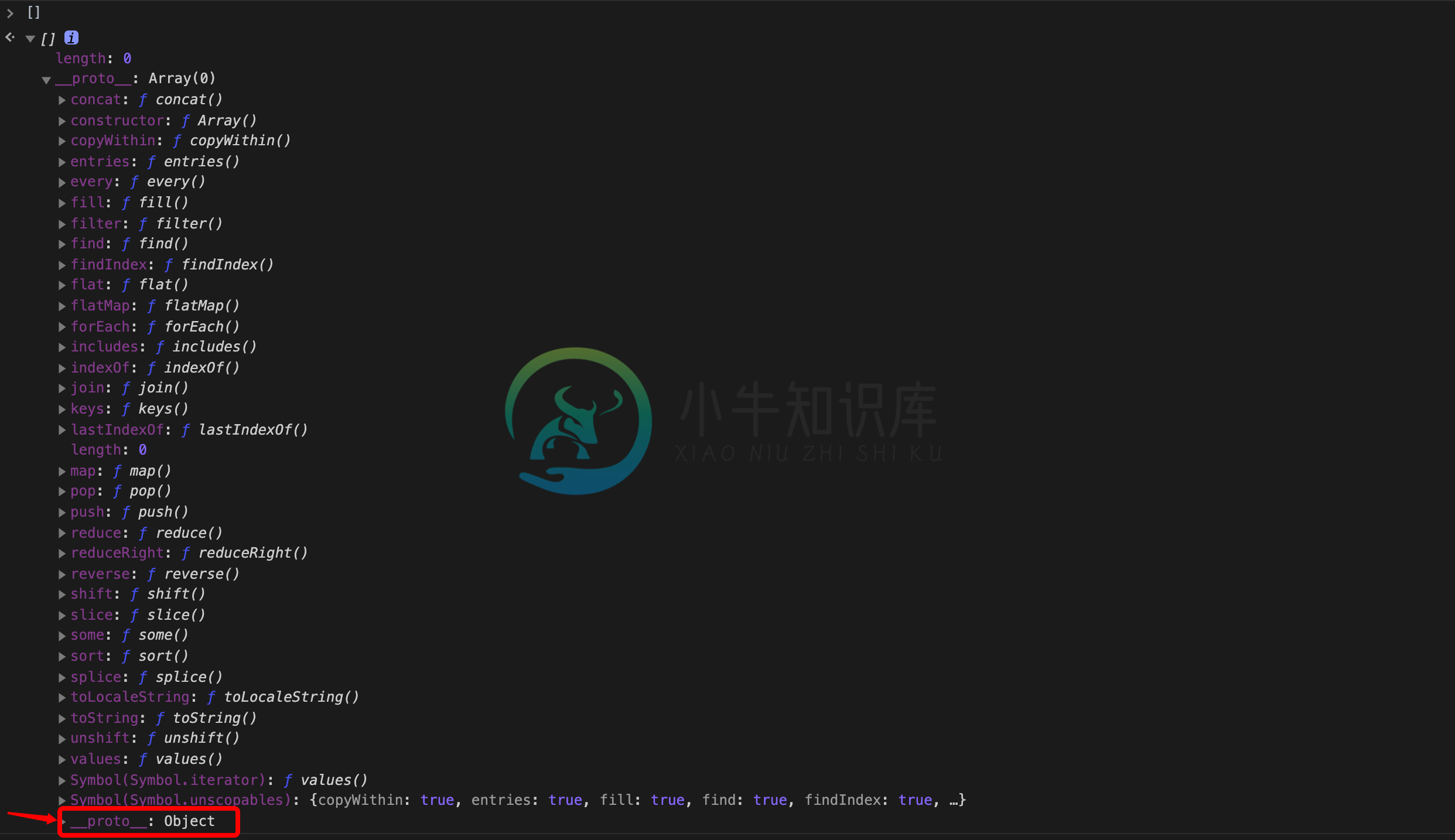
同时可以通过 instanceof 检测数组的原型链上是否有 Object。
Array instanceof Object; // 输出:true
4. 由基础对象构建的值也返回 object
事实上 typeof 只对字面量敏感。
var num = 1;
typeof num; // 输出:"number"
如果采用构造函数的形式得到一个值:
var num = new Number(1);
typeof num; // 输出:"object"
所以除了 Function,构造出来的一个值,使用 typeof 检测类型都会返回 object。
var fn = new Function('console.log("我是特例!")');
typeof fn; // 输出:"function"
5. 更精准的检测类型
使用 Object.prototype.toString.call,可以更精准的检测类型。
Object.prototype.toString.call(1); // 输出: [object Number]
Object.prototype.toString.call(false); // 输出: [object Boolean]
Object.prototype.toString.call(null); // 输出: [object Null]
Object.prototype.toString.call([1]); // 输出: [object Array]
Object.prototype.toString.call({}); // 输出: [object Object]
通过观察结果可以看到,使用这个方式可以区别出数组、对象、null这些 typeof 无法区分的类型。
可是为什么要这样用呢?不能直接调用一个值的 toString 吗?
这涉及到了原型的问题,例如 Number:
var number = 996;
console.log(number.__proto__.toString);
number 变量的 toString 方法其实就是 Number 的 prototype 属性下的 toString 方法。
var number = 996;
console.log(number.__proto__.toString === Number.prototype.toString);
从这就可以看出进行 number.toString() 操作,调用的就不是 Object.prototype.toString 了。
这两个 toString 方法的内容不同,Number.prototype.toString 做的事情其实就是根据一些规则,将值转成字符串,而 Object.prototype.toString 是将对象的一个类型标签进行组合输出。
也就是说大部分数据类型的原始对象都提供了新的 toString 方法,也就无法调用到 Object.prototype.toString,所以要用这种方式。
那为什么 Object.prototype.toString 会可以精准判断出一个值的类型呢?
这是因为每个值都有一个对应的类型标签,在标准中为 [[class]]。
在 ES6 中,则是使用Symbol.toStringTag作为标记。
Object.prototype.toString 在调用的时候,就会访问这个标记,并返回 [object 标记]。
var obj = {
[Symbol.toStringTag]: '996',
};
Object.prototype.toString.call(obj); // 输出:"[object 996]"
所有内置的类型都具有这个标记,所以使用 Object.prototype.toString.call(值) 的方式可以更精准的获取到值的类型。
一些旧的数据类型的基础对象为了兼容性,可能访问不到 Symbol.toStringTag 接口,但是其他许多内置对象可以,例如JSON、Math、BigInt等:
JSON[Symbol.toStringTag]; // 输出:"JSON"
Math[Symbol.toStringTag]; // 输出:"Math"
BigInt.prototype[Symbol.toStringTag]; // 输出:"BigInt"
6. 小结
typeof 经常被用来检测基础类型,但是不够准确,无法区分数组、对象、null,更精准的检测应考虑使用 Object.prototype.toString 方法。

