Spring Boot Starter-kit
Production ready Starter-kit for Spring Boot applications.
Table of Contents
- Philosophy
- Medium Articles
- Spring Boot
- Application
- Database Schema
- Technology
- Application Structure
- Run Locally
- Run Insider Docker
- API Documentation
- User Interface
- Contributor
- License
Philosophy
A lot of work has gone into Spring Boot to reduce complexity and dependencies, which largely alleviates our previous reservations. If you live in a Spring ecosystem and are moving to microservices, Spring Boot is now the obvious choice. Spring Boot allows easy set up of standalone Spring-based applications. It's ideal for pulling up new microservices and easy to deploy. It also makes data access less of a pain due to the hibernate mappings with much less boilerplate code. You can get started with minimum fuss due to it taking an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries. Most Spring Boot applications need very little Spring configuration.
The greatest thing about Spring Boot is the ability to be up and running in very little time. You don’t have to install a web server like JBoss, Websphere, or even Tomcat for that matter. All you need to do is pull in the proper libraries, annotate, and fire away. If you are going to do a lot of Spring Boot projects, I would highly suggest using the IntelliJ IDEA IDE. It has some great features for making Boot projects really easy to manage. You can of course choose between Maven or Gradle to manage dependencies and builds. This starter kit is based on Maven as it is what I am familiar and slightly more comfortable with.
Medium Articles
Readers can find more information about this starter-kit on my Medium publication The Resonant Web. I have written a series of two articles on Spring Boot v2, here are the links:
There is also a SQL version of this starter kit which is built with MySQL as the database. The location of GitHub repository for the same is here.
Spring Boot
Spring Boot makes it easy to create stand-alone, production-grade Spring based Applications that you can just run. We take an opinionated view of the Spring platform and third-party libraries so you can get started with minimum fuss. Most Spring Boot applications need very little Spring configuration.
Spring Boot is opinionated : This simply means that Spring Boot has its own configurations, application structures, dependencies, Servers and other environment configuration available inside its realm. Thus, to say Spring Boot has its own opinions about an application development environment. For example, most of the Java-based web applications use tomcat server. While working on Spring Boot you need not use any server, because Spring Boot already has an embedded tomcat container.
Spring Boot is stand-alone : What it means is that you don’t need to use any other third-party library or server to run or develop a spring boot application, it already has all of it.
It is production-grade : This implies that application developed using Spring Boot defaults is able to handle all complexities and requirements of a production environment.
Still very customizable : It is not worth using a framework which has its own rigid opinions, which you can’t customize or change according to your own business requirements. Although Spring Boot is opinionated you can easily change or customize its defaults to suit your own needs.
Application
This starter kit focuses on how to use Spring Boot following all the best practices that are recommended by Spring Framework 5.0, ensure the code is loosely coupled and that all the layers in the application are completely independent of each other and talk using neutral objects. While writing this kit, I have done sufficient research around the code structure and usage of appropriate design patterns to make this as an excellent starting point to begin coding your own web application.
The kit would have been incomplete if it did not have a concrete use case to implement, here I have taken a case study of a Bus Reservation System and tried to implement an Admin portal which can be operated over browsers and a series of REST APIs to interact with the system using mobile applications or frontend applications written for the browsers. The complete systems has two important actors :
- Admin user
- End user
The Admin user can access this application on browser (laptop or mobile/tablet, doesn't really matter as this is built using bootstrap, material design and is completely responsive) and can perform the following actions :
- Signup
- Login (Spring sessions)
- Update their profile
- Create an agency
- Add buses to the agency
- Add trips consisting of predefined stops and buses
The End user can use their mobile application (yet to be built, however the REST APIs are ready and could be used via Postman or Swagger) to perform the following actions :
- Signup
- Login (and get a JWT token)
- List all available stops
- Search a trip between any two stops
- Filter search results with a date option
- Book a ticket for a given trip schedule
Admin interface and REST APIs both have their independent authentication mechanisms, the web application uses the cookie based authentication (provided by default by Spring security) and the REST API uses the JWT authentication for access. This application assumes the availability of 'MongoDB' installation on the localhost where the server will run or the use of docker-compose to boot up a mongodb container and link the application with it within the realm of docker.
Any changes that the admin users will do on the web portal will impact the search results of the end users, there will be certain use cases which you may find missing here, I hope you will appreciate that the overall idea was to present a way to create such an application completely inside the realm of Spring Boot and not to actually building a fully functional reservation system.
The admin user interface is completely written in material design using Bootstrap v4 and is responsive to suite a variety of devices. The template engine used to render the admin views is Thymeleaf since the library is extremely extensible and its natural templating capability ensures templates can be prototyped without a back-end – which makes development very fast when compared with other popular template engines such as JSP.
Database Schema
The current schema looks as follows:
- The authentication and authorization is governed by User and Role collection.
- The Agency collection keeps the details of agency along with who owns it.
- The Stop collection keeps the data about all the stops in the system.
- The Bus collection has the data of all the buses for various agencies along with their capacity and make years.
- The Trip and TripSchedule collections keep the information about all the trips that agency owners create within the system. Information like source and destination stops, journey time, data of travel, tickets sold so far and the available seats is collected in them.
- Last, the Ticket collection keeps information about all the tickets issued in the application for various trips.
Technology
Following libraries were used during the development of this starter kit :
- Spring Boot - Server side framework
- Docker - Containerizing framework
- MongoDB - NoSQL database
- Swagger - API documentation
- Thymeleaf - Templating engine
- Material - UI theming/design
- Bootstrap - CSS framework
- JWT - Authentication mechanism for REST APIs
Application Structure
Spring Boot is an opinionated framework that makes our life very easy since we don't have to choose the versions of different dependencies based on the version of Spring framework, its all taken care of by Spring Boot. I have tried to follow the same ideology while creating the project structure, at first it might seem like overwhelming, but do believe me once you start writing your pieces the structure will help you immensely by saving your time and thinking about questions which are already answered. The structure look as follows :
Models & DTOs
The various models of the application are organized under the model package, their DTOs(data transfer objects) are present under the dto package. There are different opinions about whether we should use DTOs or not, I belong to the set of minds who think we definitely should and not using DTOs makes your model layer very tightly coupled with the UI layer and that is something that no enterprise project should ever get into. DTOs let us transfer only the data that we need to share with the user interface and not the entire model object that we may have aggregated using several sub-objects and persisted in the database. The mapping of models to the DTOs can be handled using ModelMapper utility, however its only useful when your DTO is almost similar (literally) to the concerned models which is not always the case and hence I prefer using custom mapper classes. You can find some examples under the dto/mapper package.
DAOs
The data access objects (DAOs) are present in the repository package. They are all extensions of the MongoRepository Interface helping the service layer to persist and retrieve the data from MongoDB. The service layer is defined under the service package, considering the current case study it made sense to create two basic services - UserService and BusReservationService to satisfy the different business operations that the users are executing using the UI.
Security
The security setting are present under the config package and the actual configurations are done under the class present in the security package. The application has different security concepts for the admin portal and the REST APIs, for the portal I have applied the default spring session mechanism that is based on the concept of sessionID and cookies. For the REST APIs I have used JWT token based authentication mechanism.
Controllers
Last, but the most important part is the controller layer. It binds everything together right from the moment a request is intercepted till the response is prepared and sent back. The controller layer is present in the controller package, the best practices suggest that we keep this layer versioned to support multiple versions of the application and the same practice is applied here. For now code is only present under v1 but over the time I expect to have different versions having different features. The Admin portal related controllers are present in the ui package and its concerning form command objects are located under the command package. The REST API controllers are located under the api package and the corresponding request classes are located under the request package.
Request and Form Commands
Again, there are different opinions amongst the fraternity regarding the usage of separate classes for mapping the incoming request vs using the DTOs, I am personally a fan of segregating the two as far as possible to promote loose coupling amongst UI and controller layer. The request objects and the form commands do give us a way to apply an additional level of validations on the incoming requests before they get converted to the DTOs which transfer valid information to the service layer for persistence and data retrieval. We could use DTOs here and some developers prefer that approach as it reduces some additional classes, however I usually prefer to keep the validation logic separate from the transfer objects and hence am inclined to use the request/command objects ahead of them.
The static resources are grouped under the resources directory. All the UI objects and their styling aspects can be located here.
Response and Exception Handling
I have tried to experiment a bit with the RuntimeExceptions and come up with a mini framework for handling the entire application's exceptions using a few classes and the properties file. If you carefully observe the exception package, it consists of two enums - EntityType and ExceptionType. The EntityType enum contains all the entity names that we are using in the system for persistence and those which can result in a run time exception. The ExceptionType enum consists of the different entity level exceptions such as the EntityNotFound and DuplicateEntity exceptions.
The BRSException class has two static classes EntityNotFoundException and DuplicateEntityException which are the two most widely thrown exceptions from the service layer. It also contains a set of overloaded methods throwException which take the EntityType, ExceptionType and arguments to come up with a formatted message whose template is present under the custom.properties file. Using this class I was able to empower the entire services layer to throw entity exceptions in a uniform manner without cluttering the code base with all sorts of NOT_FOUND and DUPLICATE entity exceptions.
For example, while login if you try to use a email address which is not registered, an exception is raised and thrown using the following single line of code -
throw exception(USER, ENTITY_NOT_FOUND, userDto.getEmail());
This results in clubbing the names of these two enums USER(user) and ENTITY_NOT_FOUND(not.found) and coming up with a key user.not.found which is present in the custom.properties files as follows :
user.not.found=Requested user with email - {0} does not exist.
By simply replacing the {0} param with the email address included in the thrown exception you can get a well formatted message to be shown to the user or to be sent back as the response of the REST API call.
Another important part of this mini framework is the CustomizedResponseEntityExceptionHandler class. This class takes care of these RuntimeExceptions before sending a response to the API requests. Its a controller advice that checks if a service layer invocation resulted in a EntityNotFoundException or a DuplicateEntityException and sends an appropriate response to the caller.
Last, the API response are all being sent in a uniform manner using the Response class present in the dto/response package. This class allows us to create uniform objects which result in a response as shown below (this one is a response for the "api/v1/reservation/stops" api) :
{
"status": "OK",
"payload": [
{
"code": "STPA",
"name": "Stop A",
"detail": "Near hills"
},
{
"code": "STPB",
"name": "Stop B",
"detail": "Near river"
}
]
}
And when there is an exception (for example searching for a trip between two stops which are not linked by any bus) the following responses are sent back (result of "api/v1/reservation/tripsbystops" GET request) :
{
"status": "NOT_FOUND",
"errors": "No trips between source stop - 'STPD' and destination stop - 'STPC' are available at this time."
}
{
"status": "NOT_FOUND",
"errors": {
"timestamp": "2019-03-13T07:47:10.990+0000",
"message": "Requested stop with code - STPF does not exist.",
"details": "Requested stop with code - STPF does not exist."
}
}
As you can observe, both type of responses, one with a HTTP-200 and another with HTTP-404 the response payload doesn't change its structure and the calling framework can blindly accept the response knowing that there is a status and a error or payload field in the JSON object.
UI Architecture
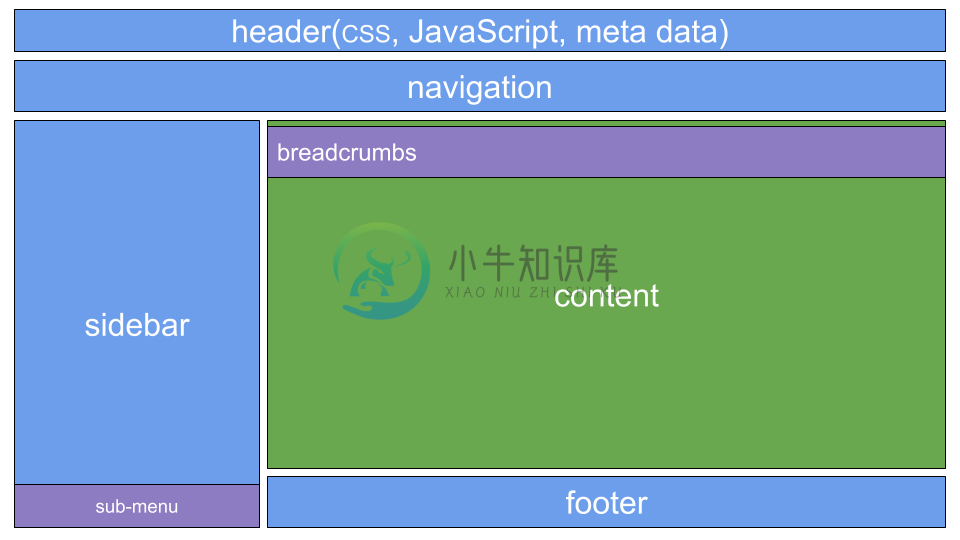
The user interface for the admin portal is designed using material design with the help of Bootstrap and responsive web app concept. The UI is server side rendered using Thymeleaf templates (preferred templating engine in Spring). The standard way of working with Thymeleaf is to use includes. This quite often leads to repetitive code, especially, when a website has many pages and each page has several reusable components (e.g. header, navigation, sidebar, and footer). It is repetitive as each content page has to include the same fragments at the same locations. This also has a negative effect when the page layout changes, e.g. when putting the sidebar from the left to the right side.
The decorator pattern used by the Thymeleaf Layout dialect solves these issues. In the context of template engines, the decorator pattern doesn't work with includes on content pages anymore, but it refers to a common template file. Each page basically only provides the main content and by describing which basic template to use the template engine can build the final page. The content is being decorated with the template file.This approach has advantages compared to the standard way of including fragments:
- The page itself only has to provide the content
- As a template file is being used to build the final page global changes can be applied easily
- The code becomes shorter and cleaner
- As each content page references which template file to use, it is easy to use different templates for different areas of the application (e.g. public area and admin area)
The layout for admin portal is arranged as follows :
The individual areas in this layout serve the following purpose :
- Header: this fragment is used for the static imports (CSS and JavaScript), the title and meta tags
- Navigation: the navigation bar
- Content: the content placeholder that will be replaced by the requested page
- Sidebar: a sidebar for additional information
- Footer: the footer area that provides the copyright info
These components can be located in the resources/templates directory at the root as well as under the sub-directories fragments and layout. The content area in this layout will host the following pages :
- Dashboard
- Agency
- Bus
- Trip
- Profile
Also, an error page for any unhandled exception is designed with the name "error.html". The login and signup pages are designed separately from the portal accessible to a logged-in user.
Running the server locally
To be able to run this Spring Boot app you will need to first build it. To build and package a Spring Boot app into a single executable Jar file with a Maven, use the below command. You will need to run it from the project folder which contains the pom.xml file.
maven package
or you can also use
mvn install
To run the Spring Boot app from a command line in a Terminal window you can you the java -jar command. This is provided your Spring Boot app was packaged as an executable jar file.
java -jar target/springboot-starterkit-1.0.jar
You can also use Maven plugin to run the app. Use the below example to run your Spring Boot app with Maven plugin :
mvn spring-boot:run
If you do not have a mongo instance running and still just want to create the JAR, then please use the following command:
mvn install -DskipTests
This will skip the test cases and won't check the availability of a mongodb instance and allow you to create the JAR.
You can follow any/all of the above commands, or simply use the run configuration provided by your favorite IDE and run/debug the app from there for development purposes. Once the server is setup you should be able to access the admin interface at the following URL :
And the REST APIs can be accessed over the following base-path :
Some of the important api endpoints are as follows :
- http://localhost:8080/api/v1/user/signup (HTTP:POST)
- http://localhost:8080/api/auth (HTTP:POST)
- http://localhost:8080/api/v1/reservation/stops (HTTP:GET)
- http://localhost:8080/api/v1/reservation/tripsbystops (HTTP:GET)
- http://localhost:8080/api/v1/reservation/tripschedules (HTTP:GET)
- http://localhost:8080/api/v1/reservation/bookticket (HTTP:POST)
Running the server in Docker Container
Docker
Command to build the container :
docker build -t spring/starterkit .
Command to run the container :
docker run -p 8080:8080 spring/starterkit
Please note when you build the container image and if mongodb is running locally on your system, you will need to provide your system's IP address (or cloud hosted database's IP) in the application.properties file to be able to connect to the database from within the container.
Docker Compose
Another alternative to run the application is to use the docker-compose.yml file and utility. To build the application using docker-compose simply execute the following command :
docker-compose build
And to run the application, please execute the following command :
docker-compose up
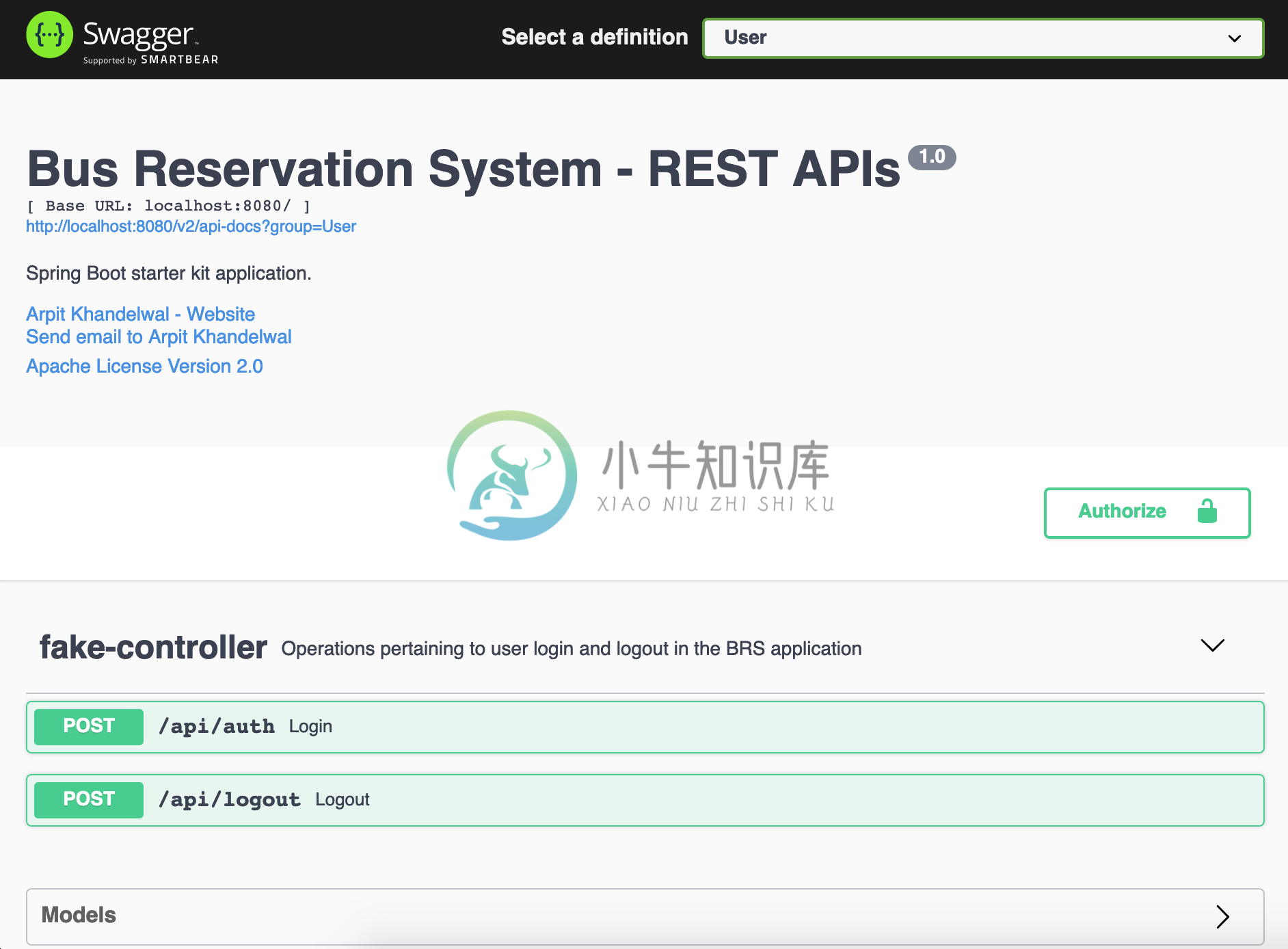
API Documentation
Its as important to document(as is the development) and make your APIs available in a readable manner for frontend teams or external consumers. The tool for API documentation used in this starter kit is Swagger3, you can open the same inside a browser at the following url -
http://localhost:8080/swagger-ui/index.html
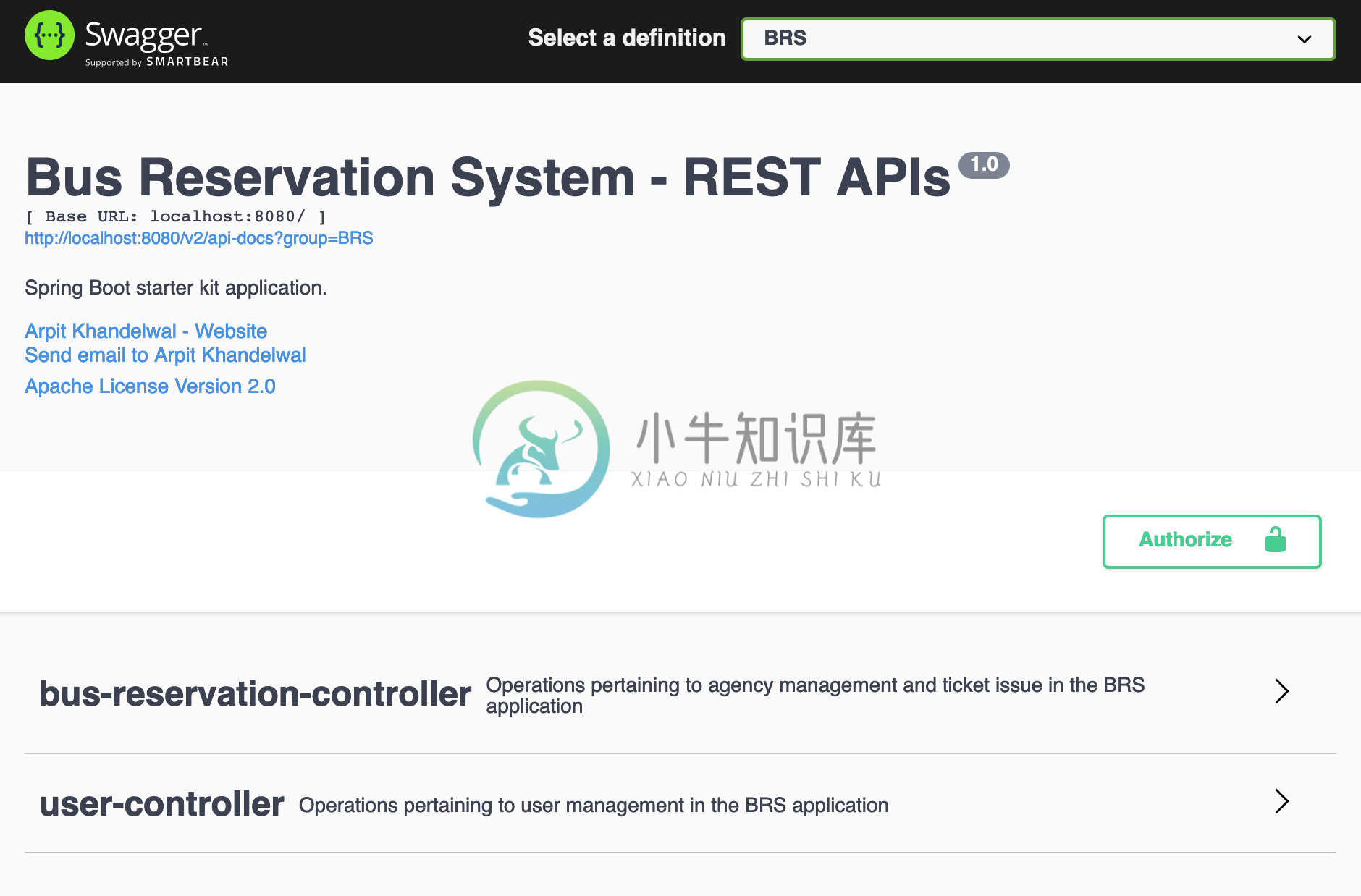
It will present you with a well structured UI which has two specs :
- User
- BRS
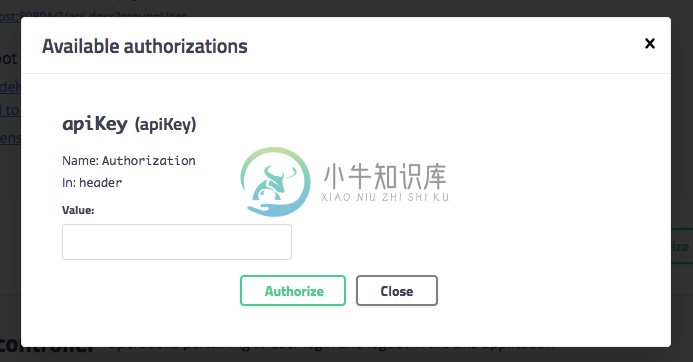
You can use the User spec to execute the login api for generating the Bearer token. The token then should be applied in the "Authorize" popup which will by default apply it to all secured apis (get and post both).
The configuration of Swagger is being taken care of by class BrsConfiguration. I have defined two specs there with the help of "swaggerBRSApi" and "swaggerUserApi" methods. Since the login part is by default taken care of by Spring Security we don't get to expose its apis implicitly as the rest of the apis defined in the system and for the same reason I have defined a controller in the config package with the name "FakeController". Its purpose is to facilitate the generation of swagger documentation for login and logout apis, it will never come into existence during the application life cycle as the "/api/auth" api is being handled by the security filters defined in the code base.
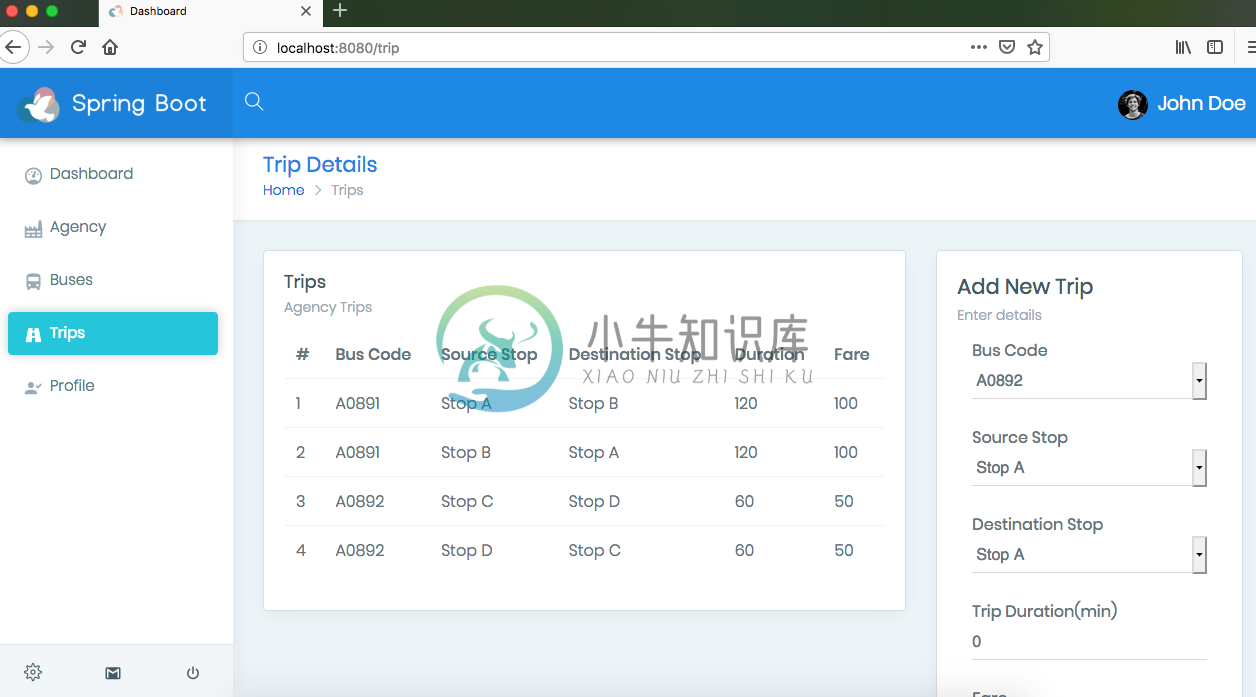
User Interface
Here are the various screens of the Admin portal that you should be able to use once the application is setup properly :
Contributors
License
This project is licensed under the terms of the MIT license.
-
1)spring-boot-starter 这是Spring Boot的核心启动器,包含了自动配置、日志和YAML。 2)spring-boot-starter-actuator 帮助监控和管理应用。 3)spring-boot-starter-amqp 通过spring-rabbit来支持AMQP协议(Advanced Message Queuing Protocol)。 4)spring-bo
-
一、springboot Starter简介 Starter是Spring Boot中的一个非常重要的概念,Starter相当于模块,它能将模块所需的依赖整合起来并对模块内的Bean根据环境( 条件)进行自动配置。使用者只需要依赖相应功能的Starter,无需做过多的配置和依赖,Spring Boot就能自动扫描并加载相应的模块。 总结: 它整合了这个模块需要的依赖库; 提供对模块的配置项给使用者
-
了解Starter SpringBoot为了简化配置,提供了非常多的Starter。它先打包好与常用模块相关的所有jar包,并完成自动配置,然后组装成Starter(例如Web相关的SpringMVC、容器等打包好后组装成 spring-boot-starter-web)。这使得在开发业务代码时不需要过多关注框架的配置,只需要关注业务逻辑即可。 SpringBoot提供了很多开箱即用的Starte
-
SpringBoot为我们提供了简化企业级开发绝大多数场景的starter pom,只要使用了应用场景所需要的start pom,相关的技术配置将会消除,就可以得到SpringBoot为我们提供的自动配置的Bean。 starter pom 名称 描述 spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf 使MVC Web applications 支持Thymeleaf spring-
-
约定大于配置(约定优于配置)。 Starters可以理解为启动器,它包含了一系列可以集成到应用里面的依赖包。 Starter命名规则:自带的以spring-boot开头。 常用的Starter: spring-boot-starter-web :提供 Spring MVC + 内嵌的 Tomcat 。 spring-boot-starter-data-jpa :提供
-
已与目标VM断开连接,地址:“javadeBug”,传输:“共享内存” 进程已完成,退出代码为0 PessoAcontroller:
-
使用 springboot 改造 jeesite,只保留最简单的系统配置 。 介绍 1、运行主类,登录 admin/admin com.wolfking.jeesite.WolfkingJeesiteDriver 2、砍掉了所有的冗余的东西,只保留系统配置,数据库脚本 wolfking-jeesite.sql 3、使用 springboot 集成,使用 HikariDataSource 数据源
-
WeChat-SpringBoot 是使用 Spring Boot 开发的微信开发后端脚手架
-
生产制造执行系统,基于 springBoot 开发。 精益生产+ISA-95 标准。 结合 MESA 战略计划方向设计框架。
-
一个简单便捷的基于springboot+RabbitMQ中间件实现的RPC调用框架 远程调用过程如下 首先:消费者和生产者spring容器初始化的时候,会根据配置的的api在RabbitMQ上建立相应的队列,消费者会监听相关队列 1)生产者(client)调用以本地调用方式调用服务; 2)client 接收到调用后通过Hessian将方法、参数等组装成能够进行网络传输的消息体; 3)client
-
SpringBoot + 前端MVVM 基于Java的微服务全栈快速开发实践。 如今Web开发领域,当有人提到Java时,总会让人觉得臃肿、古老而过时且开发效率没有某些动态语言高效,甚至在此之前还有人高喊“Java 已死!”,但是事实真是如此吗?其实如果你一直关注着Java,那你的感悟会更深,尽管它有很多的缺点和啰嗦,但不可否认,Java依然是工业界中最优秀的语言,而且它一直保持着与时俱进。本项目