压力传感器BMP180和Arduino设备进行温度,压力和高度测量
精华
小牛编辑
162浏览
2023-03-14
这是一个使用压力传感器BMP180和Arduino设备进行温度,压力和高度测量的物联网(物联网)项目。
在这个项目中,我们将建立一个温度,压力和高度测量系统。使用气压传感器模型BM 180来检测温度,大气压力和海拔高度,Arduino设备和16 X 4字符LCD显示计算的温度,压力和海拔高度。
硬件要求
- Arduino UNO主板
- 用于Arduino设备的USB电缆连接器
- 压力传感器BMP180
- 16 X 4字符LCD显示屏
- 项目主板
- 跳线(公线对公线,公线对母线)
软件要求
- Arduino软件IDE
压力传感器BMP180的工作原理
压力传感器BMP180由压阻式传感器,模拟和数字转换器,带E2PROM的控制单元和串行I2C接口组成。它提供温度,大气压力和海拔高度的贡献值。传感器设备的微控制器发送启动序列以测量温度,压力和高度。温度,压力和高度的值通过16X4字符LCD读取。
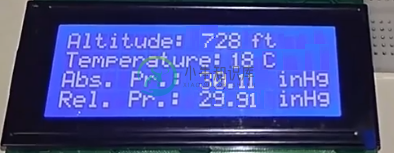
计算的温度,压力和高度分别以℃(摄氏度),hPa(hector Pascal)和英尺为单位测量。在这种情况下,测量温度,大气压力和高度的速率是每秒一次。
高度和压力彼此成反比。当海拔升高时,压力下降,当海拔降低时,导致大气压力增加。
使用压力传感器BMP180,Arduino和字符LCD编写Arduino程序来测量温度,压力和高度。
#include <LiquidCrystal.h>
LiquidCrystal lcd(13, 12, 11, 10, 9, 8);//RS,EN,D4,D5,D6,D7
#include <SFE_BMP180.h>
#include <Wire.h>
//create an SFE_BMP180 object, here called "pressure":
SFE_BMP180 pressure;
#define ALTITUDE 222.0 // altitude of Delhi in meters
void setup(){
Serial.begin(9600);
Serial.println("BMP180 Measurements");
lcd.begin(20, 4);
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("BMP180 Measurements");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print(" 1. Temperature");
lcd.setCursor(0, 2);
lcd.print(" 2. Pressure");
lcd.setCursor(0, 3);
lcd.print(" 3. Altitude");
delay (5000);
lcd.clear();//clear display
// initialize the sensor (it is important to get calibration values stored on the device).
if (pressure.begin())
Serial.println("BMP180 init success");
else{
// oops, something went wrong, this is usually a connection problem,
// see the comments at the top of this sketch for the proper connections.
Serial.println("BMP180 init fail\n\n");
while(1); // pause forever.
}
}
void loop(){
char status;
double T,P,p0,a;
// loop here getting pressure readings every 10 seconds.
// if you want sea-level-compensated pressure, as used in weather reports,
// you need to find dinamically altitude of place.
// here, we are using constant called ALTITUDE in this sketch:
Serial.println();
Serial.print("provided altitude: ");
lcd.setCursor(0, 0);
lcd.print("Altitude: ");
Serial.print(ALTITUDE,0);
Serial.print(" meters, ");
Serial.print(ALTITUDE*3.28084,0);
lcd.print(ALTITUDE*3.28084,0);
Serial.println(" feet");
lcd.print(" ft");
// start a temperature measurement:
// if request is successful, the number of ms to wait is returned.
// if request is unsuccessful, 0 is returned.
status = pressure.startTemperature();
if (status != 0){
// wait for the measurement to complete:
delay(status);
// retrieve the completed temperature measurement:
// note that the measurement is stored in the variable T.
// function returns 1 if successful, 0 if failure.
status = pressure.getTemperature(T);
if (status != 0){
// Print out the measurement:
Serial.print("temperature: ");
Serial.print(T,2);
Serial.print(" deg C, ");
Serial.print((9.0/5.0)*T+32.0,2);
Serial.println(" deg F");
lcd.setCursor(0, 1);
lcd.print("Temperature: ");
lcd.print(T,2);
lcd.print(" C ");
// start a pressure measurement:
// the parameter is the oversampling setting, from 0 to 3 (highest res, longest wait).
// if request is successful, the number of ms to wait is returned.
// if request is unsuccessful, 0 is returned.
status = pressure.startPressure(3);
if (status != 0){
// wait for the measurement to complete:
delay(status);
// Retrieve the completed pressure measurement:
// Note that the measurement is stored in the variable P.
// Note also that the function requires the previous temperature measurement (T).
// (If temperature is stable, you can do one temperature measurement for a number of pressure measurements.)
// Function returns 1 if successful, 0 if failure.
status = pressure.getPressure(P,T);
if (status != 0){
// print out the measurement:
Serial.print("absolute pressure: ");
Serial.print(P,2);
Serial.print(" mb, ");
Serial.print(P*0.0295333727,2);
Serial.println(" inHg");
lcd.setCursor(0, 2);
lcd.print("Abs. Pr.: ");
lcd.print(P*0.0295333727,2);
lcd.print(" inHg");
// The pressure sensor returns absolute pressure, which varies with altitude.
// To remove the effects of altitude, use the sea level function and your current altitude.
// This number is commonly used in weather reports.
// Parameters: P = absolute pressure in mb, ALTITUDE = current altitude in m.
// Result: p0 = sea-level compensated pressure in mb
p0 = pressure.sealevel(P,ALTITUDE); // we are at 222 meters (Delhi)
Serial.print("relative (sea-level) pressure: ");
Serial.print(p0,2);
Serial.print(" mb, ");
Serial.print(p0*0.0295333727,2);
Serial.println(" inHg");
lcd.setCursor(0, 3);
lcd.print("Rel. Pr.: ");
lcd.print(p0*0.0295333727,2);
lcd.print(" inHg");
// On the other hand, if you want to determine your altitude from the pressure reading,
// use the altitude function along with a baseline pressure (sea-level or other).
// Parameters: P = absolute pressure in mb, p0 = baseline pressure in mb.
// Result: a = altitude in m.
a = pressure.altitude(P,p0);
Serial.print("computed altitude: ");
Serial.print(a,0);
Serial.print(" meters, ");
Serial.print(a*3.28084,0);
Serial.println(" feet");
}
else
Serial.println("error retrieving pressure measurement\n");
}
else
Serial.println("error starting pressure measurement\n");
}
else
Serial.println("error retrieving temperature measurement\n");
}
else
Serial.println("error starting temperature measurement\n");
delay(5000); // Pause for 5 seconds.
}
从 https://github.com/LowPowerLab/SFE_BMP180 下载SFE_BMP180-master.zip文件
在编译上面的代码之前添加SFE_BMP180-master zip文件,否则会生成错误SFE_BMP180.h:没有这样的文件或目录。
要添加zip文件,请单击:Sketch -> Include Library -> Add .ZIP Library… 并添加下载的SFE_BMP180-master zip。
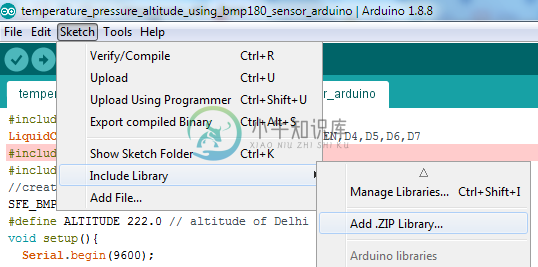
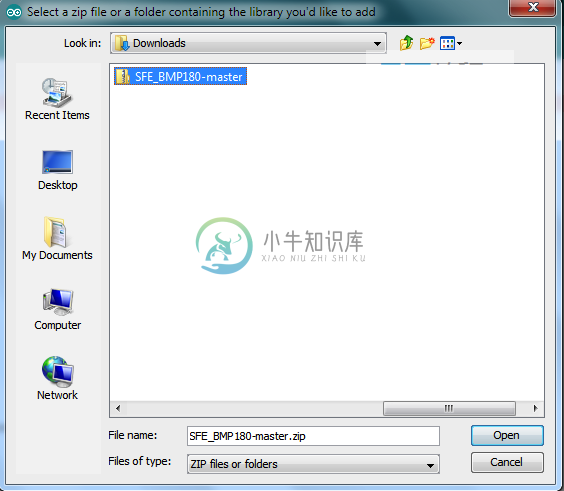
编译并将代码上传到Arduino设备。然后,相应地连接所有设备。Arduino,BMP180和16 X 4字符LED的数字电路如下:
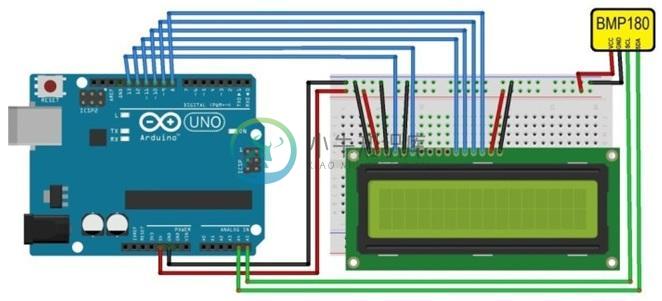
运行后,得到以下结果: