C++实现图的邻接矩阵表示
本文实例为大家分享了C++实现图的邻接矩阵表示代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
1.遇到的问题:教材中写着子类Graphmtx(我用GrapMatrix)继承基类Graph
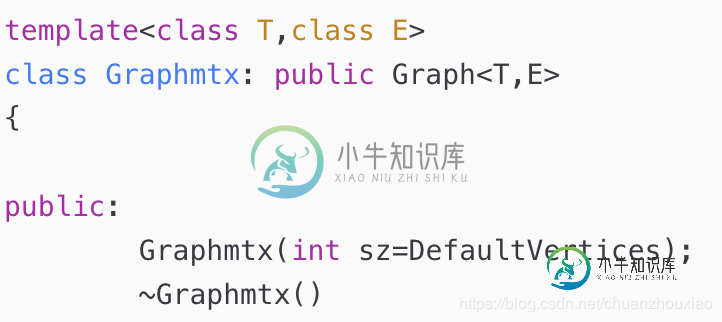
但是我在子类GraphMatrix中使用父类Graph的保护成员属性:maxVertices 显示没有声明(如下图)。

原来,c++中声明一个模板类及子类,在子类中如果需要访问父类的protected变量,需要使用父类的类作用域限定符,否则会报“identifier not found”错误。如果不是模板类,可以直接访问。
例如:要如下这样使用父类的保护成员属性,太麻烦了。
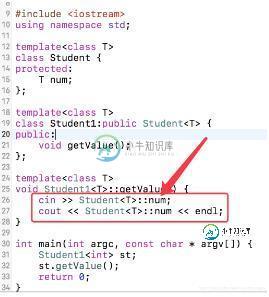
所以,我就不用继承基类的方法了。直接把Graph父类的保护成员属性放到GrapMatrix类中。
2.实现程序:
(1)GraphMatrix.h
#ifndef GraphMatrix_h #define GraphMatrix_h #include <iostream> using namespace std; const int DefaultVertices = 30; // 默认最大顶点数 template <class T, class E> class GraphMatrix { public: const E maxWeight = 100000; // 代表无穷大的值(=∞) GraphMatrix(int sz=DefaultVertices); // 构造函数 ~GraphMatrix(); // 析构函数 void inputGraph(); // 创建基于邻接矩阵的图 void outputGraph(); // 输出图的所有顶点和边信息 T getValue(int i); // 取顶点i的值,i不合理返回0 E getWeight(int v1, int v2); // 取边(v1, v2)上的权值 int getFirstNeighbor(int v); // 取顶点v的第一个邻接顶点 int getNextNeighbor(int v, int w); // 取v的邻接顶点w的下一个邻接顶点 bool insertVertex(const T& vertex); // 插入顶点vertice bool insertEdge(int v1, int v2, E cost); // 插入边(v1, v2)权值为cost bool removeVertex(int v); // 删去顶点v和所有与它相关联的边 bool removeEdge(int v1, int v2); // 在图中删去边(v1, v2) int getVertexPos(T vertex); // 给出顶点vertice在图中的位置 private: int maxVertices; // 图中最大的顶点数 int numEdges; // 当前边数 int numVertices; // 当前顶点数 T *VerticesList; // 顶点表 E **Edge; // 邻接矩阵 }; // 构造函数 template <class T, class E> GraphMatrix<T, E>::GraphMatrix(int sz) { int i, j; maxVertices = sz; numVertices = 0; numEdges = 0; VerticesList = new T[maxVertices]; // 创建顶点表数组 Edge = new E*[maxVertices]; // 创建邻接矩阵数组 for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++) Edge[i] = new E[maxVertices]; for(i = 0; i < maxVertices; i++) { // 邻接矩阵初始化 for(j = 0; j < maxVertices; j++) { if(i == j) // 矩阵对角处,即为同一顶点 Edge[i][j] = 0; else // 不是同一顶点的,即两顶点一开始没有边相连,为无穷大∞ Edge[i][j] = maxWeight; } } } // 析构函数 template <class T, class E> GraphMatrix<T, E>::~GraphMatrix() { delete []VerticesList; // 释放动态分配的空间 delete []Edge; } // 创建基于邻接矩阵的图 template <class T, class E> void GraphMatrix<T, E>::inputGraph() { int i, j, k; int n, m; // 要输入的顶点数和边数 T e1, e2; // 边的两端顶点 E weight; // 边对应的权值 cout << "请输入顶点数和边数:" << endl; cin >> n >> m; cout << "请输入顶点:" << endl; for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { // 建立顶点表数据 cin >> e1; insertVertex(e1); // 插入 } cout << "请输入边的两端顶点和权值:" << endl; i = 0; while(i < m){ // 输入边 cin >> e1 >> e2 >> weight; // 输入端点信息 j = getVertexPos(e1); // 查顶点号 k = getVertexPos(e2); if(j == -1 || k == -1) cout << "边两端点信息有误,重新输入!" << endl; else { insertEdge(j, k, weight); i++; } } // for结束 } // 输出图的所有顶点和边信息 template <class T, class E> void GraphMatrix<T, E>::outputGraph() { int i, j, n, m; T e1, e2; E w; n = numVertices; m = numEdges; cout << "顶点数为:" << n << ",边数为:" << m << endl; for(i = 0; i < n; i++) { for(j = i+1; j < n; j++) { w = getWeight(i, j); // 取边上权值 if(w > 0 && w < maxWeight) { // 有效,即这两顶点存在边 e1 = getValue(i); e2 = getValue(j); cout << "(" << e1 << "," << e2 << "," << w << ")" << endl; } } } // for } // 给出顶点vertice在图中的位置 template <class T, class E> int GraphMatrix<T, E>::getVertexPos(T vertex) { for(int i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) if(VerticesList[i] == vertex) return i; return -1; } // 取顶点i的值,i不合理返回NULL template <class T, class E> T GraphMatrix<T, E>::getValue(int i) { if(i >= 0 && i < numVertices) return VerticesList[i]; return NULL; } // 取边(v1, v2)上的权值 template <class T, class E> E GraphMatrix<T, E>::getWeight(int v1, int v2) { if(v1 != -1 && v2 != -1) // 存在这两个顶点 return Edge[v1][v2]; return 0; } // 取顶点v的第一个邻接顶点 template <class T, class E> int GraphMatrix<T, E>::getFirstNeighbor(int v) { if(v != -1) { for(int col = 0; col < numVertices; col++) if(Edge[v][col] > 0 && Edge[v][col] <maxWeight) return col; } return -1; } // 取v的邻接顶点w的下一个邻接顶点 template <class T, class E> int GraphMatrix<T, E>::getNextNeighbor(int v, int w) { if(v != -1 && w != -1) { for(int col = w+1; col < numVertices; col++) { if(Edge[v][col] > 0 && Edge[v][col] < maxWeight) return col; } } return -1; } // 插入顶点vertice template <class T, class E> bool GraphMatrix<T, E>::insertVertex(const T& vertex) { if(numVertices == maxVertices) // 顶点表满 return false; VerticesList[numVertices++] = vertex; return true; } // 插入边(v1, v2)权值为cost template <class T, class E> bool GraphMatrix<T, E>::GraphMatrix<T, E>::insertEdge(int v1, int v2, E cost) { if(v1 > -1 && v1 < numVertices && v2 > -1 && v2 < numVertices && Edge[v1][v2] == maxWeight) { // 顶点v1,v2都存在,并且v1,v2没有边 Edge[v1][v2] = Edge[v2][v1] = cost; numEdges++; return true; } return false; } // 删去顶点v和所有与它相关联的边 template <class T, class E> bool GraphMatrix<T, E>::removeVertex(int v) { if(v < 0 && v > numVertices) // v不在图中,不删除 return false; if(numVertices == 1) // 只剩一个顶点,不删除 return false; int i, j; VerticesList[v] = VerticesList[numVertices-1]; // 用最后一个顶点替代当前要删的顶点 // 删除与v相关联边数 for(i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) { if(Edge[i][v] > 0 && Edge[i][v] < maxWeight) numEdges--; } // 用最后一列,填补第v列 for(i = 0; i < numVertices; i++) Edge[i][v] = Edge[i][numVertices-1]; numVertices--; // 顶点数减1 // 用最后一行,填补第v行 for(j = 0; j < numVertices; j++) Edge[v][j] = Edge[numVertices][j]; return true; } // 在图中删去边(v1, v2) template <class T, class E> bool GraphMatrix<T, E>::removeEdge(int v1, int v2) { if(v1 > -1 && v1 < numVertices && v2 > -1 && v2 < numVertices && Edge[v1][v2] < maxWeight) { Edge[v1][v2] = Edge[v2][v1] = maxWeight; numEdges--; // 边数减1 return true; } return false; } #endif /* GraphMatrix_h */
(2)main.cpp
// 测试数据:
/*
5 7
A B C D E
A B 24 A C 46 B C 15 B E 67 C B 37 C D 53 E D 31
*/
#include "GraphMatrix.h"
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
GraphMatrix<char, int> st; // 声明对象
bool finished = false;
int choice;
char e1, e2, next;
int weight;
while(!finished) {
cout << "[1]创建基于邻接矩阵的图" << endl;
cout << "[2]输出图的所有顶点和边信息" << endl;
cout << "[3]取顶点v的第一个邻接顶点" << endl;
cout << "[4]取v的邻接顶点w的下一个邻接顶点" << endl;
cout << "[5]插入顶点" << endl;
cout << "[6]插入边" << endl;
cout << "[7]删除顶点" << endl;
cout << "[8]删除边" << endl;
cout << "[9]退出" << endl;
cout << "请输入选择[1-9]:";
cin >> choice;
switch(choice) {
case 1:
st.inputGraph();
break;
case 2:
st.outputGraph();
break;
case 3:
cout << "请输入顶点:";
cin >> e1;
e2 = st.getValue(st.getFirstNeighbor(st.getVertexPos(e1)));
if(e2)
cout << "顶点" << e1 << "的第一个邻接顶点为:" << e2 << endl;
else
cout << "顶点" << e1 << "没有邻接顶点!" << endl;
break;
case 4:
cout << "请输入顶点v和邻接顶点w:";
cin >> e1 >> e2;
next = st.getValue(st.getNextNeighbor(st.getVertexPos(e1), st.getVertexPos(e2)));
if(next)
cout << "顶点" << e1 << "的邻接顶点" << e2 << "的下一个邻接顶点为:" << next << endl;
else
cout << "顶点" << e1 << "的邻接顶点" << e2 << "没有下一个邻接顶点!" << endl;
break;
case 5:
cout << "请输入要插入的顶点:";
cin >> e1;
if(st.insertVertex(e1))
cout << "插入成功!" << endl;
else
cout << "表已满,插入失败!" << endl;
break;
case 6:
cout << "请输入要插入的边的信息:" << endl;
cin >> e1 >> e2 >> weight;
st.insertEdge(st.getVertexPos(e1), st.getVertexPos(e2), weight);
break;
case 7:
cout << "请输入要删除的顶点:";
cin >> e1;
if(st.removeVertex(st.getVertexPos(e1)))
cout << "顶点" << e1 << "已删除!" << endl;
else
cout << "顶点" << e1 << "不在图中!" << endl;
break;
case 8:
cout << "请输入要删除的边的两个端点:" << endl;
cin >> e1 >> e2;
st.removeEdge(st.getVertexPos(e1), st.getVertexPos(e2));
break;
case 9:
finished = true;
break;
default:
cout << "选择输入错误,请重新输入!" << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
测试结果:


以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
作为一项练习,我必须建立一个卫星导航系统,规划从一个位置到另一个位置的最短和最快路线。它必须尽可能快,而不需要使用太多内存。 我很难决定使用哪种结构来表示图形。我知道矩阵更适合密集图,列表更适合稀疏图。我更倾向于使用列表,因为我认为添加顶点将是这个程序中最累人的部分。 我只是想听听你们的意见。如果我把一个典型的路线图看作一个图形,其中不同的位置是节点,道路是边缘。你认为它是稀疏的还是密集的?在这种
-
实现图的最简单的方法之一是使用二维矩阵。在该矩阵实现中,每个行和列表示图中的顶点。存储在行 v 和列 w 的交叉点处的单元中的值表示是否存在从顶点 v 到顶点 w 的边。 当两个顶点通过边连接时,我们说它们是相邻的。 Figure 3 展示了 Figure 2 中的图的邻接矩阵。单元格中的值表示从顶点 v 到顶点 w 的边的权重。 Figure 3 邻接矩阵的优点是简单,对于小图,很容易看到哪些节
-
B)设是带有向图(无环多边)的一个邻接矩阵,其中是边到的一个权重。如果没有这样的边并且对于evrey我们有。矩阵。槽表示什么?最小权重?还是...? 知道吗? 编辑:我的意思是这些算法在图中找到哪一个?找到最大重量?最小重量?什么也没找到?
-
问题内容: 我对图和邻接矩阵感到困惑。我正在为 一个班级做作业,我有一个节点的文本文件和一个边的文本文件,我必须 阅读它们的每一个并将它们制成一个图,然后可以在该图上执行 操作,例如确定图是否为连接,找到最小的 生成树,遍历并找到路径。但是我之前从未使用过图形 ,并且整个过程让我很困惑,我想知道 是否有人可以帮助我解释其中的一些内容。 首先,我是否要自己建立一个图(也许有节点和边类?) ,然后从中
-
我试图实现一个无向未加权图的邻接矩阵上的BFS,它返回访问的节点数。到目前为止,我已经提出了这个,但我认为这是不对的,因为当我打印出top/vised节点时,我得到了一些节点的多次出现,而且它没有排序。我在某个地方读到过,BFS是一个拓扑排序,我得到的顺序不是排序的。
-
对于许多点,我有2D的协定子,例如点a=x,y 我想做一个图的实现使用邻接列表列表和连接某些点的无方向图在最有效的方式(不使用地图或哈希表)

