android流式布局onLayout()方法详解
在上一篇中及就写了自定义view中的onMeausre()和onDraw()两个方法。在这里就用简单的流式布局来介绍一下onLayout()方法。
在onLayout方法中有四个参数,我画了一个简单的图来分清楚值哪里。
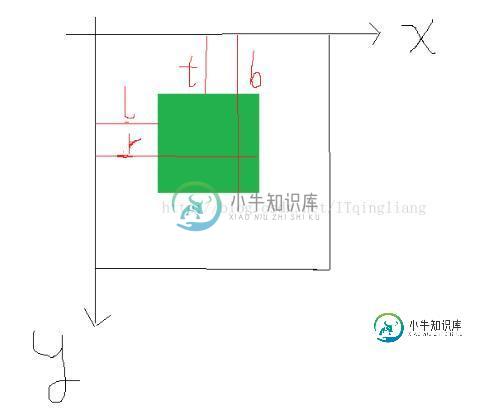
好啦,现在就直接看代码吧。
FlowLayout.Java
package com.example.my_view;
import android.content.Context;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
/**
* 自定义布局 流布局
*/
public class FlowLayout extends ViewGroup {
public FlowLayout(Context context) {
super(context);
}
public FlowLayout(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
}
/**
*
* @param changed
* @param l 左
* @param t 上
* @param r 右
* @param b 下
*/
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) {
//获得子控件的数量
int childCount = getChildCount();
//当前子控件的左边坐标
int cl = 0;
//当前子控件的上边坐标
int ct = 0;
//ViewGroup整体宽度
int width = r - l;
//行高
int lineHeight = 0;
//遍历所有子控件
for(int i = 0; i < childCount; i++){
//获取当前控件
View childAt = getChildAt(i);
//获取宽度
int cw = childAt.getMeasuredWidth();
//获取高度
int ch = childAt.getMeasuredHeight();
//当前控件右边
int cr = cl + cw;
//当前控件下边
int cb = ct + ch;
//判断是否换行
if(cr > width){
//如果换行重新计算上下左右地值
cl = 0;
cr = cl + cw;
ct += lineHeight;
cb = ct + ch;
//换行后,第一个控件作为最大行高
lineHeight = ch;
}else{
//如果不换行,需要计算最大高度
lineHeight = Math.max(lineHeight,ch);
}
childAt.layout(cl,ct,cr,cb);
//横向向后移动一个,前面控件的右边作为后面控件的左边
cl = cr;
}
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
//测量所有子控件
measureChildren(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec);
}
}
activity_main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<com.example.my_view.FlowLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context="com.example.my_view.MainActivity">
<!--
<com.example.my_view.Counter
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
app:number="10"
app:bgColor="#ff002b"
app:textColor="#0fd444"/>-->
<!--<TextView
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="我在自定义布局的下面"/>-->
<Button
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button1"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="button2"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="180dp"
android:layout_height="60dp"
android:text="button3"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button4"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="80dp"
android:layout_height="100dp"
android:text="button5"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button6"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="120dp"
android:layout_height="70dp"
android:text="button7"/>
<Button
android:layout_width="100dp"
android:layout_height="50dp"
android:text="button8"/>
</com.example.my_view.FlowLayout>
效果图:

以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
本文向大家介绍Android FlowLayout流式布局实现详解,包括了Android FlowLayout流式布局实现详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了Android FlowLayout流式布局的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 最近使用APP的时候经常看到有 这种流式布局 ,今天我就跟大家一起来动手撸一个这种自定义控件. 首先说一下自定义控件的流程: 自定
-
本文向大家介绍Bootstrap布局方式详解,包括了Bootstrap布局方式详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Bootstrap 3 是移动设备优先的,在这个意义上,Bootstrap 代码从小屏幕设备(比如移动设备、平板电脑)开始,然后扩展到大屏幕设备(比如笔记本电脑、台式电脑)上的组件和网格。 一、移动设备优先策略 1、内容: 决定什么是最重要的。 2、布局 优先设计更小的宽度。
-
本文向大家介绍Android简单实现自定义流式布局的方法,包括了Android简单实现自定义流式布局的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android简单实现自定义流式布局的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 首先来看一下 手淘HD - 商品详情 - 选择商品属性 页面的UI 商品有很多尺码,而且展现每个尺码所需要的View的大小也不同(主要是宽度),所以在从服务器端
-
在移动终端兴起的时代,可以预见的是,未来还会涌现出更多大小不一的屏幕,人们需要一种灵活的、能够适应未知设备的方法,使得我们的设计在所有屏幕中都能完美显示,这就催生了流式布局。 使用流式布局时,尺寸不再使用像素,而是使用百分百进行设置。这种布局可以自适应用户的分辨率,并根据浏览器窗口尺寸自由伸缩,非常高效的利用空间。当浏览器窗口变大,元素的尺寸会变宽,当浏览器窗口变小,元素的尺寸也会跟着变小。页面周
-
本文向大家介绍Android布局之表格布局TableLayout详解,包括了Android布局之表格布局TableLayout详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了Android表格布局TableLayout的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 1.TableLayout TableLayout表格布局模型以行列的形式管理子控件,每一行为一个TableRow的对象, 当
-
本文向大家介绍Android自定义ViewGroup实现流式布局,包括了Android自定义ViewGroup实现流式布局的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了Android自定义ViewGroup实现流式布局的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 1.概述 本篇给大家带来一个实例,FlowLayout,什么是FlowLayout,我们常在App 的搜索界面看到热门搜索词,就

