ArrayList和HashMap如何自己实现实例详解
ArrayList和HashMap
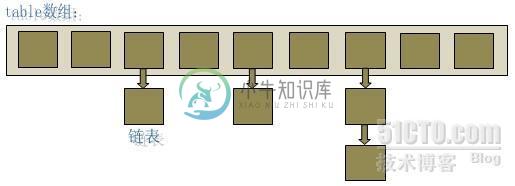
ArrayList的存储就是一个数组,
HashMap的存储是一个数组加一个链表,
以下实现的MyArrayList及MyHashMap,在实际的工作中都是用不上的,最有可能用得到的地方就是面试找工作以及忽悠别人了。工作中虽然用不上,但是并不代表没有用,它可以帮助我们去理解他们的实现原理,等实现完后再去仔细查看JDK中的源码,就会发现别人实现当中那些可供学习的地方。
MyArrayList
public class MyArrayList<E> {
private int capacity = 10;
private int size = 0;
private E[] values = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public MyArrayList() {
values = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public MyArrayList(int capacity) {
this.capacity = capacity;
values = (E[]) new Object[this.capacity];
}
public void put(E e) {
if (e == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("The value should not be null.");
}
if (size >= capacity) {
enlargeCapacity();
}
values[size] = e;
size++;
}
public E get(int index) {
if (index >= size) {
throw new RuntimeException("The index:" + index + " is out of band.");
}
return values[index];
}
public void remove(int index) {
if (index >= size) {
throw new RuntimeException("The index:" + index + " is out of band.");
}
for (int i = index; i < size - 1; i++) {
values[i] = values[i + 1];
}
values[size - 1] = null;
size--;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private void enlargeCapacity() {
capacity = capacity * 2;
E[] tmpValues = (E[]) new Object[capacity];
System.arraycopy(values, 0, tmpValues, 0, size);
values = tmpValues;
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("[");
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
sb.append(values[i]).append(",");
}
if (size > 0) {
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
sb.append("]");
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList<String> myList = new MyArrayList<String>();
myList.put("1");
myList.put("2");
myList.put("3");
myList.put("4");
myList.put("5");
myList.put("6");
myList.put("7");
myList.put("8");
myList.put("9");
myList.remove(7);
System.out.println(myList.toString());
}
}
MyHashMap
public class MyHashMap<K, V> {
//initialization capacity
private int capacity = 10;
//total entities
private int size = 0;
private Entity<K, V>[] entities = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public MyHashMap() {
entities = new Entity[capacity];
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("The key is null");
}
reHash();
Entity<K, V> newEntity = new Entity<K, V>(key, value);
put(newEntity, this.entities, this.capacity);
}
private void put(Entity<K, V> newEntity, Entity<K, V>[] entities, int capacity) {
int index = newEntity.getKey().hashCode() % capacity;
Entity<K, V> entity = entities[index];
Entity<K, V> firstEntity = entities[index];
if (entity == null) {
entities[index] = newEntity;
size++;
} else {
if (newEntity.getKey().equals(entity.getKey())) {//Find the same key for the first entity, if find then replace the old value to new value
newEntity.setNext(entity.getNext());
newEntity.setPre(entity.getPre());
if (entity.getNext() != null) {
entity.getNext().setPre(newEntity);
}
entities[index] = newEntity;
} else if (entity.getNext() != null) {
while (entity.getNext() != null) {//Find the same key for all the next entity, if find then replace the old value to new value
entity = entity.getNext();
if (newEntity.getKey().equals(entity.getKey())) {
newEntity.setPre(entity.getPre());
newEntity.setNext(entity.getNext());
if (entity.getNext() != null) {
entity.getNext().setPre(newEntity);
}
entities[index] = newEntity;
return;
}
}
//Cannot find the same key, then insert the new entity at the header
newEntity.setNext(firstEntity);
newEntity.setPre(firstEntity.getPre());
firstEntity.setPre(newEntity);
entities[index] = newEntity;
size++;
} else {
//Cannot find the same key, then put the new entity in head
newEntity.setNext(firstEntity);
firstEntity.setPre(newEntity);
entities[index] = newEntity;
size++;
}
}
}
public V get(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("The key is null");
}
int index = key.hashCode() % capacity;
Entity<K, V> entity = entities[index];
if (entity != null) {
if (entity.getKey().equals(key)) {
return entity.getValue();
} else {
entity = entity.getNext();
while (entity != null) {
if (entity.getKey().equals(key)) {
return entity.getValue();
}
entity = entity.getNext();
}
}
}
return null;
}
public void remove(K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("The key is null");
}
int index = key.hashCode() % capacity;
Entity<K, V> entity = entities[index];
if (entity != null) {
if (entity.getKey().equals(key)) {
if (entity.getNext() != null) {//remove the first entity
entity.getNext().setPre(entity.getPre());
entities[index] = entity.getNext();
entity = null;
} else {//empty this index
entities[index] = null;
}
size--;
} else {
entity = entity.getNext();
while (entity != null) {
if (entity.getKey().equals(key)) {
if (entity.getNext() != null) {
entity.getPre().setNext(entity.getNext());
entity.getNext().setPre(entity.getPre());
entity = null;
} else {
//release the found entity
entity.getPre().setNext(null);
entity = null;
}
size--;
return;
}
entity = entity.getNext();
}
}
}
}
public String toString() {
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
sb.append("index=").append(i).append("[");
boolean hasEntity = false;
Entity<K, V> entity = entities[i];
if (entity != null) {
hasEntity = true;
}
while (entity != null) {
sb.append("[").append(entity.getKey()).append("=").append(entity.getValue()).append("]").append(",");
entity = entity.getNext();
}
if (hasEntity) {
sb.deleteCharAt(sb.length() - 1);
}
sb.append("]\n");
}
return sb.toString();
}
/**
* Simple re-hash strategy, if the size is bigger than capacity, then do re-hash action
*/
private void reHash() {
if (size >= capacity) {
int newCapacity = capacity * 2;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entity<K, V>[] newEntities = new Entity[newCapacity];
for (int i = 0; i < capacity; i++) {
Entity<K, V> entity = entities[i];
while (entity != null) {
put(entity, newEntities, newCapacity);
entity = entity.getNext();
}
}
this.capacity = newCapacity;
this.entities = newEntities;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyHashMap<String, String> map = new MyHashMap<String, String>();
map.put("one", "1");
map.put("two", "2");
map.put("three", "3");
map.put("four", "4");
map.put("five", "5");
map.put("six", "6");
map.put("seven", "7");
map.put("eight", "8");
map.put("nine", "9");
map.put("ten", "10");
System.out.println(map.get("one"));
System.out.println(map.get("two"));
System.out.println(map.get("three"));
System.out.println(map.get("four"));
System.out.println(map.get("five"));
System.out.println(map.get("six"));
System.out.println(map.get("seven"));
System.out.println(map.get("eight"));
System.out.println(map.get("nine"));
System.out.println(map.get("ten"));
System.out.println(map.toString());
map.remove("nine");
map.remove("three");
System.out.println(map.get("one"));
System.out.println(map.get("two"));
System.out.println(map.get("three"));
System.out.println(map.get("four"));
System.out.println(map.get("five"));
System.out.println(map.get("six"));
System.out.println(map.get("seven"));
System.out.println(map.get("eight"));
System.out.println(map.get("nine"));
System.out.println(map.get("ten"));
System.out.println(map.toString());
}
}
class Entity<K, V> {
private K key;
private V value;
private Entity<K, V> pre;
private Entity<K, V> next;
public Entity(K key, V value) {
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
public K getKey() {
return key;
}
public void setKey(K key) {
this.key = key;
}
public V getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(V value) {
this.value = value;
}
public Entity<K, V> getPre() {
return pre;
}
public void setPre(Entity<K, V> pre) {
this.pre = pre;
}
public Entity<K, V> getNext() {
return next;
}
public void setNext(Entity<K, V> next) {
this.next = next;
}
}
感谢阅读,希望能帮助到大家,谢谢大家对本站的支持!
-
本文向大家介绍JS hashMap实例详解,包括了JS hashMap实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Hashmap是一种非常常用的、应用广泛的数据类型。本文通过实例代码给大家介绍js hashMap的相关知识,具体代码内容如下所示: 以上所述是小编给大家介绍的js hashMap实例详解的相关知识,希望对大家有所帮助!
-
本人一直很想自己造个 jQuery 的小库,第一是满足下自己,第二是去体验下 jQuery 内部的基情。
-
本文向大家介绍在knockoutjs 上自己实现的flux(实例讲解),包括了在knockoutjs 上自己实现的flux(实例讲解)的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在knockoutjs 上实现 Flux 单向数据流 状态机,主要解决多个组件之间对数据的耦合问题。 一、其实简单 flux的设计理念和实现方案,很大程度上人借鉴和参考了Vuex的实现,只是简化了某些过程,数据流向图如下:
-
本文向大家介绍详解 Java HashMap 实现原理,包括了详解 Java HashMap 实现原理的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 HashMap 是 Java 中最常见数据结构之一,它能够在 O(1) 时间复杂度存储键值对和根据键值读取值操作。本文将分析其内部实现原理(基于 jdk1.8.0_231)。 数据结构 HashMap 是基于哈希值的一种映射,所谓映射,即可以根据 key
-
本文向大家介绍如何自己实现一个bind函数?相关面试题,主要包含被问及如何自己实现一个bind函数?时的应答技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 参考回答: 原理:通过apply或者call方法来实现。 (1)初始版本 (2) 考虑到原型链 为什么要考虑?因为在new 一个bind过生成的新函数的时候,必须的条件是要继承原函数的原型 //这里需要一个寄生组合继承
-
本文向大家介绍java HashMap详解及实例代码,包括了java HashMap详解及实例代码的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 java HashMap Map集合的遍历 方式1,根据键查询值 获取所有键的集合 遍历键的集合,获取每一个键 根据键,查询值 方式2,根据键值对的对象查询键和值 获取所有键值对的对象的集合 遍历键值对的对象的集合,获取到每一个键值对的对象 根据键值对的对象

