ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的使用方法
ThreadPoolExecutor
ThreadPoolExecutor线程池,java提供开发框架,管理线程的创建、销毁、优化、监控等。
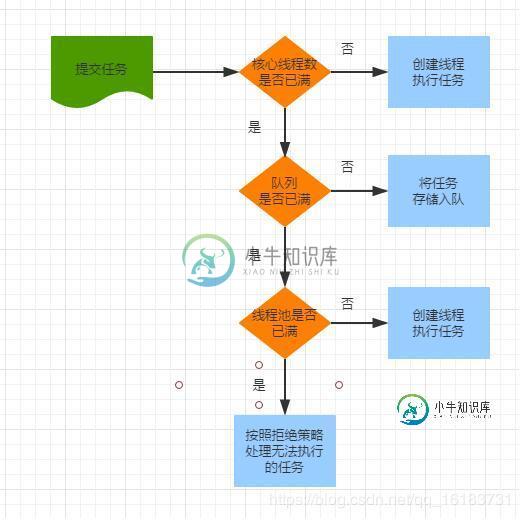
有4种不同的任务队列:
1.ArrayBlockingQueue:基于数组结构的任务队列。此队列按先进先出的原则对任务进行排序。
2.LinkedBlockingQueue:基于链表结构的任务队列。此队列也是按先进先出的原则对任务进行排序。但性能比ArrayBlockingQueue高。
3.synchronousQueue:不存储元素的任务队列。每个插入操作必须等到另一个线程调用移除操作,否则插入操作一直处于阻塞状态。
4.PriorityBlockingQueue:具有优先级的任务队列。此队列中的元素必须能够比较。
拒绝策略:
RejectedExecutionHandler(饱和策略 ):当线程池中的线程数大于maximumPoolSize时,线程池就不能在处理任何任务了,这时线程池会抛出异常。原因就是这个策略默认情况下是AbortPolicy:表示无法处理新任务时抛出异常。
1.AbortPolicy:直接抛出异常。
2.CallerRunsPolicy:只用调用者所在线程来运行任务。
3.DiscardOldestPolicy:丢弃队列里最近的一个任务,并执行当前任务
4.DiscardPolicy:不处理,丢弃掉。
自定义:
ThreadPoolExecutor.AbortPolicy()
//抛出java.util.concurrent.RejectedExecutionException异常
ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy()
//重试添加当前的任务,他会自动重复调用execute()方法
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardOldestPolicy()
//抛弃旧的任务
ThreadPoolExecutor.DiscardPolicy()
// 抛弃当前的任务
private static class RecjectThreadHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler
{
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
}
// 异常记录
private void doLog(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor)
{
System.out.println(r.toString()+"excutor failed."+executor.getCompletedTaskCount());
}
}
创建线程工厂:
用来创建线程。
public class CheckThreadFactory implements ThreadFactory
{
private String threadGroupName;
private AtomicInteger count = new AtomicInteger(0);
public CheckThreadFactory(String threadGroupName) {
this.threadGroupName = threadGroupName;
}
@Override
public Thread newThread(Runnable r)
{
Thread thread = new Thread(r);
thread.setName(threadGroupName+"--"+count.addAndGet(1));
thread.setPriority(5);
thread.setDaemon(true);.// 设置为守护线程, 默认为主线程
return thread;
}
}
线程工具类:
/**
* @author Donald
* @create 2019-09-21 21:40
*/
public class CheckExcetPool
{
// 线程池核心线程数
private static int corePoolSize = Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() * 5;
// 最大线程数
private static int maximumPoolSize = corePoolSize > 255 ? 255 : corePoolSize * 2;
// 线程池中除了核心线程,其他线程的最大存活时间
private static int keepAliveTime = 60;
// 时间单位
private static TimeUnit timeUnit = TimeUnit.SECONDS;
// 线程等待队列
private static BlockingQueue queue = new LinkedBlockingQueue();
//private static BlockingQueue queue = new ArrayBlockingQueue<Runnable>(30);
// 创建线程的工厂
private static CheckThreadFactory checkThreadFactory = new CheckThreadFactory("checkGroup");
// 拒绝策略 当提交任务数超过maxmumPoolSize+workQueue之和时,
// * 即当提交第41个任务时(前面线程都没有执行完,此测试方法中用sleep(100)),
// * 任务会交给RejectedExecutionHandler来处理
/*handler的拒绝策略:
有四种:第一种AbortPolicy:不执行新任务,直接抛出异常,提示线程池已满
第二种DisCardPolicy:不执行新任务,也不抛出异常
第三种DisCardOldSetPolicy:将消息队列中的第一个任务替换为当前新进来的任务执行
第四种CallerRunsPolicy:直接调用execute来执行当前任务*/
private static ThreadPoolExecutor threadPoolExecutor = new ThreadPoolExecutor(
corePoolSize,
maximumPoolSize,
keepAliveTime,
timeUnit,
queue,
checkThreadFactory
);
public static void submit( Runnable runnable)
{
System.out.println(corePoolSize+"::"+queue.size());
threadPoolExecutor.submit(runnable);
}
public static <T> Future submit(Callable<T> callable)
{
return threadPoolExecutor.submit(callable);
}
public static <T> void excutor( Runnable run, T result )
{
threadPoolExecutor.submit( run,result );
}
public static void excutor( Runnable run)
{
threadPoolExecutor.execute( run);
}
private static class RecjectThreadHandler implements RejectedExecutionHandler
{
@Override
public void rejectedExecution(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor) {
}
// 异常记录
private void doLog(Runnable r, ThreadPoolExecutor executor)
{
System.out.println(r.toString()+"excutor failed."+executor.getCompletedTaskCount());
}
}
}
线程服务类,实现runnable 接口:
/**
* @author Donald
* @create 2019-09-21 23:00
*/
public class ThreadService implements Runnable
{
private CountDownLatch countDownLatch;
private UserInterface userInterface;
public ThreadService(CountDownLatch countDownLatch, UserInterface userInterface) {
this.countDownLatch = countDownLatch;
this.userInterface = userInterface;
}
@Override
public void run()
{
try {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
userInterface.doSomething();
System.err.println(String.format("user time :%s",System.currentTimeMillis()-start));
Thread.sleep(1000);
}catch ( Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
countDownLatch.countDown();
}
}
}
具体业务逻辑:
/**
* @author Donald
* @create 2019-09-21 22:51
*/
public interface UserInterface
{
void doSomething();
}
业务类:
/**
* @author Donald
* @create 2019-09-21 22:51
*/
public class UserService implements UserInterface
{
private int number;
public UserService(int number) {
this.number = number;
}
@Override
public void doSomething() {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"<<<<"+number);
}
}
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
主要内容:1 核心线程预启动,1.1 prestartCoreThread启动一条,1.2 prestartAllCoreThreads启动全部,2 关闭线程池,2.1 shutdown温和停止,2.2 shutdownNow立即停止,3 hook钩子方法,4 线程池信息获取,4.1 awaitTermination等待终止,4.2 getTaskCount计划任务数量,4.3 getActiveCount工作线程数量,,,,,,,,,,,前面的文章中,我们介绍了ThreadPoolExecut
-
本文向大家介绍Java ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池的使用介绍,包括了Java ThreadPoolExecutor 线程池的使用介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Executors Executors 是一个Java中的工具类. 提供工厂方法来创建不同类型的线程池. 从上图中也可以看出, Executors的创建线程池的方法, 创建出来的线程池都实现了 Executo
-
主要内容:1 execute核心提交方法,2 addWorker尝试添加新线程,2.1 addWorkerFailed添加Worker失败处理,3 Worker线程包装类,3.1 runWorker执行工作基于JDK1.8详细介绍了ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的execute方法源码! 1 execute核心提交方法 public void execute(Runnable command) 传递一个Runnable任务对象,然后由线程池对它进行异步执行。没有办法检查Runnabl
-
本文向大家介绍线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用简介与方法实例,包括了线程池ThreadPoolExecutor使用简介与方法实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一、简介 线程池类为 java.util.concurrent.ThreadPoolExecutor,常用构造方法为: corePoolSize: 线程池维护线程的最少数量 maximumPoolSize:线程池维护
-
主要内容:1 submit方法,1.1 Future submit(Runnable),1.2 Future submit(Runnable T),1.3 Future submit(Callable< T >),2 FutureTask的原理,2.1 FutureTask的概述,2.2 FutureTask的重要属性,2.3 FutureTask的构造器,2.4 run核心方法,2.5 cancel取消任务,,,,,,详细介绍了ThreadPoolExecutor线程池的submit方法的源码
-
本文向大家介绍Android之线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的简介,包括了Android之线程池ThreadPoolExecutor的简介的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Android中的线程池ThreadPoolExecutor解决了单线程下载数据的效率慢和线程阻塞的的问题,它的应用也是优化实现的方式。所以它的重要性不言而喻,但是它的复杂性也大,理解上可能会有问题,不过作为

