遍历2.5D网格
我正试图找出如何以有效的方式遍历2.5D网格。栅格本身是二维的,但栅格中的每个单元都有一个最小/最大浮动高度。要遍历的线由两个三维浮点坐标定义。如果进入/退出网格单元之间的z值范围与该单元的最小/最大高度不重叠,我希望停止遍历该线。
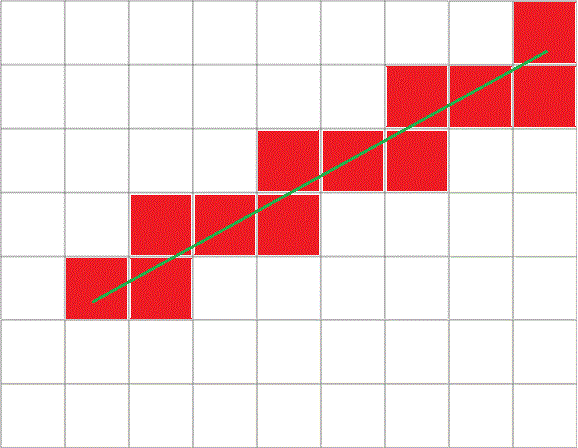
我目前正在使用2D DDA算法按顺序遍历网格单元格(见图),但我不确定如何在到达每个网格单元格时计算z值。如果可以的话,我可以在进入/离开单元格时根据单元格的最小/最大高度测试z值。
有没有办法修改这个算法,允许在输入每个网格单元格时计算z?或者有没有更好的遍历算法允许我这样做?
以下是我当前使用的代码:
void Grid::TraceGrid(Point3<float>& const start, Point3<float>& const end, GridCallback callback )
{
// calculate and normalize the 2D direction vector
Point2<float> direction=end-start;
float length=direction.getLength( );
direction/=length;
// calculate delta using the grid resolution
Point2<float> delta(m_gridresolution/fabs(direction.x), m_gridresolution/fabs(direction.y));
// calculate the starting/ending points in the grid
Point2<int> startGrid((int)(start.x/m_gridresolution), (int)(start.y/m_gridresolution));
Point2<int> endGrid((int)(end.x/m_gridresolution), (int)(end.y/m_gridresolution));
Point2<int> currentGrid=startGrid;
// calculate the direction step in the grid based on the direction vector
Point2<int> step(direction.x>=0?1:-1, direction.y>=0?1:-1);
// calculate the distance to the next grid cell from the start
Point2<float> currentDistance(((step.x>0?start.x:start.x+1)*m_gridresolution-start.x)/direction.x, ((step.y>0?start.y:start.y+1)*m_gridresolution-start.y)/direction.y);
while(true)
{
// pass currentGrid to the callback
float z = 0.0f; // need to calculate z value somehow
bool bstop=callback(currentGrid, z);
// check if the callback wants to stop or the end grid cell was reached
if(bstop||currentGrid==endGrid) break;
// traverse to the next grid cell
if(currentDistance.x<currentDistance.y) {
currentDistance.x+=delta.x;
currentGrid.x+=step.x;
} else {
currentDistance.y+=delta.y;
currentGrid.y+=step.y;
}
}
}
共有3个答案
我想出了一个好办法。在函数开头添加:
float fzoffset=end.z-start.z;
Point2<float> deltaZ(fzoffset/fabs(end.x-start.x), fzoffset/fabs(end.y-start.y));
Point2<float> currentOffset((step.x>0?start.x:start.x+1)*m_gridresolution-start.x, (step.y>0?start.y:start.y+1)*m_gridresolution-start.y);
在currentDistance所在的回路内。x/。y递增,添加:
currentOffset.x+=m_gridresolution; //When stepping in the x axis
currentOffset.y+=m_gridresolution; //When stepping in the y axis
然后在每一步计算z:
z=currentOffset.x*deltaZ.x+start.z; //When stepping in the x axis
z=currentOffset.y*deltaZ.y+start.z; //When stepping in the y axis
对于每个单元格,你知道你来自哪个单元格。这意味着你知道你来自哪一边。在绿线和给定网格线的交叉点计算z似乎微不足道。
Bresenham线算法的3D扩展似乎可以奏效。您将迭代X并独立跟踪线段的Y和Z分量的错误,以确定每个对应X值的Y和Z值。当Z中的累积误差达到某个临界水平时,您只需停止,这表明它超出了最小/最大值。
-
主要内容:什么是遍历?,遍历 DOM什么是遍历? jQuery 遍历,意为"移动",用于根据其相对于其他元素的关系来"查找"(或选取)HTML 元素。以某项选择开始,并沿着这个选择移动,直到抵达您期望的元素为止。 下图展示了一个家族树。通过 jQuery 遍历,您能够从被选(当前的)元素开始,轻松地在家族树中向上移动(祖先),向下移动(子孙),水平移动(同胞)。这种移动被称为对 DOM 进行遍历。 图示解析: <div> 元素是 <
-
本文向大家介绍Swift遍历,包括了Swift遍历的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 例子
-
我试图在Java中使用Selenium遍历一个表(目前使用的是chromedriver)。该表的内容由不同的人组成,他们的个人资料有链接,对于该表中的每个人,我将进入他们的个人资料并提取一些信息。我将为X数量的人做这件事。该表每页包含5人,我通过单击分页按钮浏览页面” 现在来看这个问题:举个例子,我现在在exampleUrl。com/page\u包含表I,然后输入用户的配置文件并提取他们的信息,他
-
编辑:在@Prashant回答后,我明白我的输出顺序需要保留,因此我相应地编辑了我的原始问题并重新发布。 我想从根节点(2)遍历到叶节点(1、6、8、3、11和12)。在这种遍历过程中,我希望获取连接到产品节点13(即)的节点,我希望编写一个返回1、8、9、3、11和12的查询。 @Prashant的回答: 输出 然而,我所需输出的顺序是1、8、9、3、11和12,即在每个级别上,要求选择一个子节
-
无论是调试的需要还是修改节点和边,你可能都需要在现有的有向有环图中进行遍历,下面就介绍图遍历的一些方法。 简单访问 节点和边有很多属性和方法是用来遍历的,边的 from 和 to 属性就是例子,而节点更多: 类型 名称 作用 属性 upstreamNodes 当前节点的所有上游节点 属性 downstreamNodes 当前节点的所有下游节点 属性 upstreamTransforms 当前节点的
-
jQuery是一个非常强大的工具,它提供了各种DOM遍历方法,以帮助我们随机选择文档中的元素以及顺序方法。 大多数DOM遍历方法都不修改jQuery对象,它们用于根据给定条件过滤掉文档中的元素。 按索引查找元素 考虑一个包含以下HTML内容的简单文档 - <html> <head> <title>The JQuery Example</title> </head> <

