spark流检查点恢复非常缓慢
- 目标:从Kinesis读取数据,并通过火花流将数据以拼花格式存储到S3
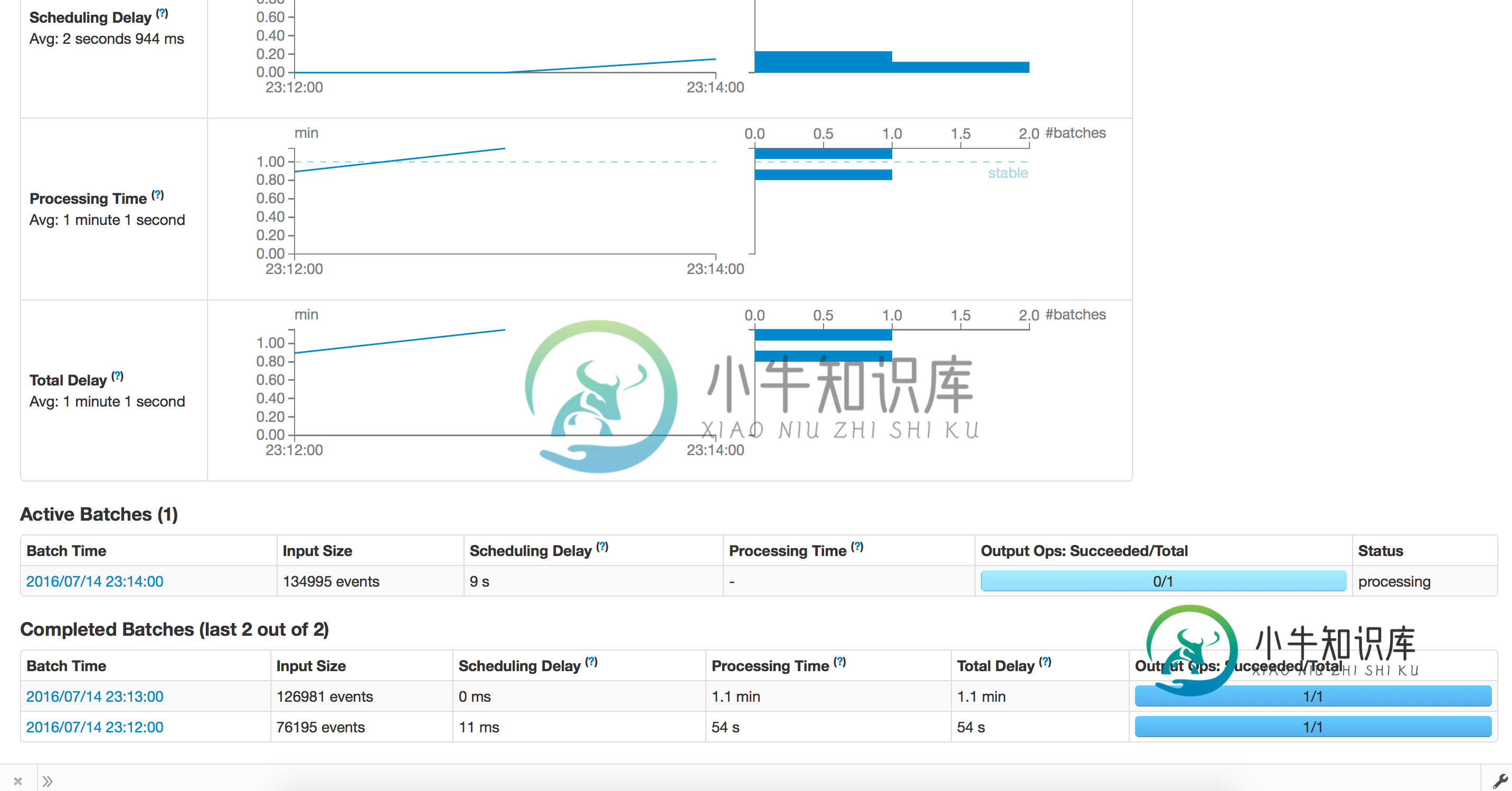
- 情况:应用程序最初运行良好,批量运行1小时,平均处理时间不到30分钟。出于某种原因,假设应用程序崩溃,我们尝试从检查点重新启动。现在,处理过程需要很长时间,不会向前推进。我们尝试以1分钟的分批间隔测试相同的东西,处理运行良好,分批完成需要1.2分钟。当我们从检查点恢复时,每批大约需要15分钟
- 注意:我们使用s3作为检查点,使用1个执行器,19g内存
附上截图:



Config.scala
object Config {
val sparkConf = new SparkConf
val sc = new SparkContext(sparkConf)
val sqlContext = new HiveContext(sc)
val eventsS3Path = sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("eventsS3Path")
val useIAMInstanceRole = sc.hadoopConfiguration.getBoolean("useIAMInstanceRole",true)
val checkpointDirectory = sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("checkpointDirectory")
// sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("spark.sql.parquet.output.committer.class","org.apache.spark.sql.parquet.DirectParquetOutputCommitter")
DateTimeZone.setDefault(DateTimeZone.forID("America/Los_Angeles"))
val numStreams = 2
def getSparkContext(): SparkContext = {
this.sc
}
def getSqlContext(): HiveContext = {
this.sqlContext
}
}
S3盆地.斯卡拉
object S3Basin {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
Kinesis.startStreaming(s3basinFunction _)
}
def s3basinFunction(streams : DStream[Array[Byte]]): Unit ={
streams.foreachRDD(jsonRDDRaw =>{
println(s"Old partitions ${jsonRDDRaw.partitions.length}")
val jsonRDD = jsonRDDRaw.coalesce(10,true)
println(s"New partitions ${jsonRDD.partitions.length}")
if(!jsonRDD.isEmpty()){
val sqlContext = SQLContext.getOrCreate(jsonRDD.context)
sqlContext.read.json(jsonRDD.map(f=>{
val str = new String(f)
if(str.startsWith("{\"message\"")){
str.substring(11,str.indexOf("@version")-2)
}
else{
str
}
})).registerTempTable("events")
sqlContext.sql(
"""
|select
|to_date(from_utc_timestamp(from_unixtime(at), 'US/Pacific')) as event_date,
|hour(from_utc_timestamp(from_unixtime(at), 'US/Pacific')) as event_hour,
|*
|from events
""".stripMargin).coalesce(1).write.mode(SaveMode.Append).partitionBy("event_date", "event_hour","verb").parquet(Config.eventsS3Path)
sqlContext.dropTempTable("events")
}
})
}
}
Kinesis.scala
object Kinesis{
def functionToCreateContext(streamFunc: (DStream[Array[Byte]]) => Unit): StreamingContext = {
val streamingContext = new StreamingContext(Config.sc, Minutes(Config.sc.hadoopConfiguration.getInt("kinesis.StreamingBatchDuration",1))) // new context
streamingContext.checkpoint(Config.checkpointDirectory) // set checkpoint directory
val sc = Config.getSparkContext
var awsCredentails : BasicAWSCredentials = null
val kinesisClient = if(Config.useIAMInstanceRole){
new AmazonKinesisClient()
}
else{
awsCredentails = new BasicAWSCredentials(sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("kinesis.awsAccessKeyId"),sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("kinesis.awsSecretAccessKey"))
new AmazonKinesisClient(awsCredentails)
}
val endpointUrl = sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("kinesis.endpointUrl")
val appName = sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("kinesis.appName")
val streamName = sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("kinesis.streamName")
kinesisClient.setEndpoint(endpointUrl)
val numShards = kinesisClient.describeStream(streamName).getStreamDescription().getShards().size
val batchInterval = Minutes(sc.hadoopConfiguration.getInt("kinesis.StreamingBatchDuration",1))
// Kinesis checkpoint interval is the interval at which the DynamoDB is updated with information
// on sequence number of records that have been received. Same as batchInterval for this
// example.
val kinesisCheckpointInterval = batchInterval
// Get the region name from the endpoint URL to save Kinesis Client Library metadata in
// DynamoDB of the same region as the Kinesis stream
val regionName = sc.hadoopConfiguration.get("kinesis.regionName")
val kinesisStreams = (0 until Config.numStreams).map { i =>
println(s"creating stream for $i")
if(Config.useIAMInstanceRole){
KinesisUtils.createStream(streamingContext, appName, streamName, endpointUrl, regionName,
InitialPositionInStream.TRIM_HORIZON, kinesisCheckpointInterval, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2)
}else{
KinesisUtils.createStream(streamingContext, appName, streamName, endpointUrl, regionName,
InitialPositionInStream.TRIM_HORIZON, kinesisCheckpointInterval, StorageLevel.MEMORY_AND_DISK_2,awsCredentails.getAWSAccessKeyId,awsCredentails.getAWSSecretKey)
}
}
val unionStreams = streamingContext.union(kinesisStreams)
streamFunc(unionStreams)
streamingContext
}
def startStreaming(streamFunc: (DStream[Array[Byte]]) => Unit) = {
val sc = Config.getSparkContext
if(sc.defaultParallelism < Config.numStreams+1){
throw new Exception(s"Number of shards = ${Config.numStreams} , number of processor = ${sc.defaultParallelism}")
}
val streamingContext = StreamingContext.getOrCreate(Config.checkpointDirectory, () => functionToCreateContext(streamFunc))
// sys.ShutdownHookThread {
// println("Gracefully stopping Spark Streaming Application")
// streamingContext.stop(true, true)
// println("Application stopped greacefully")
// }
//
streamingContext.start()
streamingContext.awaitTermination()
}
}


共有3个答案
我以前也遇到过类似的问题,我的应用程序越来越慢。
使用rdd后尝试释放内存,调用< code > rdd . un persist() https://spark . Apache . org/docs/latest/API/Java/org/Apache/spark/rdd/rdd . html # un persist(boolean)
或 Spark.streaming.backpressure.enabled 为 true
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-programming-guide.html#setting-the-right-batch-interval
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/streaming-programming-guide.html#requirements
此外,检查您的locity设置,可能有太多数据移动。
重新启动失败的驱动程序时,将发生以下情况:
-
< li >恢复计算–检查点信息用于重启驱动程序、重建上下文和重启所有接收器。 < li >恢复块元数据–将恢复继续处理所需的所有块的元数据。 < li >重新生成未完成的作业–对于因失败而未完成处理的批处理,使用恢复的块元数据重新生成rdd和相应的作业。 < li >读取保存在日志中的块-当执行这些作业时,直接从预写日志中读取块数据。这将恢复所有可靠地保存到日志中的必要数据。 < li >重新发送未确认的数据–失败时未保存到日志的缓冲数据将由源再次发送。因为它没有被接收者确认。
参考这里。
提出了一个Jira问题:https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SPARK-19304
问题是因为我们每次迭代读取的数据比所需的多,然后丢弃数据。这可以通过向get的aws调用添加限制来避免。
修复:https://github.com/apache/spark/pull/16842
-
我有一份flink的工作,它使用Kafka的数据,制作一些无状态平面图,并向Kafka生成数据,这是一份工作量非常小的工作。 例如,在作业需要从检查点还原之前,它通常会无问题地获取检查点,而它只是无法使用下面的堆栈跟踪还原状态。 状态非常小,我相信它只是Kafka偏移量,它至少运行了一次语义。 所有操作员都有。uid()集,我完全没有主意了。 这是尝试从检查点重新启动时的错误: 任务管理器在正常操
-
我对闪身是个新手。我正在尝试在我的应用程序中启用检查点和状态。我从Flink文档中看到了我们是如何存储键控状态的。但是我想知道我们是否可以存储非键控状态(的状态)
-
1)以上假设是否正确。2)当发生故障时,滚动窗口有状态是否有意义,我们从最后一个kafka分区提交的偏移量开始。3)当滚动窗口有状态时,这个状态什么时候可以被flink使用。4)为什么检查点和保存点的状态大小不同。5)当发生故障时,flink总是从sorce运算符开始。对吗?
-
我正在检查Flink Sql Table与kafka连接器是否可以在EXACTLY_ONCE模式下执行,我的方法是创建一个表,设置合理的检查点间隔,并在event_time字段上使用简单的翻滚函数,最后重新启动我的程序。 以下是我的详细进度: 1:创建一个Kafka表 2:启动我的 Flink 作业,如下所示配置 3:执行我的sql 如我们所见,翻转窗口间隔为5分钟,检查点间隔为30秒,每个翻转窗
-
我只想问一下如何在Spark中成功使用checkpointInterval的细节。你在ALS代码中的这个注释是什么意思https://github.com/apache/spark/blob/master/mllib/src/main/scala/org/apache/spark/mllib/recommendation/ALS.scala 如果未在[[org . Apache . spark .
-
问题内容: 在defer函数中,我想查看一次恢复调用是否会产生非nil值(不恢复) 可能吗? 问题答案: 那确切的事情是不可能的。您可能只想重新恐慌,就像在其他语言中重新引发异常一样。

