KISSFFT中2D阵列之间的逐元素乘法结果与SciPy FFT不同
我正在与试验KISSFFT在 C ++
气馁使用后FFTPACK处理二维数组。
我编写了 逐个元素的乘法* 函数,将两个2D数组用转换后再相乘kiss_fftnd()。然后,通过逆FFT函数将乘法结果转换回去。不幸的是,我在
C语言 中从 kissfft 获得的结果与我在 python中 通过 SciPy 获得的结果不同,如下图所示:
*
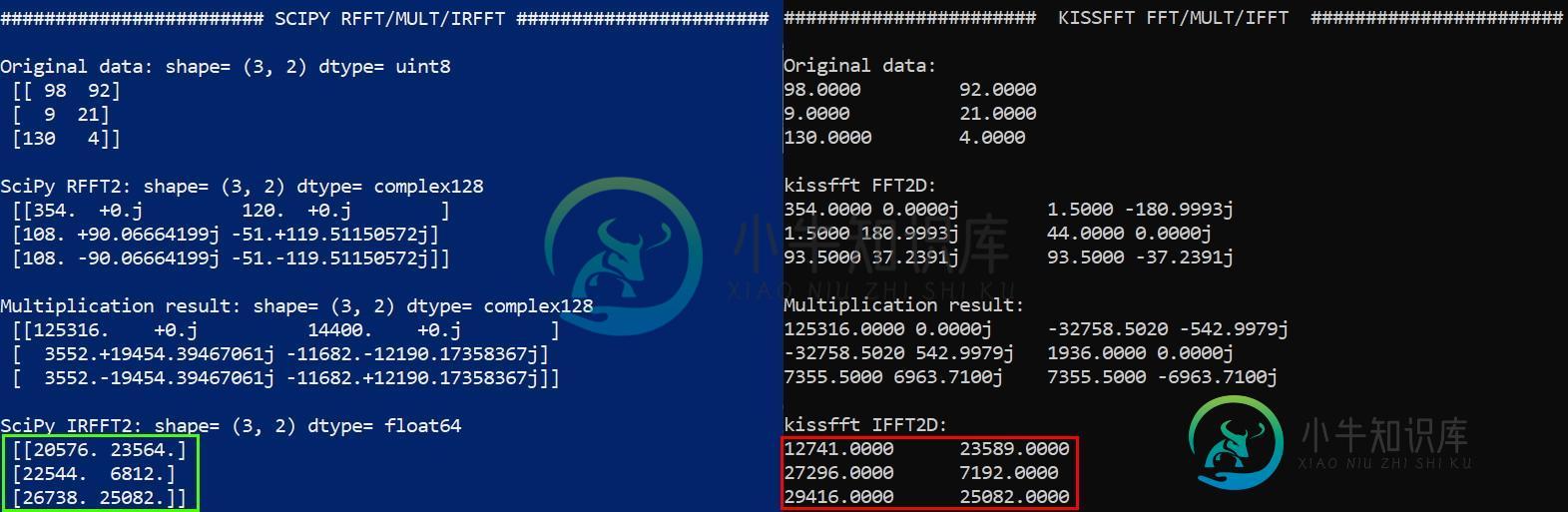
为了测试乘法函数,在转换2D输入数组后,为简单起见,我将其与自身相乘。这是Python的简化版本,用于说明算法:
import numpy as np
from scipy import fft as scipy_fft
in1 = np.array([[ 98, 92], \
[ 9, 21], \
[ 130, 4]], dtype=np.uint8)
fft_out = scipy_fft.rfft2(in1)
fft_mult = fft_out * fft_out
ifft_data = scipy_fft.irfft2(fft_mult, in1.shape)
print('\nSciPy IRFFT2: shape=', ifft_data.shape, 'dtype=', ifft_data.dtype, '\n', ifft_data)
我想不出用 kissfft
无法完成此简单操作的原因,这意味着我的乘法方法可能是错误的。由于的输出kiss_fftnd()是一维数组而不是2D数组,因此我用来对该数组进行迭代并执行逐元素乘法的逻辑可能不正确。
为什么这些结果不同?如何使Kissfft返回与SciPy相同的值?
如果您知道 kissfft 中已经正确执行乘法的函数, 那么 这对我也将起作用。请不要建议其他图书馆来完成这项工作。我正在寻找专门针对
kissfft 的答案。
这是Python中的完整源代码:
import numpy as np
from scipy import fft as scipy_fft
# complex_mult: multiplies two complex numbers
def complex_mult(n1, n2):
real_part = n1.real*n2.real - n1.imag*n2.imag
imag_part = n1.real*n2.imag + n2.real*n1.imag
return complex(real_part, imag_part)
# fft2d_mult: multiplies two 2D arrays of complex numbers
def fft2d_mult(array1, array2):
array_mult = np.empty(array1.shape, dtype=array1.dtype)
h, w = in1.shape
for j in range(h):
for i in range(w):
array_mult[j,i] = complex_mult(array1[j,i], array2[j,i])
return array_mult
print("\n######################## SCIPY RFFT/MULT/IRFFT #######################\n");
# initialize input data
in1 = np.array([[ 98, 92], \
[ 9, 21], \
[ 130, 4]], dtype=np.uint8)
print('Original data: shape=', in1.shape, 'dtype=', in1.dtype, '\n', in1)
# perform 2D RFFT
fft_out = scipy_fft.rfft2(in1)
print('\nSciPy RFFT2: shape=', fft_out.shape, 'dtype=', fft_out.dtype, '\n', fft_out)
# perform element-wise multiplication
fft_mult = fft2d_mult(fft_out, fft_out) # equivalent to: fft_mult = fft_out * fft_out
print('\nMultiplication result: shape=', fft_mult.shape, 'dtype=', fft_mult.dtype, '\n', fft_mult)
# perform inverse 2D RFFT
ifft_data = scipy_fft.irfft2(fft_mult, in1.shape)
print('\nSciPy IRFFT2: shape=', ifft_data.shape, 'dtype=', ifft_data.dtype, '\n', ifft_data)
这是C ++中的完整源代码:
// compile with: g++ so_issue.cpp -o so_issue -I kissfft kissfft/kiss_fft.c kissfft/tools/kiss_fftnd.c
#include "kissfft/kiss_fft.h"
#include "kissfft/tools/kiss_fftnd.h"
// fft2d: receives a 2D array of floats, performs the forward transform with kiss_fftnd() and converts it into a kiss_fft_cpx array
kiss_fft_cpx* fft2d(float* input, int width, int height)
{
const int numDim = 2;
int shape[numDim] = { width, height };
int nfft = width * height;
// allocate 2D input array for FFT
kiss_fft_cpx* cin = new kiss_fft_cpx[nfft];
memset(cin, 0, nfft * sizeof(kiss_fft_cpx));
// allocate 2D output array for FFT
kiss_fft_cpx* cout = new kiss_fft_cpx[nfft];
memset(cout, 0, nfft * sizeof(kiss_fft_cpx));
// copy the input data to cin
int k = 0;
int idx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < height; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < width; ++i)
{
idx = i + width * j; // access 1D array as 2D
cin[k++].r = input[idx];
}
}
// execute 2D FFT
bool inverse_fft = false;
kiss_fftnd_cfg cfg_f = kiss_fftnd_alloc(shape, numDim, inverse_fft, 0, 0);
kiss_fftnd(cfg_f, cin , cout);
// release resources
kiss_fft_free(cfg_f);
delete[] cin;
return cout;
}
// fft2d: receives an array of kiss_fft_cpx elements, performs the inverse transform with kiss_fftnd() and returns the result in a new kiss_fft_cpx array
kiss_fft_cpx* ifft2d(kiss_fft_cpx* input, int width, int height)
{
const int numDim = 2;
int shape[numDim] = { width, height };
int nfft = width * height;
// allocate 2D output array for FFT
kiss_fft_cpx* cout = new kiss_fft_cpx[nfft];
memset(cout, 0, nfft * sizeof(kiss_fft_cpx));
// execute inverse 2D FFT
bool inverse_fft = true;
kiss_fftnd_cfg cfg_i = kiss_fftnd_alloc(shape, numDim, inverse_fft, 0, 0);
kiss_fftnd(cfg_i, input , cout);
// release resources
kiss_fft_free(cfg_i);
return cout;
}
// complex_mult: performs element-wise multiplication between two complex numbers
kiss_fft_cpx complex_mult(const kiss_fft_cpx& a, const kiss_fft_cpx& b)
{
kiss_fft_cpx c;
// real_part = a.real*b.real - a.imag*b.imag
c.r = a.r*b.r - a.i*b.i;
// imag_part = a.real*b.imag + b.real*a.imag
c.i = a.r*b.i + b.r*a.i;
return c;
}
// complex_mult: performs element-wise multiplication between two kiss_fft_cpx arrays
kiss_fft_cpx* fft2d_mult(kiss_fft_cpx* input1, kiss_fft_cpx* input2, int width, int height)
{
int nfft = width * height;
kiss_fft_cpx* output = new kiss_fft_cpx[nfft];
memset(output, 0, nfft * sizeof(kiss_fft_cpx));
int idx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < height; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < width; ++i)
{
idx = i + width * j; // access 1D array as 2D
output[idx] = complex_mult(input1[idx], input2[idx]);
}
}
return output;
}
void run_test(float* in1, const int& w, const int& h)
{
printf("\n####################### KISSFFT FFT/MULT/IFFT #######################\n\n");
printf("Original data:\n");
int idx = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < h; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i)
{
idx = i + w * j;
printf("%.4f \t", in1[idx]);
}
printf("\n");
}
/* perform FFT */
kiss_fft_cpx* cout = fft2d((float*)in1, w, h);
printf("\nkissfft FFT2D:\n");
for (int j = 0; j < h; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i)
{
idx = i + w * j;
printf("%.4f %.4fj \t", cout[idx].r, cout[idx].i);
}
printf("\n");
}
/* perform element-wise multiplication */
kiss_fft_cpx* cout_mult = fft2d_mult(cout, cout, w, h);
printf("\nMultiplication result:\n");
for (int j = 0; j < h; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i)
{
idx = i + w * j;
printf("%.4f %.4fj \t", cout_mult[idx].r, cout_mult[idx].i);
}
printf("\n");
}
/* perform inverse FFT */
kiss_fft_cpx* cinput = ifft2d(cout_mult, w, h);
printf("\nkissfft IFFT2D:\n");
int nfft = w * h;
for (int j = 0; j < h; ++j)
{
for (int i = 0; i < w; ++i)
{
idx = i + w * j;
printf("%.4f \t", cinput[idx].r / nfft); // div by N to scale data back to the original range
}
printf("\n");
}
// release resources
delete[] cout_mult;
delete[] cinput;
delete[] cout;
}
int main()
{
int h = 3, w = 2;
float in1[h][w] =
{
{ 98, 92 },
{ 9, 21 },
{ 130, 4 }
};
run_test((float*)in1, w, h);
return 0;
}
问题答案:
问题是width和height中使用的顺序shape。此变量随后kiss_fftnd_alloc()作为参数传递给,height必须首先定义:
const int numDim = 2;
int shape[numDim] = { height, width };
使得在此之后改变内部fft2d()和ifft2d()应用程序中显示正确的结果。
-
在R中,我可以在矩阵和(共形)向量之间进行分段乘法,例如: 矩阵的每一行都与相应的向量元素相乘。我也可以对维度大于2的数组做同样的事情: 同样,每一行都与相应的向量元素相乘。我能为3d阵列和2d矩阵做类似的事情吗?我只想让数组中的每个子矩阵都按元素乘以一个矩阵。
-
> 值1:8值2:16值3:3值4:13值5:24 它应该检查值是否在上限和下限之间。例如 0-9=2//(3,8)10-20=2//(13,16)20-30=1//(24)30-40=0等等。。。 但在代码中它只是显示。。。0-9=110-20=2 20-30=3 30-40=4,依此类推。
-
在使用numpy的python中,假设我有两个矩阵: 稀疏矩阵 密集的x*y矩阵 现在我想做,它将返回一个密集的矩阵。 但是,我只关心中非零的单元格,这意味着如果我这样做了,对我的应用程序不会有任何影响 <代码>S\u=S*S\u 显然,这将是对操作的浪费,因为我想把在
-
我有几个维度的多维矩阵,其中中的每个元素都是一个单独的传感器输入,是时间。我想做的是只分析中每个元素在上的峰值,因此我将得到一个的二维矩阵,其中只包含最大值。 我知道有很多方法可以获得单个整体最大值,但是有没有一种方法可以将它与逐个元素的操作相结合,比如,这样它就可以通过检查每个单独的元素? 如果你能给我任何帮助,我将感激不尽,因为我现在真的被困住了。提前谢谢!
-
问题内容: 我正在自学一些Java,并且坚持创建2D数组,该数组使用随机值对其进行初始化,然后创建该数组的转置。 示例输出为: 原始矩阵 转置矩阵 ^应该是最终输出。代码的一些帮助将不胜感激! 如果行或列的数量超出指定范围,我想编写代码以生成错误消息。以及是否从命令行读取矩阵元素而不是随机生成它们。 问题答案: 这是返回转置矩阵的int [] []的简单方法… 比起打印二维矩阵,您可以使用如下方法
-
给出了一个长度为n的数组。求子数组元素的乘积之和。 解释 长度为3的数组A=[2,3,4]。 因为,对于以模1000000007计算的较长的子数组,乘积可以更大。 对于所有可能长度的子数组,即1,2,3,....,n,求这些和的有效方法是什么,其中n是数组的长度。

