Digestif
Digestif is a code analyzer, and a language server, for LaTeX,ConTeXt et caterva. It provides context-sensitive completion,documentation, code navigation, and related functionality to any texteditor that speaks the LSP protocol.
Check it out online: Digestif is the autocompletion engine of theSwiftLaTeX web-based editor.
Features
Completion for commands, environments, key-value options (forinstance, TikZ options), cross-references and citations.
Popup help messages, including command signature and documentation.For the best results, make sure you have the LaTeX referencemanual installed as an info node.
Find definition and references to labels and citations.
Document outline.
Multi-file documents are supported via TeXShop-style magic comments.Just add a comment like this near the top of each child document:
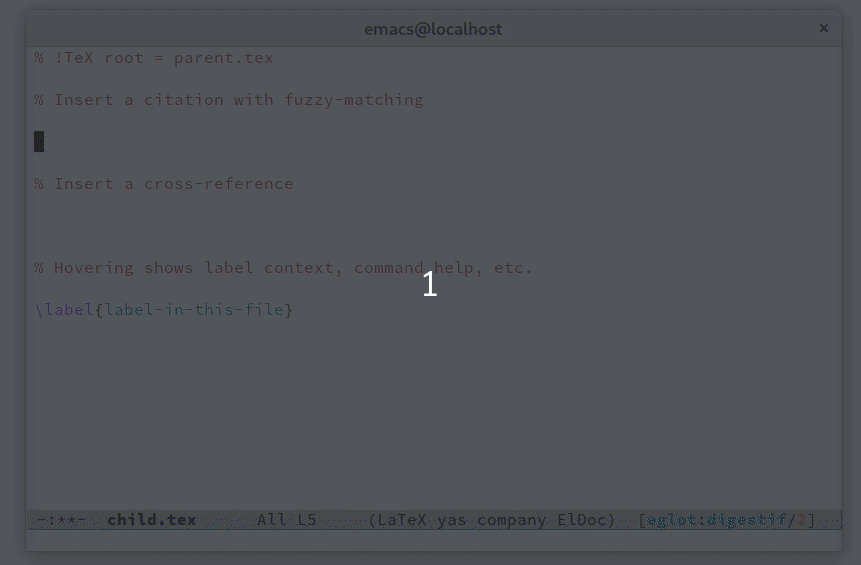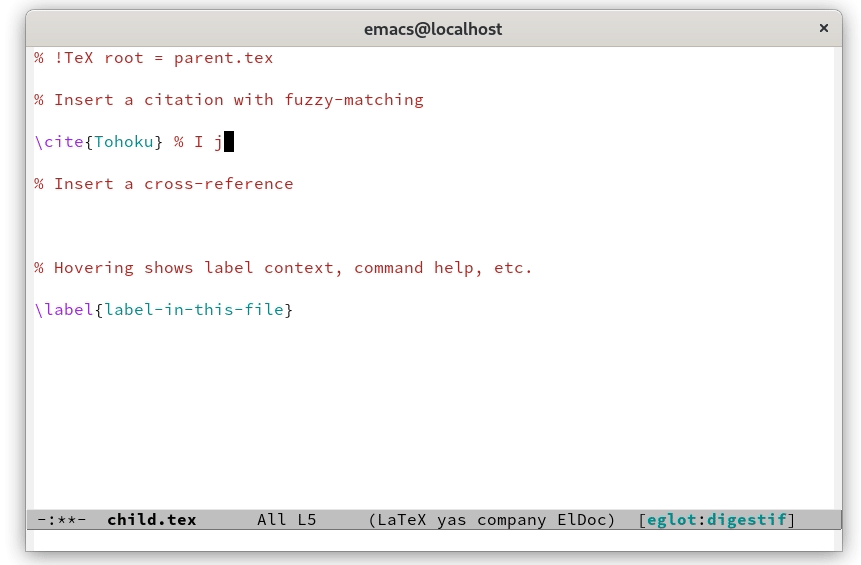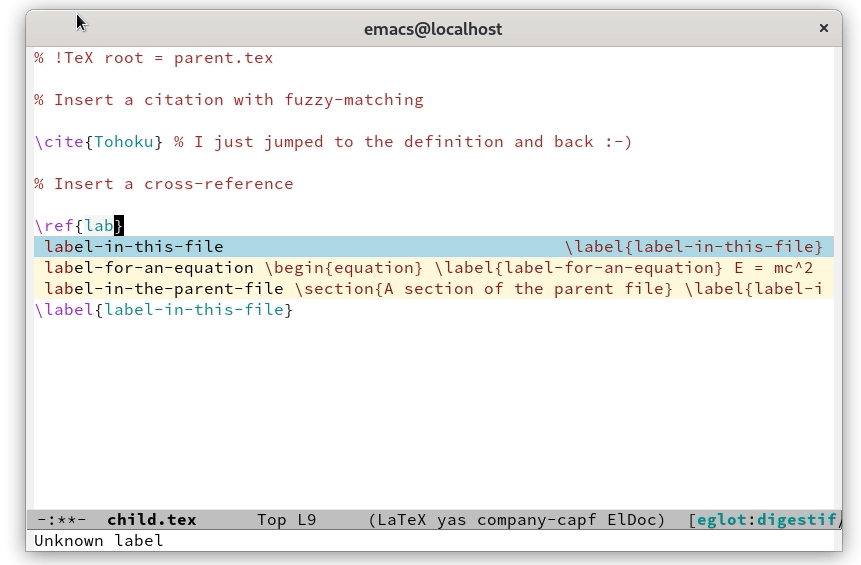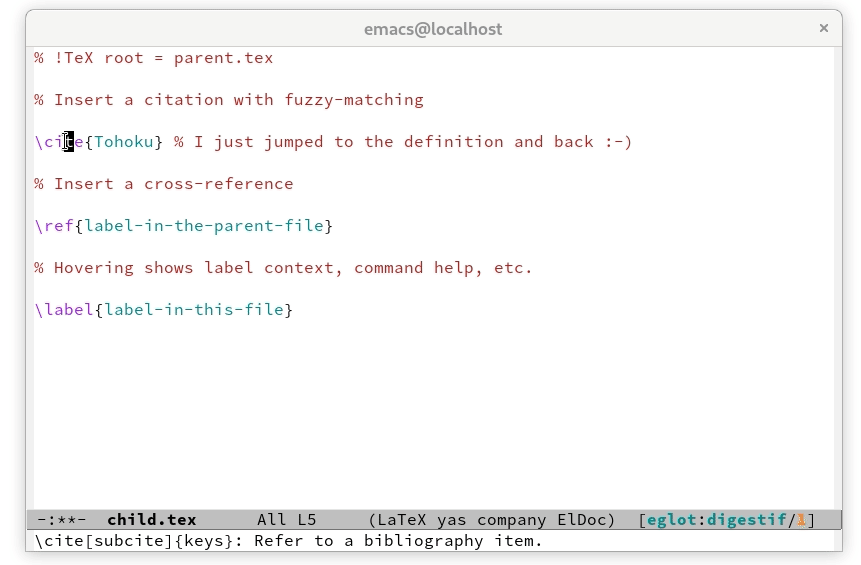
% !TeX root = somefile.texDigestif is fuzzy! For citations, it tries an exact match againstthe BibTeX identifier and a fuzzy match against author and title.In the GIF above, the user types
groalhom, which matchesGrothendieck's “Sur quelques points d'algébrehomologique”; selecting this inserts the BibTeX identifierTohoku. Similarly, for cross-references, Digestif tries an exactmatch against the label and a fuzzy match against the text aroundthe label.Support for LaTeX, ConTeXt, plain TeX and Texinfo.
Bibliography support via BibTeX and amsrefs.
Lua API, independent of the language server protocol, for use ineditors capable of loading Lua modules. See API on the wikifor details.
Installation and set-up
Digestif has minimal dependencies and can run on LuaTeX or on astandalone Lua interpreter. Correspondingly, there are two ways toinstall it.
For LuaTeX with the self-installing script: The onlydependencies for this are git and a recent TeX installation.

- Download the digestif wrapper script.
- Place it in your
$PATH(say,~/.local/bin). - Make it executable (
chmod +x ~/.local/bin/digestif).
In the first run, the script will automatically download thepackage, by default to
~/.digestif. To update or uninstall,simply delete that folder.For standalone Lua via LuaRocks: Run
luarocks install digestif. This should be done either as root or with the--localoption, in which case the executable script will land in~/.luarocks/bin/digestif; make sure this is in your$PATHoradapt your text editor configuration accordingly.
Next, you need to enable Digestif as a language server in yourfavorite text editor.
Emacs with the Eglot package: Digestif works out-of-the-boxwith Eglot. Just install the package (
M-x package-install RET eglot RET), open some TeX document and enable Eglot (M-x eglot).Voilà! Make sure to activateyas-minor-modebefore starting upEglot if you want to have code snippets inserted automatically afterchoosing a completion candidate.Emacs with the lsp-mode package: Just add
(setq lsp-tex-server 'digestif)
to your init file to ensure that Digestif is used.
Supported TeX packages
Digestif tries to learn about the commands provided by a package bylooking at its source code, but this has limitations, since thetypical TeX literate documentation is ostensibly not machine readable.
For full support, a detailed “tags” file should be created for eachpackage. Among other things, this file lists all defined macrostogether with their signatures and docstrings. To generate a stubtags file from a .sty, .cls or .dtx file, use the command
digestif --generate FILES
After filling in the missing details, the resulting tags file can beadded to this repository (pull requests are welcome!). The format ofthe tags files should be more or less self explanatory. See the datafolder for examples.
License
The Digestif program and library, that is, everything outside thedata folder, are available under the MIT license.
Some files in the data folder are extracted or adapted from othersources, such as source code, manuals or reference materials, andtherefore may inherit specific licensing details. At a minimum, theyare free to use and redistribute. When no restriction exists, the MITlicense also applies.