What is this repository for?
Node.js app architecture showcase using Express, MongoDB and Mongoose as ORM. The project has an implementation of an authentication system that uses JSON Web Token to manage users' login data in Node.js web server. You can start your Node.js projects building on this boilerplate.
Architecture Overview
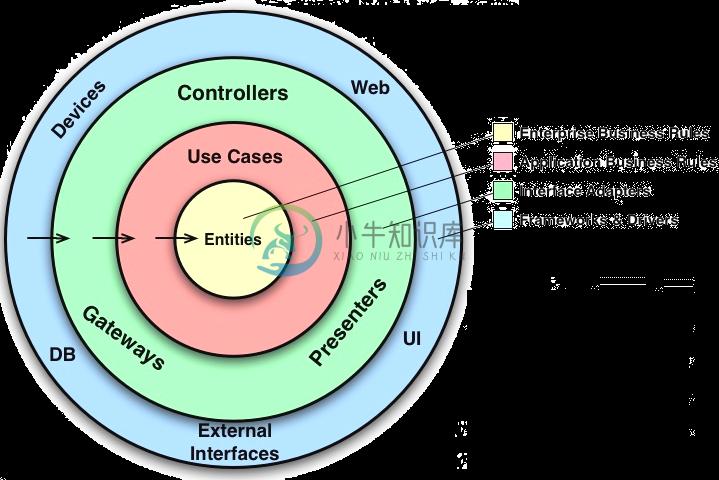
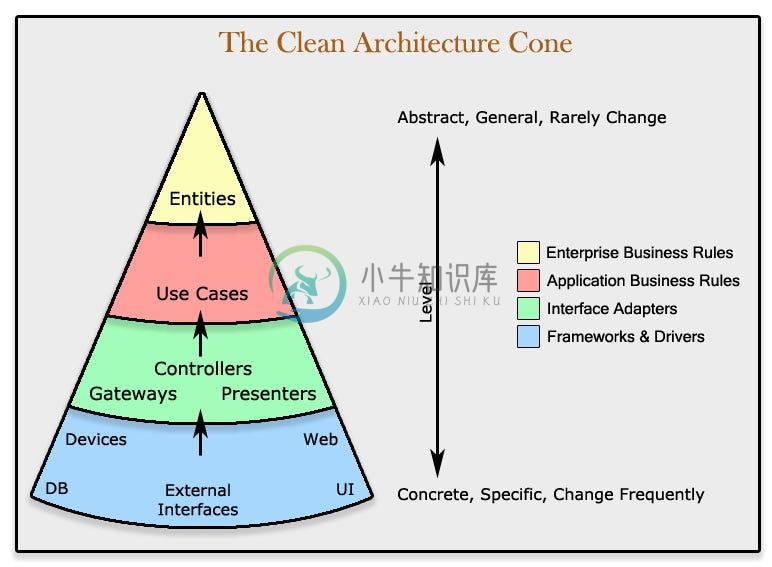
The app is designed to use a layered architecture. The architecture is heavily influenced by the Clean Architecture.Clean Architecture is an architecture where:
- does not depend on the existence of some framework, database, external agency.
- does not depend on UI
- the business rules can be tested without the UI, database, web server, or any external element.
Also, in entry point(server.js), I use Dependency Injection(DI). There are many reasons using Dependency Injection as:
- Decoupling
- Easier unit testing
- Faster development
- Dependency injection is really helpful when it comes to testing. You can easily mock your modules' dependencies using this pattern.
You can take a look at this tutorial: https://blog.risingstack.com/dependency-injection-in-node-js/.According to DI:A. High-level modules should not depend on low-level modules. Both should depend on abstractions.B. Abstractions should not depend on details.
The code style being used is based on the airbnb js style guide.
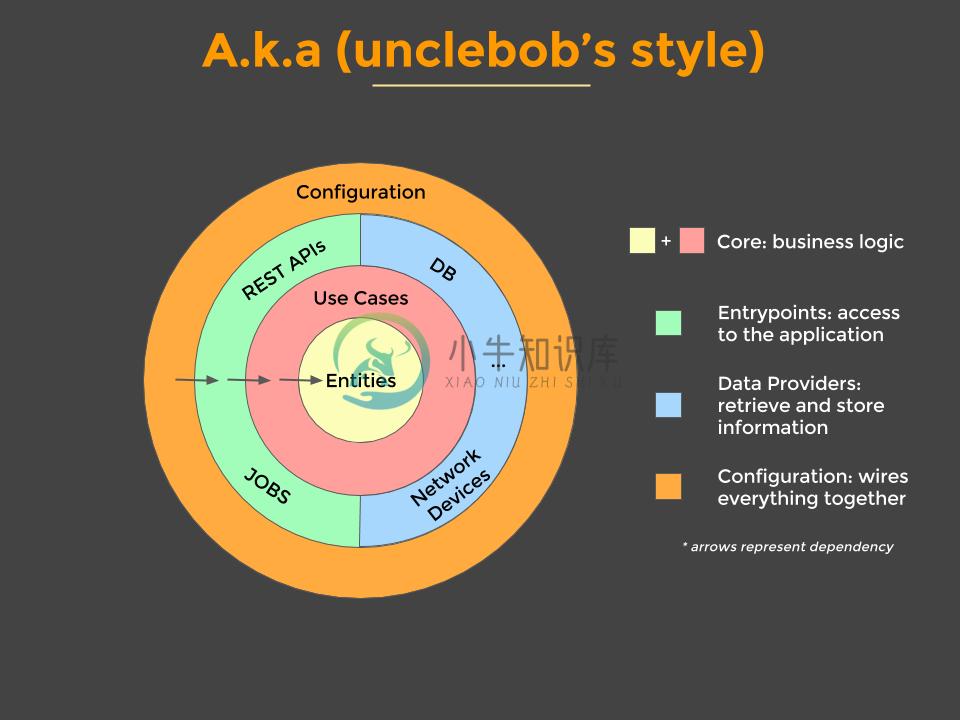
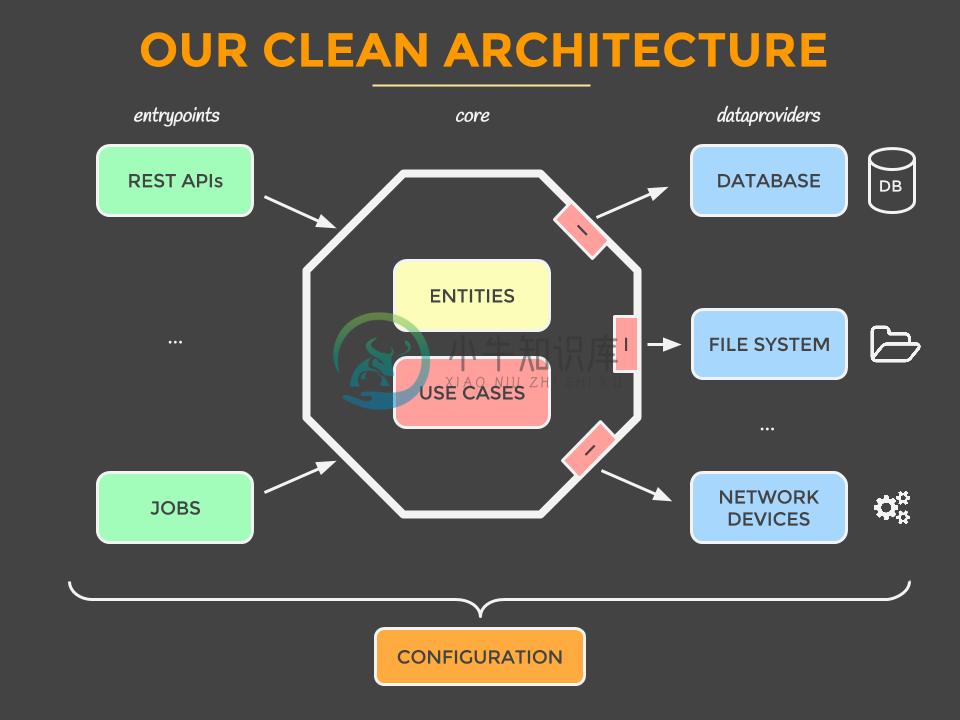
Data Layer
The data layer is implemented using repositories, that hide the underlying data sources (database, network, cache, etc), and provides an abstraction over them so other parts of the application that make use of the repositories, don't care about the origin of the data and are decoupled from the specific implementations used, like the Mongoose ORM that is used by this app. Furthermore, the repositories are responsible to map the entities they fetch from the data sources to the models used in the applications. This is important to enable the decoupling.
Domain Layer
The domain layer is implemented using services. They depend on the repositories to get the app models and apply the business rules on them. They are not coupled to a specific database implementation and can be reused if we add more data sources to the app or even if we change the database for example from MongoDB to Couchbase Server.
Routes/Controller Layer
This layer is being used in the express app and depends on the domain layer (services). Here we define the routes that can be called from outside. The services are always used as the last middleware on the routes and we must not rely on res.locals from express to get data from previous middlewares. That means that the middlewares registered before should not alter data being passed to the domain layer. They are only allowed to act upon the data without modification, like for example validating the data and skipping calling next().
Entry point
The entry point for the applications is the server.js file. It does not depend on express.js or other node.js frameworks. It is responsible for instantiating the application layers, connecting to the db and mounting the http server to the specified port.
Quick start
Prerequisites
Create an .env file in project root to register the following required environment variables:
DATABASE_URL- MongoDB connection URLHTTP_PORT- port of serverJWT_SECRET- we will use secret to generate our JSON web tokensREDIS_URL- redis client
Use Docker:
You can use Docker to start the app locally. The Dockerfile and the docker-compose.yml are already provided for you. For this option you must specify following var in the .env file:
DATABASE_URL
then run the following command:
docker-compose up
Use the npm scripts:
npm run test
for running tests.
Endpoints
Auth Routes
Register
POST /auth/register
Body Params:
{
name,
surname,
username,
email,
password
}
Description: creates a new user. Password is stored in bcrypt format.
Login
POST /auth/login
Body Params:
{
email,
password
}
Description: logs in to the server. Server will return a JWT token and user's info as:
{
"status": "success",
"data": {
"token": {
id: "eyJhbGciOiJIUzxxxxxxx.eyJlbWFpbCI6ImRpbW9zdGhlbxxxxxxxxxxxxx.axxxxxxxxxx",
expiresIn: 86400,
},
"user": {
"id": "mongoID",
"fullName": "clark kent",
"username": "superman",
"email": "clarkkent@test.com",
"created": "2018-01-08T14:43:32.480Z"
}
}
}
User Routes
In order to be able to retrieve posts list, user should send a Bearer token using Authorization header, otherwise server will answer with 401.
Get specific user
GET /users/:userId
Description: Gets specific user.
Posts Routes
In order to be able to retrieve posts list, user should send a Bearer token using Authorization header, otherwise server will answer with 401.
Posts List
GET /users/:userId/posts
Query Params:
{
publisher, {String} (optional)
}
Description: retrieves user's posts docs, based on his token and his id.
POST /users/:userId/posts
Body Params:
{
imageUrl, {String}
publisher, {String}
description, {String} (optional)
}
Description: creates a new post doc in DB for user.
GET /users/:userId/posts/:postId
Description: Gets specific user's post.
Packages and Tools
-
前言 近期把自用的微信公众号微信分享模块从 php 修改为 nodejs 的版本,虽然这是一个很小的功能,但仍然选择了 egg 框架,也算是为未来继续开发公众号,做点扩展的准备。 本文章仅为项目介绍,不涉及 egg 的原理,请不要问我为啥不直接用koa。 一、 egg本地环境搭建 1. egg简介 koa框架:基于 Node.js 平台的新的 web 框架,由 Express 幕后的原班人马打造,
-
nodejs-restful-api How to create a RESTful CRUD API using Nodejs? This tutorial will demo how to set up a bare bonesAPI using mongodb as the database. It consist of a User model and controller. The mo
-
NodeJS-API-Boilerplate Always in progress �� Get Started Installation Install Mongodb Raven Log Body Whitelist Api Doc Pre-Commit Hook Scripts Dev-Debug Why toJSON() on methods model For validation o
-
Nodejs Expressjs MongoDB Ready-to-use API Project Structure A ready-to-use boilerplate for REST API Development with Node.js, Express, and MongoDB Getting started This is a basic API skeleton written
-
Setup $ yarn install && open http://localhost:4000 && yarn run start Medium: https://medium.com/@wesharehoodies/how-to-setup-a-powerful-api-with-nodejs-graphql-mongodb-hapi-and-swagger-e251ac189649?
-
这是我的代码,我试图通过它发送请求http://localhost:3000/api/post/article使用邮递员,但我收到无法获取的错误。它不用路由器就可以工作。获取,但使用应用程序。所以我认为问题出在路由器上。 这是server.js文件 这是应用程序文件 这是路由器文件 这是控制器文件
-
我们有以下DAML合同: 数据某物=选项A |选项B派生(显示,等式) 数据详细信息=id为的详细信息:文本名称:文本状态:文本 模板主带a:方b:方 我知道我们可以为“a”和“b”做以下事情: 字段:{a:daml.party(a),b:daml.party(b),}但是我如何为c和d编写代码呢?