_______________________________
( ____ \__ __|__ __( ___ )
| ( \/ ) ( ) ( | ( ) |
| | | | | | | (___) |
| | ____ | | | | | ___ |
| | \_ ) | | | | | ( ) |
| (___) |__) (___ | | | ) ( |
(_______)_______/ )_( |/ \| v0.15
Gita: a command-line tool to manage multiple git repos
This tool does two things
- display the status of multiple git repos such as branch, modification, commit message side by side
- (batch) delegate git commands/aliases from any working directory
If several repos are related, it helps to see their status together.I also hate to change directories to execute git commands.
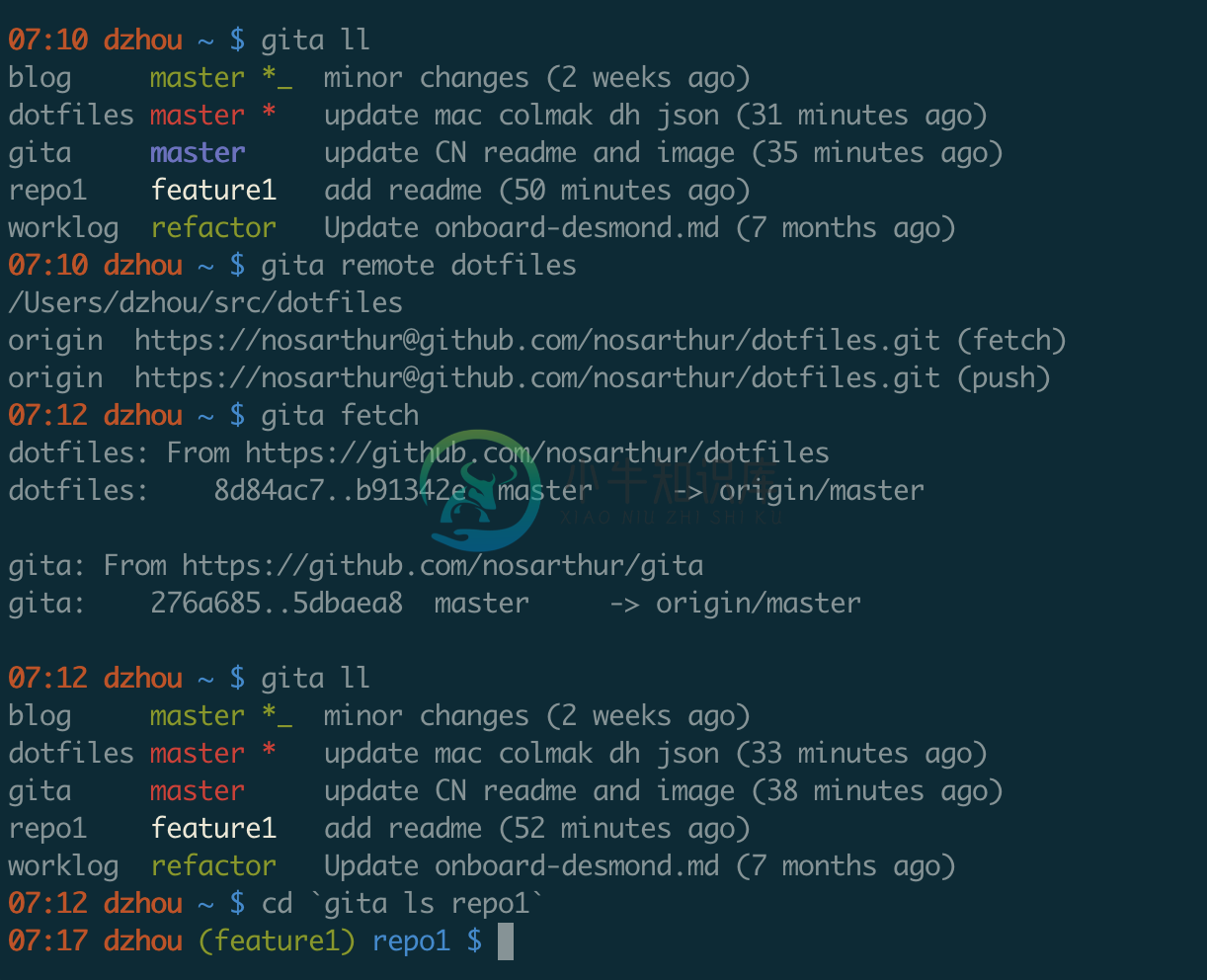
In this screenshot, the gita ll command displays the status of all repos.The gita remote dotfiles command translates to git remote -vfor the dotfiles repo, even though we are not in the repo.The gita fetch command fetches from all repos and two of them have updates.To see the pre-defined commands, run gita -h or take a look atcmds.json.To add your own commands, see the customization section.To run arbitrary git command, see the superman mode section.To run arbitrary shell command, see the shell mode section.
The branch color distinguishes 5 situations between local and remote branches:
| color | meaning |
|---|---|
| white | local has no remote |
| green | local is the same as remote |
| red | local has diverged from remote |
| purple | local is ahead of remote (good for push) |
| yellow | local is behind remote (good for merge) |
The choice of purple for ahead and yellow for behind is motivated byblueshift and redshift,using green as baseline.You can change the color scheme using the gita color command.See the customization section.
The additional status symbols denote
| symbol | meaning |
|---|---|
+ |
staged changes |
* |
unstaged changes |
_ |
untracked files/folders |
The bookkeeping sub-commands are
gita add <repo-path(s)>: add repo(s) togitagita add -a <repo-parent-path(s)>: add repo(s) in <repo-parent-path(s)> recursivelyand automatically generate hierarchical groups. See the customization section for more details.gita add -b <bare-repo-path(s)>: add bare repo(s) togita. See the customization section for more details on setting custom worktree.gita add -r <repo-parent-path(s)>: add repo(s) in <repo-parent-path(s)> recursivelygita clone <config-file>: clone repos inconfig-file(generated bygita freeze) to current directory.gita clone -p <config-file>: clone repos inconfig-fileto prescribed paths.gita context: context sub-commandgita context: show current contextgita context <group-name>: set context togroup-name, all operations then only apply to repos in this groupgita context auto: set context automatically according to the current working directorygita context none: remove context
gita color: color sub-commandgita color [ll]: Show available colors and the current coloring schemegita color set <situation> <color>: Use the specified color for the local-remote situation
gita flags: flags sub-commandgita flags set <repo-name> <flags>: add customflagsto repogita flags [ll]: display repos with custom flags
gita freeze: print information of all repos such as URL, name, and path. Use withgita clone.gita group: group sub-commandgita group add <repo-name(s)> -n <group-name>: add repo(s) to a new or existing groupgita group [ll]: display existing groups with reposgita group ls: display existing group namesgita group rename <group-name> <new-name>: change group namegita group rm <group-name(s)>: delete group(s)gita group rmrepo <repo-name(s)> -n <group-name>: remove repo(s) from existing group
gita info: info sub-commandgita info [ll]: display the used and unused information itemsgita info add <info-item>: enable information itemgita info rm <info-item>: disable information item
gita ll: display the status of all reposgita ll <group-name>: display the status of repos in a groupgita ll -g: display the repo summaries by groupsgita ls: display the names of all reposgita ls <repo-name>: display the absolute path of one repogita rename <repo-name> <new-name>: rename a repogita rm <repo-name(s)>: remove repo(s) fromgita(won't remove files on disk)gita -v: display gita version
The git delegating sub-commands are of two formats
gita <sub-command> [repo-name(s) or group-name(s)]:optional repo or group input, and no input means all repos.gita <sub-command> <repo-name(s) or groups-name(s)>:required repo name(s) or group name(s) input
They translate to git <sub-command> for the corresponding repos.By default, only fetch and pull take optional input. In other words,gita fetch and gita pull apply to all repos.To see the pre-defined sub-commands, run gita -h or take a look atcmds.json.To add your own sub-commands or override the default behaviors, see the customization section.To run arbitrary git command, see the superman mode section.
If more than one repos are specified, the git command runs asynchronously,with the exception of log, difftool and mergetool,which require non-trivial user input.
Repo configuration is saved in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/gita/repos.csv(most likely ~/.config/gita/repos.csv).
Installation
To install the latest version, run
pip3 install -U gita
If you prefer development mode, download the source code and run
pip3 install -e <gita-source-folder>
In either case, calling gita in terminal may not work,then put the following line in the .bashrc file.
alias gita="python3 -m gita"
Windows users may need to enable the ANSI escape sequence in terminal forthe branch color to work.See this stackoverflow post for details.
Auto-completion
Download.gita-completion.bashor.gita-completion.zshand source it in shell.
Superman mode
The superman mode delegates any git command or alias.Usage:
gita super [repo-name(s) or group-name(s)] <any-git-command-with-or-without-options>
Here repo-name(s) or group-name(s) are optional, and their absence means all repos.For example,
gita super checkout masterputs all repos on the master branchgita super frontend-repo backend-repo commit -am 'implement a new feature'executesgit commit -am 'implement a new feature'forfrontend-repoandbackend-repo
Shell mode
The shell mode delegates any shell command.Usage:
gita shell [repo-name(s) or group-name(s)] <any-shell-command>
Here repo-name(s) or group-name(s) are optional, and their absence means all repos.For example,
gita shell lllists contents for all reposgita shell repo1 repo2 mkdir docscreate a new directorydocsinrepo1andrepo2gita shell "git describe --abbrev=0 --tags | xargs git checkout": check out the latest tag for all repos
Customization
define repo group and context
When the project contains several independent but related repos,we can define a group and execute gita command on this group.For example,
gita group add repo1 repo2 -n my-group
gita ll my-group
gita pull my-group
To save more typing, one can set a group as context, then any gita commandis scoped to the group
gita context my-group
gita ll
gita pull
The most useful context maybe auto.In this mode, the context is automatically determined from thecurrent working directory (CWD): the context is the group whose member repo'spath contains CWD. To set it, run
gita context auto
To remove the context, run
gita context none
It is also possible to recursively add repos within a directory andgenerate hierarchical groups automatically. For example, running
gita add -a src
on the following folder structure
src
├── project1
│ ├── repo1
│ └── repo2
├── repo3
├── project2
│ ├── repo4
│ └── repo5
└── repo6
gives rise to 3 groups:
src:repo1,repo2,repo3,repo4,repo5,repo6
src-project1:repo1,repo2
src-project2:repo4,repo5
add user-defined sub-command using json file
Custom delegating sub-commands can be defined in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/gita/cmds.json(most likely ~/.config/gita/cmds.json)And they shadow the default ones if name collisions exist.
Default delegating sub-commands are defined incmds.json.For example, gita stat <repo-name(s)> is registered as
"stat":{
"cmd": "git diff --stat",
"help": "show edit statistics"
}
which executes git diff --stat for the specified repo(s).
To disable asynchronous execution, set disable_async to be true.See the difftool example:
"difftool":{
"cmd": "git difftool",
"disable_async": true,
"help": "show differences using a tool"
}
If you want a custom command to behave like gita fetch, i.e., to apply to allrepos when no repo is specified, set allow_all to be true.For example, the following snippet creates a new commandgita comaster [repo-name(s)] with optional repo name input.
"comaster":{
"cmd": "checkout master",
"allow_all": true,
"help": "checkout the master branch"
}
Any command that runs in the superman mode mode or theshell mode can be defined in this json format.For example, the following command runs in shell mode and fetches only thecurrent branch from upstream.
"fetchcrt":{
"cmd": "git rev-parse --abbrev-ref HEAD | xargs git fetch --prune upstream",
"allow_all": true,
"shell": true,
"help": "fetch current branch only"
}
customize the local/remote relationship coloring displayed by the gita ll command
You can see the default color scheme and the available colors via gita color.To change the color coding, use gita color set <situation> <color>.The configuration is saved in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/gita/color.csv.
customize information displayed by the gita ll command
You can customize the information displayed by gita ll.The used and unused information items are shown with gita info, and theconfiguration is saved in $XDG_CONFIG_HOME/gita/info.csv.
For example, the default setting corresponds to
branch,commit_msg,commit_time
customize git command flags
One can set custom flags to run git commands. For example, with
gita flags set my-repo --git-dir=`gita ls dotfiles` --work-tree=$HOME
any git command/alias triggered from gita on dotfiles will use these flags.Note that the flags are applied immediately after git. For example,gita st dotfiles translates to
git --git-dir=$HOME/somefolder --work-tree=$HOME status
running from the dotfiles directory.
This feature was originally added to deal withbare repo dotfiles.
Requirements
Gita requires Python 3.6 or higher, due to the use off-stringand asyncio module.
Under the hood, gita uses subprocess to run git commands/aliases.Thus the installed git version may matter.I have git 1.8.3.1, 2.17.2, and 2.20.1 on my machines, andtheir results agree.
Tips
| effect | shell command |
|---|---|
enter <repo> directory |
cd `gita ls <repo>` |
delete repos in <group> |
gita group ll <group> | xargs gita rm |
Contributing
To contribute, you can
- report/fix bugs
- request/implement features
- star/recommend this project
Read this article if you have never contribute code to open source project before.
To run tests locally, simply pytest in the source code folder.Note that context should be set as none.More implementation details are indesign.md.A step-by-step guide to reproduce this project is here.
You can also sponsor me on GitHub. Any amount is appreciated!
Other multi-repo tools
I haven't tried them but I heard good things about them.
-
一、下载git.exe # Windows上安装 $ https://git-scm.com/download $ 双击git.exe安装git(一直点下一步,直到完成) $ 点击电脑桌面空白地方右键看到Git GUI Here和Git Bash Here即安装成功 二、设置ssh 1.打开本地git bash,使用如下命令生成ssh公钥和私钥对 $ ssh-keygen -t rsa -C '
-
名称 gitattributes - 定义每个路径的属性 概要 $GIT_DIR/info/attributes, .gitattributes 描述 一个gitattributes文件是一个给attributes路径名的简单文本文件。 gitattributes文件中的每一行都是以下格式: pattern attr1 attr2 ... 也就是说,一个模式后跟一个属性列表,由空格分
-
Gitako 是一款支持 Gitee/GitHub 等网站的文件树浏览器插件,可用于 Chrome & Firefox & Edge 浏览器。 特性 通过文件树展示仓库或 Pull Request 相关的文件 极速搜索文件,在其间快速跳转 支持私有仓库、企业版 GitHub 、Gitee 即使在巨型项目中也流畅无比(相反的,Octotree 能卡到页面崩溃) 内置符合直觉的快捷键操作 支持 git
-
Gitamin是一款基于 Laravel5.2 和 Twig 模板引擎实现的 Git仓储管理系统,提供基于web的仓储浏览和管理。 演示地址:http://gitamin.com/
-
gitage 基于 NodeJS 的 git-pages 静态 WEB服务 依赖: git nodejs>8 目前支持的托管系统: gogs gitea 概述 gitage 运行在 nodejs 上,依赖 git (gitea, gogs, gitlab) 等托管系统的 web 勾子。 gitage 主要为团队/公司等非公开组织提供一个易于部署的 pages 服务。 gitage 提供 markd
-
Gitalist 是一个基于浏览器的 Git 资料库浏览器 主要特点: 支持多库 支持多分支 提交的比较 Atom feeds Color coded commit history Gitweb.cgi URL compatibility
-
Gitaly是一个Git RPC服务,用于处理GitLab发出的所有git调用。目前Gitaly仍在发展。 我们期望它成为一个标准组件,并在2017年第三季度达到全覆盖。 项目目标: 制作大型GitLab实例的git数据存储层,特别是GitLab.com,速度快。 这将通过关注两个领域(按此顺序)来实现: 允许高效缓存 GitLab的Git数据层的弹性水平缩放 由来: 对于GitLab.com g