python机器学习库xgboost的使用
1.数据读取
利用原生xgboost库读取libsvm数据
import xgboost as xgb data = xgb.DMatrix(libsvm文件)
使用sklearn读取libsvm数据
from sklearn.datasets import load_svmlight_file X_train,y_train = load_svmlight_file(libsvm文件)
使用pandas读取完数据后在转化为标准形式
2.模型训练过程
1.未调参基线模型
使用xgboost原生库进行训练
import xgboost as xgb
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
dtrain = xgb.DMatrix(f_train, label = l_train)
dtest = xgb.DMatrix(f_test, label = l_test)
param = {'max_depth':2, 'eta':1, 'silent':0, 'objective':'binary:logistic' }
num_round = 2
bst = xgb.train(param, dtrain, num_round)
train_preds = bst.predict(dtrain)
train_predictions = [round(value) for value in train_preds] #进行四舍五入的操作--变成0.1(算是设定阈值的符号函数)
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(l_train, train_predictions) #使用sklearn进行比较正确率
print ("Train Accuary: %.2f%%" % (train_accuracy * 100.0))
from xgboost import plot_importance #显示特征重要性
plot_importance(bst)#打印重要程度结果。
pyplot.show()
使用XGBClassifier进行训练
# 未设定早停止, 未进行矩阵变换
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_svmlight_file #用于直接读取svmlight文件形式, 否则就需要使用xgboost.DMatrix(文件名)来读取这种格式的文件
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from matplotlib import pyplot
num_round = 100
bst1 =XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=1, n_estimators=num_round, #弱分类树太少的话取不到更多的特征重要性
silent=True, objective='binary:logistic')
bst1.fit(f_train, l_train)
train_preds = bst1.predict(f_train)
train_accuracy = accuracy_score(l_train, train_preds)
print ("Train Accuary: %.2f%%" % (train_accuracy * 100.0))
preds = bst1.predict(f_test)
test_accuracy = accuracy_score(l_test, preds)
print("Test Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (test_accuracy * 100.0))
from xgboost import plot_importance #显示特征重要性
plot_importance(bst1)#打印重要程度结果。
pyplot.show()
2.两种交叉验证方式
使用cross_val_score进行交叉验证
#利用model_selection进行交叉训练
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from matplotlib import pyplot
param = {'max_depth':2, 'eta':1, 'silent':0, 'objective':'binary:logistic' }
num_round = 100
bst2 =XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=0.1,n_estimators=num_round, silent=True, objective='binary:logistic')
bst2.fit(f_train, l_train)
kfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=10, random_state=7)
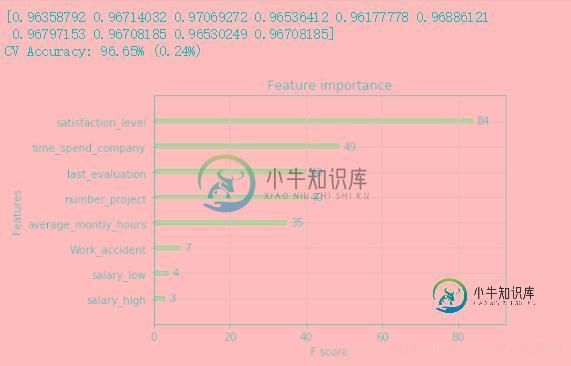
results = cross_val_score(bst2, f_train, l_train, cv=kfold)#对数据进行十折交叉验证--9份训练,一份测试
print(results)
print("CV Accuracy: %.2f%% (%.2f%%)" % (results.mean()*100, results.std()*100))
from xgboost import plot_importance #显示特征重要性
plot_importance(bst2)#打印重要程度结果。
pyplot.show()
使用GridSearchCV进行网格搜索
#使用sklearn中提供的网格搜索进行测试--找出最好参数,并作为默认训练参数
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from matplotlib import pyplot
params = {'max_depth':2, 'eta':0.1, 'silent':0, 'objective':'binary:logistic' }
bst =XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=0.1, silent=True, objective='binary:logistic')
param_test = {
'n_estimators': range(1, 51, 1)
}
clf = GridSearchCV(estimator = bst, param_grid = param_test, scoring='accuracy', cv=5)# 5折交叉验证
clf.fit(f_train, l_train) #默认使用最优的参数
preds = clf.predict(f_test)
test_accuracy = accuracy_score(l_test, preds)
print("Test Accuracy of gridsearchcv: %.2f%%" % (test_accuracy * 100.0))
clf.cv_results_, clf.best_params_, clf.best_score_
3.早停止调参–early_stopping_rounds(查看的是损失是否变化)
#进行提早停止的单独实例
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from matplotlib import pyplot
param = {'max_depth':2, 'eta':1, 'silent':0, 'objective':'binary:logistic' }
num_round = 100
bst =XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=num_round, silent=True, objective='binary:logistic')
eval_set =[(f_test, l_test)]
bst.fit(f_train, l_train, early_stopping_rounds=10, eval_metric="error",eval_set=eval_set, verbose=True) #early_stopping_rounds--当多少次的效果差不多时停止 eval_set--用于显示损失率的数据 verbose--显示错误率的变化过程
# make prediction
preds = bst.predict(f_test)
test_accuracy = accuracy_score(l_test, preds)
print("Test Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (test_accuracy * 100.0))
4.多数据观察训练损失
#多参数顺
import xgboost as xgb
from xgboost import XGBClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
from matplotlib import pyplot
num_round = 100
bst =XGBClassifier(max_depth=2, learning_rate=0.1, n_estimators=num_round, silent=True, objective='binary:logistic')
eval_set = [(f_train, l_train), (f_test, l_test)]
bst.fit(f_train, l_train, eval_metric=["error", "logloss"], eval_set=eval_set, verbose=True)
# make prediction
preds = bst.predict(f_test)
test_accuracy = accuracy_score(l_test, preds)
print("Test Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (test_accuracy * 100.0))

5.模型保存与读取
#模型保存
bst.save_model('demo.model')
#模型读取与预测
modelfile = 'demo.model'
# 1
bst = xgb.Booster({'nthread':8}, model_file = modelfile)
# 2
f_test1 = xgb.DMatrix(f_test) #尽量使用xgboost的自己的数据矩阵
ypred1 = bst.predict(f_test1)
train_predictions = [round(value) for value in ypred1]
test_accuracy1 = accuracy_score(l_test, train_predictions)
print("Test Accuracy: %.2f%%" % (test_accuracy1 * 100.0))
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持呐喊教程。
-
Scikit-learn (http://scikit-learn.org/) 是一个机器学习领域的开源套件。整个专案起始于 2007年由David Cournapeau所执行的Google Summer of Code 计画。而2010年之后,则由法国国家资讯暨自动化研究院(INRIA, http://www.inria.fr) 继续主导及后续的支持及开发。近几年(2013-2015)则由 IN
-
这份文件的目的是要提供 Python 之机器学习套件 scikit-learn (http://scikit-learn.org/) 的中文使用说明。一开始的主要目标是详细说明 scikit-learn 套件中的范例程式的使用流程以及相关函式的使用方法。目前使用版本为 scikit-learn version 0.19 以上
-
Scikit-learn 套件的安装 目前Scikit-learn同时支持Python 2及 3,安装的方式也非常多种。对于初学者,最建议的方式是直接下载 Anaconda Python (https://www.continuum.io/downloads)。同时支持 Windows / OSX/ Linux 等作业系统。相关数据分析套件如Scipy, Numpy, 及图形绘制库 matplot
-
机器学习是一门研究如何使用计算机模拟人类行为,以获取新的知识与技能的学科。它是人工智能的核心,同时也是处理大数据的关键技术之一。机器学习的主要目标是自动地从数据中发现价值的模式,亦即将原始信息自动转换为人们可以加以利用的知识。
-
从sklearn加载流行数字数据集。数据集模块,并将其分配给可变数字。 分割数字。将数据分为两组,分别命名为X_train和X_test。还有,分割数字。目标分为两组Y_训练和Y_测试。 提示:使用sklearn中的训练测试分割方法。模型选择;将随机_状态设置为30;并进行分层抽样。使用默认参数,从X_序列集和Y_序列标签构建SVM分类器。将模型命名为svm_clf。 在测试数据集上评估模型的准确
-
Python 是一种通用的高级编程语言,越来越多地用于数据科学和设计机器学习算法。 本教程简要介绍了 Python 及其库,如 numpy,scipy,pandas,matplotlib,并解释了如何应用它来开发解决实际问题的机器学习算法。

