TabLayout用法详解及自定义样式
TabLayout的默认样式:
app:theme="@style/Widget.Design.TabLayout"
从系统定义的该样式继续深入:
<style name="Widget.Design.TabLayout" parent="Base.Widget.Design.TabLayout"> <item name="tabGravity">fill</item> <item name="tabMode">fixed</item> </style> <style name="Base.Widget.Design.TabLayout" parent="android:Widget"> <item name="tabMaxWidth">264dp</item> <item name="tabIndicatorColor">?attr/colorAccent</item> <item name="tabIndicatorHeight">2dp</item> <item name="tabPaddingStart">12dp</item> <item name="tabPaddingEnd">12dp</item> <item name="tabBackground">?attr/selectableItemBackground</item> <item name="tabTextAppearance">@style/TextAppearance.Design.Tab</item> <item name="tabSelectedTextColor">?android:textColorPrimary</item> </style>
接着,看看系统定义Tab文本的样式(注意textAllcaps这个属性):
<style name="TextAppearance.Design.Tab" parent="TextAppearance.AppCompat.Button"> <item name="android:textSize">14dp</item> <item name="android:textColor">?android:textColorSecondary</item> <item name="textAllCaps">true</item> </style>
从系统定义TabLayout的默认样式可以看出,我们可以改变TabLayout对应的系统样式的属性值来适配我们自己的需求.
TabLayout的基本用法
TabLayout独立使用使用时,可以xml布局中静态添加tab个数及其样式,也可以动态添加Tab的个数及其样式,如:
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout android:id="@+id/tablayout" android:background="@color/colorPrimary" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <android.support.design.widget.TabItem android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Android"/> <android.support.design.widget.TabItem android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:icon="@mipmap/ic_launcher"/> </android.support.design.widget.TabLayout>
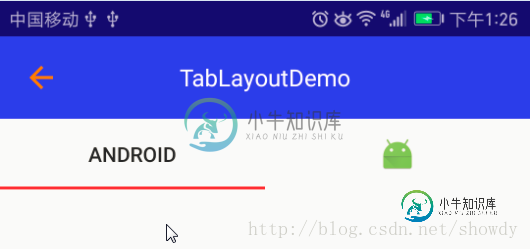
或者:
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout android:id="@+id/tablayout" android:background="@color/colorPrimary" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/>
private int[] images = new int[]{
R.drawable.ic_account_balance_wallet_black,
R.drawable.ic_android_black,
R.drawable.ic_account_box_black};
private String[] tabs = new String[]{"小说", "电影", "相声"};
TabLayout tabLayout = (TabLayout) findViewById(R.id.tablayout);
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setIcon(images[0]).setText(tabs[0]),true);
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setIcon(images[1]).setText(tabs[1]),false);
tabLayout.addTab(tabLayout.newTab().setIcon(images[2]).setText(tabs[2]),false);

TabLayout在实际开发中最多的是与ViewPager联合使用,实现TabLayout与ViewPager的联动:
<android.support.design.widget.TabLayout android:id="@+id/tablayout" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="@color/colorPrimary" app:tabGravity="fill" app:tabIndicatorColor="@android:color/holo_orange_dark" app:tabIndicatorHeight="2dp" app:tabMode="fixed" app:tabSelectedTextColor="@android:color/holo_orange_dark" app:tabTextAppearance="@style/CustomTabTextAppearanceStyle" app:tabTextColor="@android:color/white" app:theme="@style/Widget.Design.TabLayout"/> <android.support.v4.view.ViewPager android:id="@+id/view_pager" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/>
TabLayout tabLayout = (TabLayout) findViewById(R.id.tablayout); ViewPager viewPager = (ViewPager) findViewById(R.id.view_pager); viewPager.setAdapter(new TabPagerAdapter(getSupportFragmentManager())); tabLayout.setupWithViewPager(viewPager);

值得注意的是:
在TabPagerAdapter中需要实现getPagerTitle()否则,TabLayout的Tab将不显示,先看TabLayout#setupWithPager()源码,发现Tab的添加是在populateFromPagerAdapter()中实现,实现源码如下,可以看出该方法调用了PagerAdpater#getPagerTitle()为Tab设置文本信息,如果我们自定义的Adapter没有实现getPagerTitle()将会导致Tab不显示文本信息.
void populateFromPagerAdapter() {
removeAllTabs();
if (mPagerAdapter != null) {
final int adapterCount = mPagerAdapter.getCount();
for (int i = 0; i < adapterCount; i++) {
addTab(newTab().setText(mPagerAdapter.getPageTitle(i)), false);
}
// Make sure we reflect the currently set ViewPager item
if (mViewPager != null && adapterCount > 0) {
final int curItem = mViewPager.getCurrentItem();
if (curItem != getSelectedTabPosition() && curItem < getTabCount()) {
selectTab(getTabAt(curItem));
}
}
}
}
另外, 我们发现getPagerTitle()方法的返回值CharSequence而不是String,那么Tab的文本信息的设置将变得更加灵活,比如设置一个SpanableString,将图片和文本设置Tab的文本.
@Override
public CharSequence getPageTitle(int position) {
Drawable image = TablayoutActivity.this.getResources().getDrawable(images[position]);
image.setBounds(0, 0, image.getIntrinsicWidth()/2, image.getIntrinsicHeight()/2);
ImageSpan imageSpan = new ImageSpan(image, ImageSpan.ALIGN_BOTTOM);
SpannableString ss = new SpannableString(" "+tabs[position]);
ss.setSpan(imageSpan, 0, 1, Spannable.SPAN_EXCLUSIVE_EXCLUSIVE);
return ss;
}

但是Tab缺没有显示任何信息,一片空白,从上面提到的TabLayout的系统默认样式中我们发现: <item name="textAllCaps">true</item>,这会阻止ImageSpan渲染出来,我们只需要将textAllCaps改为false即可,如下定义,再次运行,成功显示
<style name="CustomTabTextAppearanceStyle" parent="TextAppearance.Design.Tab"> <item name="textAllCaps">false</item> </style>

修改Indicator的长度:
从TabLayout的源码可以看出Indicator的绘制,是在其内部类SlidingTabStrip中绘制,而SlingTabStrip类继承LinearLayout,源码如下:
@Override
public void draw(Canvas canvas) {
super.draw(canvas);
// Thick colored underline below the current selection
if (mIndicatorLeft >= 0 && mIndicatorRight > mIndicatorLeft) {
canvas.drawRect(mIndicatorLeft, getHeight() - mSelectedIndicatorHeight,
mIndicatorRight, getHeight(), mSelectedIndicatorPaint);
}
}
在onDraw()中主要是就绘制一个Rect,并且宽度是根据mIndicatorLeft和mIndicatorRight设置的,而mIndicatorLeft等的宽度来自SlidingTabStrip的child,而Child就相当于一个Tab,这样我们就通过修改Child的margin来设置mIndicatorLeft的值.
public void setIndicator(TabLayout tabs, int leftDip, int rightDip) {
Class<?> tabLayout = tabs.getClass();
Field tabStrip = null;
try {
tabStrip = tabLayout.getDeclaredField("mTabStrip");
} catch (NoSuchFieldException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
tabStrip.setAccessible(true);
LinearLayout llTab = null;
try {
llTab = (LinearLayout) tabStrip.get(tabs);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
int left = (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, leftDip, Resources.getSystem().getDisplayMetrics());
int right = (int) TypedValue.applyDimension(TypedValue.COMPLEX_UNIT_DIP, rightDip, Resources.getSystem().getDisplayMetrics());
for (int i = 0; i < llTab.getChildCount(); i++) {
View child = llTab.getChildAt(i);
child.setPadding(0, 0, 0, 0);
LinearLayout.LayoutParams params = new LinearLayout.LayoutParams(0, LinearLayout.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, 1);
params.leftMargin = left;
params.rightMargin = right;
child.setLayoutParams(params);
child.invalidate();
}
}
然后在代码中调用即可,但是要注意,必须要在Tablayout渲染出来后调用,我们可以选择view.post()方法来实现:
tabLayout.post(new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
setIndicator(tabLayout, 20, 20);
}
});
最后得到效果图如下:

自定义TabLayout的TabItem及TabItem的点击事件
在TabLayout的Api是没有提供TabItem点击事件的方法,如果我们想实现如下效果图,怎么办?
先自定义一个TabItem:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center" android:orientation="horizontal"> <TextView android:id="@+id/txt_title" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:gravity="center" android:textSize="14sp" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/img_title" android:src="@drawable/indicator" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginLeft="5dp" /> </LinearLayout>
在自定义的Adapter中可以定义一个getTabView的方法:
public View getTabView(int position){
View view = LayoutInflater.from(context).inflate(R.layout.tab_item, null);
TextView tv= (TextView) view.findViewById(R.id.textView);
tv.setText(tabTitles[position]);
ImageView img = (ImageView) view.findViewById(R.id.imageView);
img.setImageResource(imageResId[position]);
return view;
}
重新设置点击事件:
viewPager.setAdapter(pagerAdapter);
tabLayout.setupWithViewPager(viewPager);
for (int i = 0; i < tabLayout.getTabCount(); i++) {
TabLayout.Tab tab = tabLayout.getTabAt(i);
if (tab != null) {
tab.setCustomView(pagerAdapter.getTabView(i));
if (tab.getCustomView() != null) {
View tabView = (View) tab.getCustomView().getParent();
tabView.setTag(i);
tabView.setOnClickListener(mTabOnClickListener);
}
}
}
viewPager.setCurrentItem(1);
以上所述是小编给大家介绍的TabLayout用法详解及自定义样式,希望对大家有所帮助,如果大家有任何疑问请给我留言,小编会及时回复大家的。在此也非常感谢大家对小牛知识库网站的支持!
-
本文向大家介绍TabLayout使用方法详解,包括了TabLayout使用方法详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 TabLayout是design库提供的控件,可以方便的使用指示器,功能类似ViewPagerIndicator. 使用非常方便,Android Studio只需要在gradle中引入即可使用 . TabLayout即可以单独使用,也可以配合ViewPager来使用. 先来看
-
本文向大家介绍Android编程自定义AlertDialog样式的方法详解,包括了Android编程自定义AlertDialog样式的方法详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android编程自定义AlertDialog样式的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 开发的时候,通常我们要自定义AlertDialog来满足我们的功能需求: 比如弹出对话框中可以输入信息,或者要
-
本文向大家介绍详解Java注解教程及自定义注解,包括了详解Java注解教程及自定义注解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Java注解提供了关于代码的一些信息,但并不直接作用于它所注解的代码内容。在这个教程当中,我们将学习Java的注解,如何定制注解,注解的使用以及如何通过反射解析注解。 Java1.5引入了注解,当前许多java框架中大量使用注解,如Hibernate、Jersey、Spr
-
本文向大家介绍IOS 自定义UIPickView详解及实例代码,包括了IOS 自定义UIPickView详解及实例代码的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 IOS 自定义UIPickView 苹果一直推崇使用原生的组件,自带的UIPickView其实也很漂亮了,看起来也很美观。但是有时候,产品会有一些特殊的设计和需求。本文将会讲解如何修改苹果原生的组件的属性,达到自定义UIPickView的效
-
本文向大家介绍javaWeb自定义标签用法实例详解,包括了javaWeb自定义标签用法实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了javaWeb自定义标签用法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 自定义标签创建 自定义标签主要用于移除Jsp页面中的Java代码。 移除jsp页面中的java代码,只需要完成两个步骤: - 编写一个继承TagSupport的Java类,并覆盖doSt
-
本文向大家介绍NodeJS自定义模块写法(详解),包括了NodeJS自定义模块写法(详解)的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 如下所示: 以上这篇NodeJS自定义模块写法(详解)就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持呐喊教程。

