Android仿小红书欢迎界面
1,觉得小红书的欢迎界面感觉很漂亮,就想来学习学习一下来实现类似于这种效果 。 原效果图如下:

2,根据效果我们来一点点分析
第一步:首先看一下我们的主界面布局文件视图效果如下:

main_activity.xml文件代码如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:background="@color/white" android:orientation="vertical" > <com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.parallaxpager.ParallaxContainer android:id="@+id/parallax_container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_man" android:layout_width="67dp" android:layout_height="202dp" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginBottom="10dp" android:background="@drawable/intro_item_manrun_1" android:visibility="visible" /> </RelativeLayout>
可以看到我们主界面的布局文件主要是两个控件,一个是包含上面小人行走效果的ImageView,然后是一个自定义ParallaxContainer控件,这个自定义控件的具体是什么我们先不要管,后面再和大家来慢慢解释
第二步:看一下我们主界面的MainActivity的代码
MainActivity.java
package com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ActivityNotFoundException;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.net.Uri;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.Window;
import android.view.WindowManager;
import android.widget.ImageView;
import com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.parallaxpager.ParallaxContainer;
/**
* @author zhongdaxia 2014-12-15
*/
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
ImageView iv_man;
ImageView rl_weibo;
ParallaxContainer parallaxContainer;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
//获取当前窗体
final Window window = getWindow();
window.setFlags(WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN, WindowManager.LayoutParams.FLAG_FULLSCREEN);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
/**
* 动画支持11以上sdk,11以下默认不显示动画
* 若需要支持11以下动画,也可导入https://github.com/JakeWharton/NineOldAndroids
*/
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT > 10) {
iv_man = (ImageView) findViewById(R.id.iv_man);
parallaxContainer = (ParallaxContainer) findViewById(R.id.parallax_container);
if (parallaxContainer != null) {
parallaxContainer.setImage(iv_man);
parallaxContainer.setLooping(false);
iv_man.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
parallaxContainer.setupChildren(getLayoutInflater(),
R.layout.view_intro_1, R.layout.view_intro_2,
R.layout.view_intro_3, R.layout.view_intro_4,
R.layout.view_intro_5, R.layout.view_intro_6 ,R.layout.view_login);
}
}
else{
setContentView(R.layout.view_login);
}
}
}
我们看到代码很简单,主要是这几句有用的代码:
if (parallaxContainer != null) {
parallaxContainer.setImage(iv_man);
parallaxContainer.setLooping(false);
iv_man.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
parallaxContainer.setupChildren(getLayoutInflater(),
R.layout.view_intro_1, R.layout.view_intro_2,
R.layout.view_intro_3, R.layout.view_intro_4,
R.layout.view_intro_5, R.layout.view_intro_6 ,R.layout.view_login);
}
① 将我们小人走路的那个ImageView添加到自定义控件ParallaxContainer中
② 将我们每一个的布局文件set到ParallaxContainer控件中去
这里给出R.layout.view_intro_1.xml文件代码,其他的类似,就不给出来了(这里的x_in、x_out、y_in等属性注意一下)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" > <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_0" android:layout_width="103dp" android:layout_height="19dp" android:layout_centerInParent="true" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_0" app:x_in="1.2" app:x_out="1.2" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_1" android:layout_width="181dp" android:layout_height="84dp" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_marginLeft="13dp" android:layout_marginTop="60dp" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_1" app:x_in="0.8" app:x_out="0.8" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_2" android:layout_width="143dp" android:layout_height="58dp" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_marginTop="109dp" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_2" app:x_in="1.1" app:x_out="1.1" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_3" android:layout_width="48dp" android:layout_height="48dp" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_3" app:x_in="0.8" app:x_out="0.8" app:a_in="0.8" app:a_out="0.8" android:layout_below="@+id/iv_0" android:layout_toRightOf="@+id/iv_5" android:layout_toEndOf="@+id/iv_5" android:layout_marginLeft="21dp" android:layout_marginStart="21dp" android:layout_marginTop="12dp"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_4" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="128dp" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_marginBottom="29dp" android:background="@drawable/intro1_item_4" app:a_in="0.8" app:a_out="0.8" app:x_in="0.8" app:x_out="0.8" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_5" android:layout_width="260dp" android:layout_height="18dp" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_marginBottom="16dp" android:layout_marginLeft="15dp" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_5" app:a_in="0.9" app:a_out="0.9" app:x_in="0.9" app:x_out="0.9" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_6" android:layout_width="24dp" android:layout_height="116dp" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_marginBottom="35dp" android:layout_marginLeft="46dp" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_6" app:x_in="0.6" app:x_out="0.6" /> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_7" android:layout_width="45dp" android:layout_height="40dp" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_marginBottom="23dp" android:layout_marginLeft="76dp" android:src="@drawable/intro1_item_7" app:a_in="0.3" app:a_out="0.3" app:x_in="0.5" app:x_out="0.5" /> </RelativeLayout>
第三步:好了现在我们一定很好奇ParallaxContainer里面的内容,那我们从上面的方法慢慢去看,首先看一下ParallaxContainer中的setImage()方法,代码如下:
ImageView iv;
//将小人图片添加进来
public void setImage(ImageView iv) {
this.iv = iv;
}
貌似没有什么,只是将它赋值给成员变量iv,我们接着看下一个setUpChildren()方法
//添加子view
public void setupChildren(LayoutInflater inflater, int... childIds) {
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("setupChildren should only be called once when ParallaxContainer is empty");
}
//创建打气筒
ParallaxLayoutInflater parallaxLayoutInflater = new ParallaxLayoutInflater(
inflater, getContext());
//将所有的view添加到本控件上去
for (int childId : childIds) {
View view = parallaxLayoutInflater.inflate(childId, this);
viewlist.add(view);
}
//添加视觉view
pageCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < pageCount; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
addParallaxView(view, i);
}
//更新ViewPagerAdapter的数量
updateAdapterCount();
//创建viewpager
viewPager = new ViewPager(getContext());
viewPager.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT));
viewPager.setId(R.id.parallax_pager);
//给viewpager添加滑动监听
attachOnPageChangeListener();
//设置适配器
viewPager.setAdapter(adapter);
//将viewpager添加到主控件中
addView(viewPager, 0);
}
让我们一行行代码慢慢分析
if (getChildCount() > 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("setupChildren should only be called once when ParallaxContainer is empty");
}
//创建打气筒 ParallaxLayoutInflater parallaxLayoutInflater = new ParallaxLayoutInflater( inflater, getContext());
首先看一下这段代码只是if判断是否已经调用过setUpChildren()方法,没什么重要的,在看创建ParallaxLayoutInflater打气筒对象,我们来看看ParallaxLayoutInflater的具体代码,没什么重要的,只是里面有一个ParallaxFactory类我们没见过,留心一下!
package com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.parallaxpager;
import android.content.Context;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
public class ParallaxLayoutInflater extends LayoutInflater {
protected ParallaxLayoutInflater(LayoutInflater original, Context newContext) {
super(original, newContext);
setUpLayoutFactory();
}
private void setUpLayoutFactory() {
if (!(getFactory() instanceof ParallaxFactory)) {
setFactory(new ParallaxFactory(this, getFactory()));
}
}
@Override
public LayoutInflater cloneInContext(Context newContext) {
return new ParallaxLayoutInflater(this, newContext);
}
}
再看下面一段代码,主要是将所有的布局文件添加到viewList集合中去,并填充到我们的布局中,我们继续往下看
//将所有的view添加到本控件上去
for (int childId : childIds) {
View view = parallaxLayoutInflater.inflate(childId, this);
viewlist.add(view);
}
下面一段代码主要是看拿到对应所有的子view,关键是我们的addParallaxView()方法,具体代码如下:
//添加视觉view
pageCount = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < pageCount; i++) {
View view = getChildAt(i);
addParallaxView(view, i);
}
/**
* 添加视觉view方法
*
* @param view
* @param pageIndex
*/
private void addParallaxView(View view, int pageIndex) {
//通过递归方法拿到最小单元的view
if (view instanceof ViewGroup) {
ViewGroup viewGroup = (ViewGroup) view;
for (int i = 0, childCount = viewGroup.getChildCount(); i < childCount; i++) {
addParallaxView(viewGroup.getChildAt(i), pageIndex);
}
}
//创建视觉差view绑定,并添加到集合中去
ParallaxViewTag tag = (ParallaxViewTag) view.getTag(R.id.parallax_view_tag);
if (tag != null) {
tag.index = pageIndex;
parallaxViews.add(view);
}
}
通过递归将每个布局文件中的最小单元view保存到parallaxView集合中去,但是等等,这里我们又发现了一个新的类ParallaxViewTag,让我们来具体代码
package com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.parallaxpager;
public class ParallaxViewTag {
//绑定每一个view对应的是哪一个下标的
protected int index;
//x轴进入的速度
protected float xIn;
protected float xOut;
protected float yIn;
protected float yOut;
protected float alphaIn;
protected float alphaOut;
}
貌似很简单,xIn、xOut貌似很熟悉和我们之前的布局文件属性app:x_in等属性对应了, 这样我们就懂了,这个类是相当于一个tag类,用于记录我们设置的特殊一些属性,然是我们这里有一个疑问,下面这个代码是get到tag,那我们是在哪里set里面的属性呢?
ParallaxViewTag tag = (ParallaxViewTag) view.getTag(R.id.parallax_view_tag);
这时候我们要看看我们前面提到过的一个陌生类ParallaxFactory,看一下具体代码
package com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.parallaxpager;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.res.TypedArray;
import android.util.AttributeSet;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.R;
public class ParallaxFactory implements LayoutInflater.Factory {
private final LayoutInflater.Factory factory;
private ParallaxLayoutInflater mInflater;
private static final String[] sClassPrefixList = {
"android.widget.",
"android.webkit.",
"android.view."
};
public ParallaxFactory(ParallaxLayoutInflater inflater, LayoutInflater.Factory factory) {
mInflater = inflater;
this.factory = factory;
}
@Override
public View onCreateView(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
View view = null;
if (context instanceof LayoutInflater.Factory) {
view = ((LayoutInflater.Factory) context).onCreateView(name, context, attrs);
}
if (factory != null && view == null) {
view = factory.onCreateView(name, context, attrs);
}
if (view == null) {
view = createViewOrFailQuietly(name, context, attrs);
}
if (view != null) {
onViewCreated(view, context, attrs);
}
return view;
}
protected View createViewOrFailQuietly(String name, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
if (name.contains(".")) {
return createViewOrFailQuietly(name, null, context, attrs);
}
for (final String prefix : sClassPrefixList) {
final View view = createViewOrFailQuietly(name, prefix, context, attrs);
if (view != null) {
return view;
}
}
return null;
}
protected View createViewOrFailQuietly(String name, String prefix, Context context,
AttributeSet attrs) {
try {
return mInflater.createView(name, prefix, attrs);
} catch (Exception ignore) {
return null;
}
}
/**
* 主要是在viewCreated的时候将tag和view绑定起来
*
* @param view
* @param context
* @param attrs
*/
protected void onViewCreated(View view, Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
int[] attrIds =
{R.attr.a_in, R.attr.a_out, R.attr.x_in, R.attr.x_out, R.attr.y_in, R.attr.y_out,};
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, attrIds);
if (a != null) {
if (a.length() > 0) {
ParallaxViewTag tag = new ParallaxViewTag();
tag.alphaIn = a.getFloat(0, 0f);
tag.alphaOut = a.getFloat(1, 0f);
tag.xIn = a.getFloat(2, 0f);
tag.xOut = a.getFloat(3, 0f);
tag.yIn = a.getFloat(4, 0f);
tag.yOut = a.getFloat(5, 0f);
view.setTag(R.id.parallax_view_tag, tag);
}
a.recycle();
}
}
}
主要看onViewCreated()方法,可以看到,这里我们将对应的每个属性的值都set到了我们ParallaxViewTag中,我们接着看下面的代码,调用updateAdapterCount()方法让适配器去更新adapter的数量,这里我们可以看到适配器是继承PagerAdapter类,用于ViewPager的适配器,这里使用LinkedList来存储View,这个方法很好,赞一下
//更新ViewPagerAdapter的数量
updateAdapterCount();
//具体代码
//被调用的时候好像是0
private void updateAdapterCount() {
adapter.setCount(isLooping ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : pageCount);
}
//下面是adapter的具体代码
package com.qianmo.xiaohongshuwelcome.parallaxpager;
import android.content.Context;
import android.support.v4.view.PagerAdapter;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import static android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams;
import static android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT;
public class ParallaxPagerAdapter extends PagerAdapter {
private int count = 0;
private final Context context;
private final LinkedList<View> recycleBin = new LinkedList<View>();
public ParallaxPagerAdapter(Context context) {
this.context = context;
}
public void setCount(int count) {
this.count = count;
}
@Override public int getCount() {
return count;
}
@Override public Object instantiateItem(ViewGroup container, int position) {
View view;
if (!recycleBin.isEmpty()) {
view = recycleBin.pop();
} else {
view = new View(context);
view.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(MATCH_PARENT, MATCH_PARENT));
}
container.addView(view);
return view;
}
@Override public void destroyItem(ViewGroup container, int position, Object object) {
View view = (View) object;
container.removeView(view);
recycleBin.push(view);
}
@Override public boolean isViewFromObject(View view, Object object) {
return view.equals(object);
}
}
我们继续往下看,后面的就是创建viewpager对象,并addview到主控件上,在attachOnPagerChangeListener()方法中添加viewpager的滑动监听
/创建viewpager viewPager = new ViewPager(getContext()); viewPager.setLayoutParams(new LayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT)); viewPager.setId(R.id.parallax_pager); //给viewpager添加滑动监听 attachOnPageChangeListener(); //设置适配器 viewPager.setAdapter(adapter); //将viewpager添加到主控件中 addView(viewPager, 0);
这里我们在onPageScrollStateChanged()方法判断是否开启下面小人行走的动画,通过onPageScrolled()方法监听滑动的具体偏移量,通过view.setTranslationX()方法来改变对应的属性
protected void attachOnPageChangeListener() {
mCommonPageChangeListener = new ViewPager.OnPageChangeListener() {
/**
* 此方法是在状态改变的时候调用,其中arg0这个参数
有三种状态(0,1,2)。arg0 ==1的时辰默示正在滑动,arg0==2的时辰默示滑动完毕了,arg0==0的时辰默示什么都没做。
* @param state
*/
@Override
public void onPageScrollStateChanged(int state) {
Log.v(TAG, "onPageScrollStateChanged" + state);
iv.setBackgroundResource(R.drawable.man_run);
final AnimationDrawable animationDrawable = (AnimationDrawable) iv.getBackground();
switch (state) {
case 0:
//处于展示阶段
finishAnim(animationDrawable);
break;
case 1:
//正在滑动
isEnd = false;
animationDrawable.start();
break;
case 2:
//滑动完毕
finishAnim(animationDrawable);
break;
}
}
//判断是否还是在左边
boolean isleft = false;
/**
* onPageScrolled(int arg0,float arg1,int arg2) ,当页面在滑动的时候会调用此方法,在滑动被停止之前,此方法回一直得到调用。其中三个参数的含义分别为:
* @param pageIndex 当前页面,及你点击滑动的页面
* @param offset 当前页面偏移的百分比
* @param offsetPixels 当前页面偏移的像素位置
*/
@Override
public void onPageScrolled(int pageIndex, float offset, int offsetPixels) {
// Log.v(TAG, "onPageScrolled" + pageIndex + " offset" + offset + " offsetPixels" + offsetPixels);
if (offsetPixels < 10) {
isleft = false;
}
if (pageCount > 0) {
pageIndex = pageIndex % pageCount;
}
if (pageIndex == 3) {
if (isleft) {
} else {
iv.setX(iv.getLeft() - offsetPixels);
}
}
ParallaxViewTag tag;
for (View view : parallaxViews) {
tag = (ParallaxViewTag) view.getTag(R.id.parallax_view_tag);
if (tag == null) {
continue;
}
if ((pageIndex == tag.index - 1 || (isLooping && (pageIndex == tag.index
- 1 + pageCount)))
&& containerWidth != 0) {
// make visible
view.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
// slide in from right
view.setTranslationX((containerWidth - offsetPixels) * tag.xIn);
// slide in from top
view.setTranslationY(0 - (containerWidth - offsetPixels) * tag.yIn);
// fade in
view.setAlpha(1.0f - (containerWidth - offsetPixels) * tag.alphaIn / containerWidth);
} else if (pageIndex == tag.index) {
// make visible
view.setVisibility(VISIBLE);
// slide out to left
view.setTranslationX(0 - offsetPixels * tag.xOut);
// slide out to top
view.setTranslationY(0 - offsetPixels * tag.yOut);
// fade out
view.setAlpha(1.0f - offsetPixels * tag.alphaOut / containerWidth);
} else {
view.setVisibility(GONE);
}
}
}
@Override
public void onPageSelected(int position) {
Log.v(TAG, "onPageSelected" + position);
currentPosition = position;
}
};
viewPager.setOnPageChangeListener(mCommonPageChangeListener);
}
4,这里基本上就把源码分析完了,so,既然分析完别人的源码了下面就是结合到自己项目中去用了,当我们,想要实现一个翻页从顶部斜飞入的view,那我们的布局文件代码可以如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:background="@color/transparent"> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentTop="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginLeft="133dp" android:layout_marginTop="39dp" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" app:x_in="1" app:x_out="1" app:y_in="0.6" app:y_out="0.9"/> <ImageView android:id="@+id/iv_11" android:layout_width="44dp" android:layout_height="47dp" android:layout_alignParentBottom="true" android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" android:layout_marginBottom="66dp" android:layout_marginLeft="140dp" android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher" app:x_in="1" app:x_out="1" app:y_in="-1.3" app:y_out="-1.3"/> </RelativeLayout>
来看一下我们的效果:
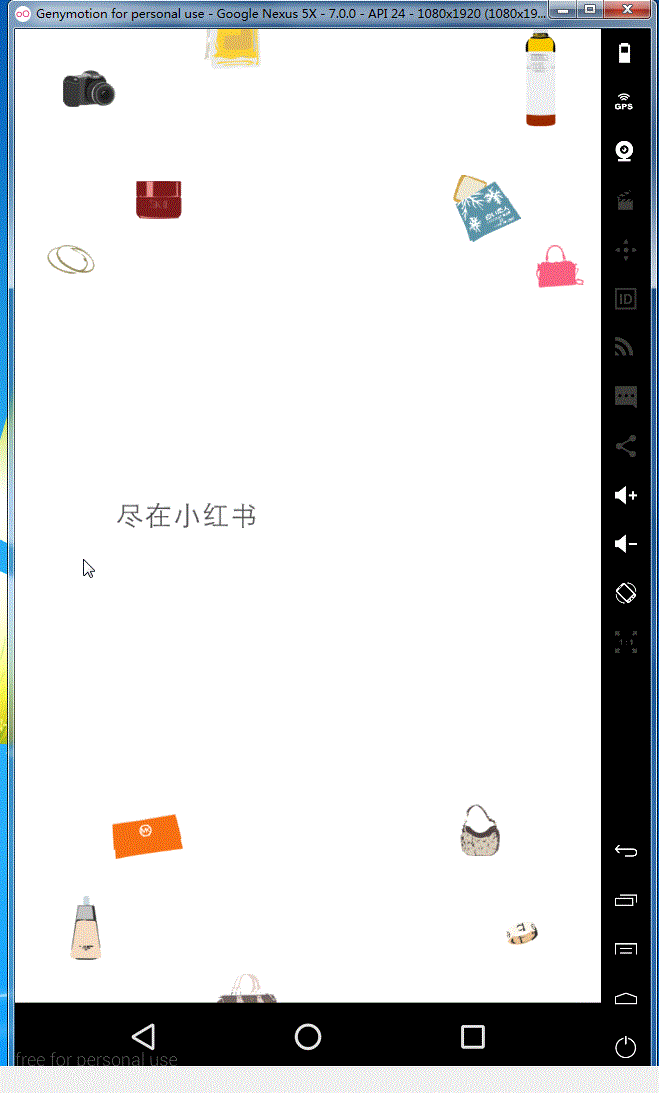
这是Github下载地址,由于要源码的同学可以去下载一下,See You Next Time !!!
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,同时也希望多多支持小牛知识库!
-
本文向大家介绍Android实现闪屏欢迎界面,包括了Android实现闪屏欢迎界面的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 闪屏:在打开App时,展示,持续数秒后,自动关闭,进入另外的一个界面,SplashActivity跳转到MainActivity Android中有三种实现方法 xml代码: (1)利用Handler对象的postDelayed方法可以实现,传递一个Runnable对象和一个
-
Ceph 独一无二地在一个统一的系统中同时提供了对象、块、和文件存储功能。div.body h3{margin:5px 0px 0px 0px;} CEPH 对象存储 REST 风格的接口 与 S3 和 Swift 兼容的 API S3 风格的子域 统一的 S3/Swift 命名空间 用户管理 利用率跟踪 条带化对象 云解决方案集成 多站点部署 灾难恢复 Ceph 块设备 瘦接口支持 映像尺寸最大
-
本文向大家介绍Android 应用的欢迎界面实现代码,包括了Android 应用的欢迎界面实现代码的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文详细描述了如何实现如下图中的微信启动界面. 该类启动界面的特点是在整个Application的生命周期里, 它只会出现在第一次进入应用时, 即便按回退键到桌面之后. 使用该类启动界面的应用还有: QQ, QQ音乐, 网易云音乐和微博等等. 知识要点: An
-
本文向大家介绍Android仿百度福袋红包界面,包括了Android仿百度福袋红包界面的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 首先来看一下效果图: 1.编程思路 看看界面,不难发现,其就是一个放入九张图片的容器,绘制其实可以在其上面另创建一个透明View负责绘制线与圆圈。下面我们将介绍一下实现过程。 ㈠自定义ViewGroup 我们知道,自定义ViewGroup一定需要实现其onLayout()
-
欢迎来到OpenGL的世界。这个工程只是我(Joey de Vries)的一次小小的尝试,希望能够建立起一个完善的OpenGL教学平台。无论你学习OpenGL是为了学业,找工作,或仅仅是因为兴趣,这个网站都将能够教会你现代(Core-profile) OpenGL从基础,中级,到高级的知识。LearnOpenGL的目标是使用易于理解的形式,使用清晰的例子,展现现代OpenGL的所有知识点,并与此同
-
该站点的目标是成为 Jekyll 的全面指南。包括一些内容如:搭建和运行你的站点、创建以及管理内容、定制站点的展现和外观、在不同的环境中发布、以及参与到 Jekyll 将来的开发的一些建议。 Jekyll 究竟是什么? Jekyll 是一个简单的博客形态的静态站点生产机器。它有一个模版目录,其中包含原始文本格式的文档,通过一个转换器(如 Markdown)和我们的 Liquid 渲染器转化成一个完

