android自定义进度条渐变圆形
在安全卫生上,经常看到有圆形的进度条在转动,效果非常好看,于是就尝试去实现一下,具体实现过程不多说了,直接上效果图,先炫耀下。
效果图:
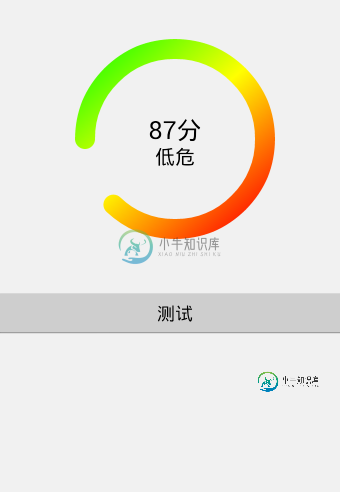
分析:比较常见于扫描结果、进度条等场景
利用canvas.drawArc(RectF oval, float startAngle, float sweepAngle, boolean useCenter, Paint paint)绘制圆弧
Paint的一些属性定义粗细、颜色、样式等
LinearGradient实现颜色的线型渐变
同样的道理,可以画出长条进度条,扇图饼图等,感兴趣可以试下..
package com.liujing.progressviewdemo; /*** * 自定义圆弧进度条 * * @author liujing */ public class ProgressView extends View { //分段颜色 private static final int[] SECTION_COLORS = { Color.GREEN, Color.YELLOW, Color.RED }; private static final String[] ALARM_LEVEL = { "安全", "低危", "中危", "高危" }; private float maxCount; private float currentCount; private int score; private String crrentLevel; private Paint mPaint; private Paint mTextPaint; private int mWidth, mHeight; public ProgressView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) { super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr); init(context); } public ProgressView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) { this(context, attrs, 0); } public ProgressView(Context context) { this(context, null); } private void init(Context context) { mPaint = new Paint(); mTextPaint = new Paint(); } @Override protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) { super.onDraw(canvas); initPaint(); RectF rectBlackBg = new RectF(20, 20, mWidth - 20, mHeight - 20); canvas.drawArc(rectBlackBg, 0, 360, false, mPaint); mPaint.setColor(Color.BLACK); canvas.drawText(score + "分", mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, mTextPaint); mTextPaint.setTextSize(40); if (crrentLevel != null) { canvas.drawText(crrentLevel, mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2 + 50, mTextPaint); } float section = currentCount / maxCount; if (section <= 1.0f / 3.0f) { if (section != 0.0f) { mPaint.setColor(SECTION_COLORS[0]); } else { mPaint.setColor(Color.TRANSPARENT); } } else { int count = (section <= 1.0f / 3.0f * 2) ? 2 : 3; int[] colors = new int[count]; System.arraycopy(SECTION_COLORS, 0, colors, 0, count); float[] positions = new float[count]; if (count == 2) { positions[0] = 0.0f; positions[1] = 1.0f - positions[0]; } else { positions[0] = 0.0f; positions[1] = (maxCount / 3) / currentCount; positions[2] = 1.0f - positions[0] * 2; } positions[positions.length - 1] = 1.0f; LinearGradient shader = new LinearGradient(3, 3, (mWidth - 3) * section, mHeight - 3, colors, null, Shader.TileMode.MIRROR); mPaint.setShader(shader); } canvas.drawArc(rectBlackBg, 180, section * 360, false, mPaint); } private void initPaint() { mPaint.setAntiAlias(true); mPaint.setStrokeWidth((float) 40.0); mPaint.setStyle(Style.STROKE); mPaint.setStrokeCap(Cap.ROUND); mPaint.setColor(Color.TRANSPARENT); mTextPaint.setAntiAlias(true); mTextPaint.setStrokeWidth((float) 3.0); mTextPaint.setTextAlign(Paint.Align.CENTER); mTextPaint.setTextSize(50); mTextPaint.setColor(Color.BLACK); } private int dipToPx(int dip) { float scale = getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density; return (int) (dip * scale + 0.5f * (dip >= 0 ? 1 : -1)); } public int getScore() { return score; } public String getCrrentLevel() { return crrentLevel; } public void setCrrentLevel(String crrentLevel) { this.crrentLevel = crrentLevel; } public float getMaxCount() { return maxCount; } public float getCurrentCount() { return currentCount; } public void setScore(int score) { this.score = score; if (score == 100) { this.crrentLevel = ALARM_LEVEL[0]; } else if (score >= 70 && score < 100) { this.crrentLevel = ALARM_LEVEL[1]; } else if (score >= 30 && score < 70) { this.crrentLevel = ALARM_LEVEL[2]; } else { this.crrentLevel = ALARM_LEVEL[3]; } invalidate(); } /*** * 设置最大的进度值 * * @param maxCount */ public void setMaxCount(float maxCount) { this.maxCount = maxCount; } /*** * 设置当前的进度值 * * @param currentCount */ public void setCurrentCount(float currentCount) { this.currentCount = currentCount > maxCount ? maxCount : currentCount; invalidate(); } @Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY || widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { mWidth = widthSpecSize; } else { mWidth = 0; } if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST || heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.UNSPECIFIED) { mHeight = dipToPx(15); } else { mHeight = heightSpecSize; } setMeasuredDimension(mWidth, mHeight); } }
Demo:
http://xiazai.jb51.net/201507/yuanma/ProgressViewDemo(jb51.net).rar
以上内容就是实现android自定义进度条渐变圆形的代码,希望对大家有所帮助。
-
本文向大家介绍Android动态自定义圆形进度条,包括了Android动态自定义圆形进度条的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 效果图: A.绘制圆环,圆弧,文本 B.自定义属性的具体步骤 具体步骤: 1. 定义属性: 在values目录下创建attrs.xml 2. 在布局文件中引用当前应用的名称空间 3. 在自定义视图标签中使用自定义属性 4. 在自定义View类的构造方法中, 取出布局中
-
本文向大家介绍Android实现自定义圆形进度条,包括了Android实现自定义圆形进度条的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 今天无意中发现一个圆形进度,想想自己实现一个,如下图: 基本思路是这样的: 1.首先绘制一个实心圆 2.绘制一个白色实心的正方形,遮住实心圆 3.在圆的中心动态绘制当前进度的百分比字符 4.绘制一个与之前实心圆相同颜色的空心圆 5.逐渐改变当前的百分比 6.根据百分比
-
本文向大家介绍自定义Android圆形进度条(附源码),包括了自定义Android圆形进度条(附源码)的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Android自定义圆形进度条,分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下: 运行效果截图如下: 具体代码如下: 自定义的View: 所需要的资源文件:attrs.xml 布局文件如下: 其中我们使用了这一句: xmlns:android_custom是
-
本文向大家介绍Android自定义圆形倒计时进度条,包括了Android自定义圆形倒计时进度条的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了Android倒计时进度条展示的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 效果预览 源代码传送门:https://github.com/yanzhenjie/CircleTextProgressbar 实现与原理 这个文字圆形的进度条我们在很多APP
-
本文向大家介绍Android自定义水平进度条的圆角进度,包括了Android自定义水平进度条的圆角进度的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 平时项目中经常用到自定义进度条样式,我们一般实现的也是下面的第一种,至于第二种的圆角进度,网上介绍的资料也不是很多,这里一起展示一下这两种的实现。 下面开始看代码,先从主界面布局开始看起: 两个进度条布局,然后是不同的progressDrawable布局:
-
本文向大家介绍Android实现带数字的圆形进度条(自定义进度条),包括了Android实现带数字的圆形进度条(自定义进度条)的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 开发 设计搞了一个带圆形进度的进度条,在GitHub上逛了一圈,发现没有,自己撸吧。 先看界面效果: 主要思路是写一个继承ProgressBar的自定义View,不废话,直接上代码: 使用 在布局文件中加入: progress_re

