MOSN 源码解析 - Plugin 机制
概述
Plugin 机制是 MOSN 提供的一种方式,可以让 MOSN 和一个独立的进程进行交互,这个进程可以用任何语言开发,只要满足 gRPC 的 proto 定义。
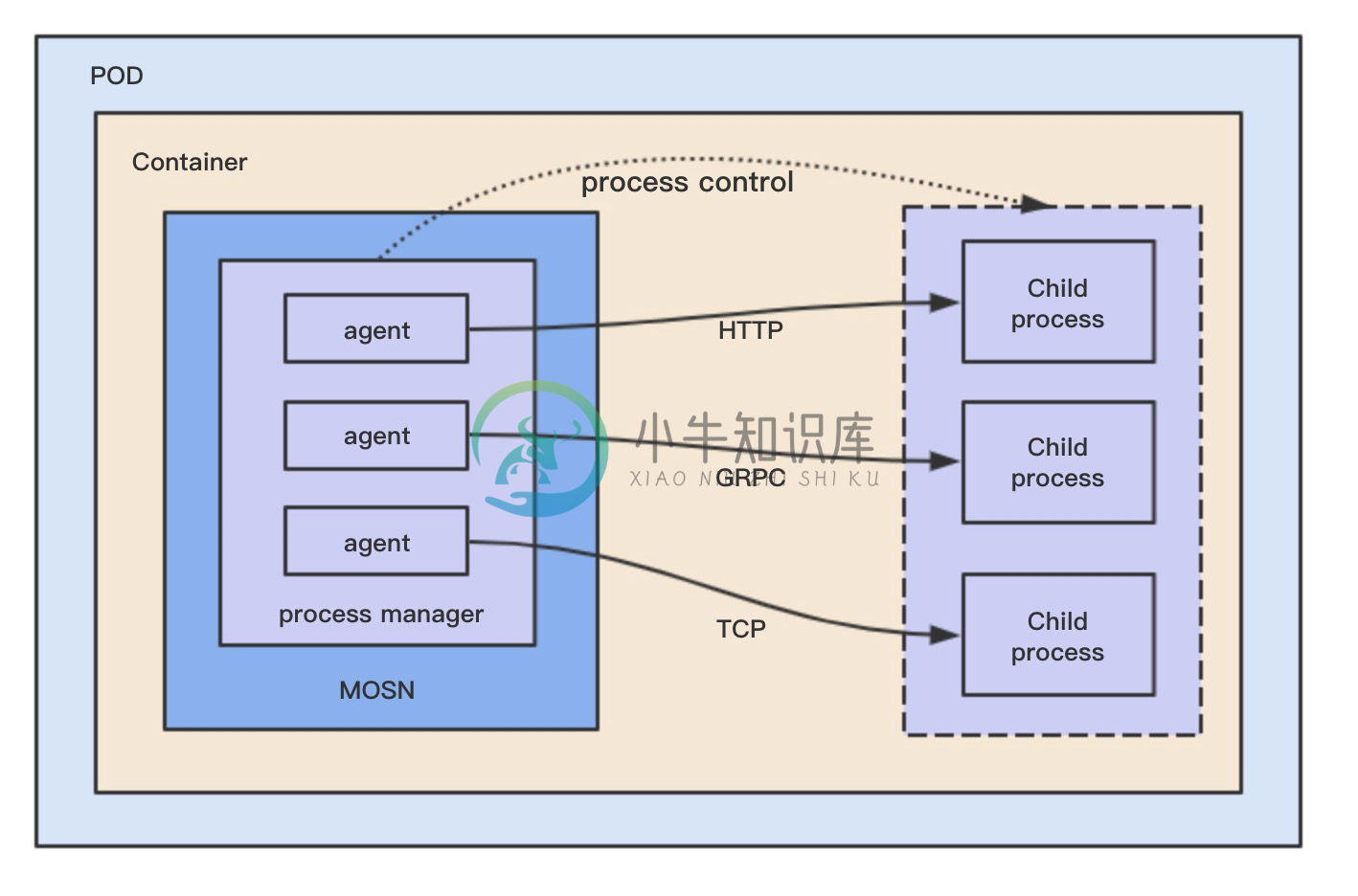
为什么我们支持这个功能,跟我们遇到的一些业务场景有关:
- 比如 log 打印,在 io 卡顿的时候会影响 Go Runtime 的调度,导致请求延迟。我们需要把 log 独立成进程做隔离。
- 我们会有一些异构语言的扩展,比如 streamfilter 的实际逻辑是一个 Java 语言实现的。
- 我们需要快速更新一些业务逻辑,但不能频繁的去更新 MOSN 的代码。
- 作为类似 Supervisor 的管理工具,管理一些其他进程。
总结下来就是隔离性,支持异构语言扩展,模块化,进程管理等场景,大家也可以看看还有哪些场景可以用到。
使用方法
examples/codes/plugin/pluginfilter/提供了一个使用示例,通过 streamfilter 把数据传递给一个独立进程处理并反馈。
我们这儿简单看下pkg/plugin/example/:
client
client, err := plugin.Register("plugin-server", nil)
if err != nil {
fmt.Println(err)
return
}
response, err := client.Call(&proto.Request{
Body: []byte("hello"),
}, time.Second)
}
- 通过
plugin.Register注册一个 plugin,name 需要和编译的二进制名字一样,然后函数会去启动这个程序,这个程序就是下面的 server 代码。 - 调用
client.Call发送请求给 server 进程,然后收到响应并处理。
server
type filter struct{}
func (s *filter) Call(request *proto.Request) (*proto.Response, error) {
if string(request.GetBody()) != "hello" {
return nil, errors.New("request body error")
}
response := new(proto.Response)
response.Body = []byte("world")
response.Status = 1
return response, nil
}
func main() {
plugin.Serve(&filter{})
}
- 首先实现
plugin.Service接口,Call函数将接收 client 的请求,处理之后返回响应。 - main函数执行
plugin.Serve,运行服务监听 client 的请求。
运行
执行如下命令:
$ go build -o plugin-client client/plugin.go
$ go build -o plugin-server server/plugin.go
$ ./plugin-client 2> /tmp/1
success! response body: world
初始化
MOSN 的 plugin 底层使用了github.com/hashicorp/go-plugin库,该库是 HashiCorp 公司提供的一个成熟的扩展系统,可以方便的扩展自己的插件机制。
先看一下配置文件:
"plugin": {
"log_base": "/home/admin/mosn/logs/"
}
log_baseplugin 传递给扩展进程的日志目录
在看一下 proto 定义,Request 和 Resonse 定义了几个通用的数据结构,在使用的时候可以选择使用,比如打印 log 就需要使用 Request 的 boy 字段。Call 方法就是我们需要实现的,来进行请求的发送和处理处理。
syntax = "proto3";
package proto;
message Request {
map<string, string> header=1;
map<string, string> trailer=2;
bytes body = 3;
string type = 4;
}
message Response {
map<string, string> header=1;
map<string, string> trailer=2;
bytes body = 3;
int32 status = 4;
}
service Plugin {
rpc Call(Request) returns (Response);
}
Client管理 client 的整个生命周期,用户使用该结构体发送请求。
// Client is a plugin client, It's primarily used to call request.
type Client struct {
pclient *plugin.Client
config *Config
name string
fullName string
service *client
enable bool
on bool
sync.Mutex
}
Config初始化 Client 的时候使用,MaxProcs表示独立进程的 GOMAXPROCS 配置,Args表示独立进程的启动参数。
type Config struct {
MaxProcs int
Args []string
}
启动
Register用于 client 端注册 plugin,参数name表示 server 的二进制名字,文件路径同于 client 的二进制路径。返回的 Client 用于管理整个 agent-client 的生命周期。
// Register called by plugin client and start up the plugin main process.
func Register(name string, config *Config) (*Client, error) {
pluginLock.Lock()
defer pluginLock.Unlock()
if c, ok := pluginFactories[name]; ok {
return c, nil
}
c, err := newClient(name, config)
if err != nil {
return nil, err
}
pluginFactories[name] = c
return c, nil
}
newClient生成 Client,其中最重要的是Check方法,用于启动 server。
- 首先把
GOMAXPROCS和日志路径通过环境变量传递给server进程。 plugin.NewClient开启 plugin 框架之后,pclient.Client()启动 server 子进程。rpcClient.Dispense("MOSN_SERVICE")返回真正的实例 client。
client 的整个启动过程就完成了,主要就是启动了 server 子进程,然后初始化了 client GRPC 的实例,用于请求发送和接收。
func (c *Client) Check() error {
.
.
cmd := exec.Command(c.fullName, c.config.Args...)
procs := 1
if c.config != nil && c.config.MaxProcs >= 0 && c.config.MaxProcs <= 4 {
procs = c.config.MaxProcs
}
cmd.Env = append(cmd.Env, fmt.Sprintf("MOSN_PROCS=%d", procs))
cmd.Env = append(cmd.Env, fmt.Sprintf("MOSN_LOGBASE=%s", pluginLogBase))
pclient := plugin.NewClient(&plugin.ClientConfig{
HandshakeConfig: Handshake,
Plugins: PluginMap,
Cmd: cmd,
AllowedProtocols: []plugin.Protocol{
plugin.ProtocolGRPC},
})
rpcClient, err := pclient.Client()
if err != nil {
return err
}
raw, err := rpcClient.Dispense("MOSN_SERVICE")
.
.
}
接下来是 server,server 端的代码也可以用其他语言实现,只要满足一定的规范,下面看看 Go 的实现:
- 首先执行
checkParentAlive()主要是检查父进程(也就是 client )是否退出,如果退出了,自己也需要退出。 - 然后读取环境变量,来设置
GOMAXPROCS。 - 最后调用
plugin.Serve启动 GRPC Server 服务接收处理请求。
// Serve is a function used to serve a plugin. This should be ran on the plugin's main process.
func Serve(service Service) {
checkParentAlive()
p := os.Getenv("MOSN_PROCS")
if procs, err := strconv.Atoi(p); err == nil {
runtime.GOMAXPROCS(procs)
}
plugin.Serve(&plugin.ServeConfig{
HandshakeConfig: Handshake,
Plugins: map[string]plugin.Plugin{
"MOSN_SERVICE": &Plugin{Impl: service},
},
GRPCServer: plugin.DefaultGRPCServer,
})
}
server 最主要的就是实现Service接口,用于处理请求,之前的 exmple 就有一个简单的实现。
// Service is a service that Implemented by plugin main process
type Service interface {
Call(request *proto.Request) (*proto.Response, error)
}
执行
client 只需要执行Call函数就可以发送和接收请求,实现会先通过Check()来检查 server 是否健康,如果不健康会先启动 server,然后调用真正的实现。
// Call invokes the function synchronously.
func (c *Client) Call(request *proto.Request, timeout time.Duration) (*proto.Response, error) {
if err := c.Check(); err != nil {
return nil, err
}
return c.service.Call(request, timeout)
}
首先设置 timeout 请求超时时间,然后在调用 GRPC 的接口发送请求。
func (c *client) Call(request *proto.Request, timeout time.Duration) (*proto.Response, error) {
var ctx context.Context
var cancel context.CancelFunc
if timeout > 0 {
ctx, cancel = context.WithTimeout(context.Background(), timeout)
defer cancel()
} else {
ctx = context.Background()
}
response, err := c.PluginClient.Call(ctx, request)
return response, err
}
在 server 端会直接执行我们实现的 Call 接口。
func (s *server) Call(ctx context.Context, req *proto.Request) (*proto.Response, error) {
return s.Impl.Call(req)
}
管理
MOSN 提供了 HTTP 接口来查看 plugin 的运行状态,以及开启关闭 Plugin。
Usage:
/plugin?status=all
/plugin?status=pluginname
/plugin?enable=pluginname
/plugin?disable=pluginname
在 disable 之后,server 就会被关闭,并且不会再启动,主要为了防止 server 有问题的时候可以关闭掉。
总结
寄托于开源社区,我们方便的搭建了自己的扩展机制,MOSN 也把自己的想法反馈给社区,共同进步。
拥抱开源,反哺开源。

