WinPcap: 收集并统计网络流量
这一讲,我们将展示WinPcap的另一个高级特性:收集并统计网络流量。统计引擎利用了内核级的数据包过滤器,来有效地为收集到的数据包进行分类。如果你想阅读更多细节,请参阅 NPF驱动核心手册。
为了使用这个特性,编程人员必须打开一个适配器,并且,可以使用 pcap_setmode() 将它设置为统计模式(statistical mode)。特别注意,必须使用MODE_STAT来作为这个函数的mode参数。
在统计模式下,编写一个用于监听TCP网络流量的程序并不复杂,代码也不多。下面的范例程序将展示如何实现这个程序。
/*
* Copyright (c) 1999 - 2005 NetGroup, Politecnico di Torino (Italy)
* Copyright (c) 2005 - 2006 CACE Technologies, Davis (California)
* All rights reserved.
*
* Redistribution and use in source and binary forms, with or without
* modification, are permitted provided that the following conditions
* are met:
*
* 1. Redistributions of source code must retain the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer.
* 2. Redistributions in binary form must reproduce the above copyright
* notice, this list of conditions and the following disclaimer in the
* documentation and/or other materials provided with the distribution.
* 3. Neither the name of the Politecnico di Torino, CACE Technologies
* nor the names of its contributors may be used to endorse or promote
* products derived from this software without specific prior written
* permission.
*
* THIS SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED BY THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND CONTRIBUTORS
* "AS IS" AND ANY EXPRESS OR IMPLIED WARRANTIES, INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR
* A PARTICULAR PURPOSE ARE DISCLAIMED. IN NO EVENT SHALL THE COPYRIGHT
* OWNER OR CONTRIBUTORS BE LIABLE FOR ANY DIRECT, INDIRECT, INCIDENTAL,
* SPECIAL, EXEMPLARY, OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES (INCLUDING, BUT NOT
* LIMITED TO, PROCUREMENT OF SUBSTITUTE GOODS OR SERVICES; LOSS OF USE,
* DATA, OR PROFITS; OR BUSINESS INTERRUPTION) HOWEVER CAUSED AND ON ANY
* THEORY OF LIABILITY, WHETHER IN CONTRACT, STRICT LIABILITY, OR TORT
* (INCLUDING NEGLIGENCE OR OTHERWISE) ARISING IN ANY WAY OUT OF THE USE
* OF THIS SOFTWARE, EVEN IF ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGE.
*
*/
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pcap.h>
void usage();
void dispatcher_handler(u_char *, const struct pcap_pkthdr *, const u_char *);
void main(int argc, char **argv)
{
pcap_t *fp;
char errbuf[PCAP_ERRBUF_SIZE];
struct timeval st_ts;
u_int netmask;
struct bpf_program fcode;
/* 检查命令行参数的合法性 */
if (argc != 2)
{
usage();
return;
}
/* 打开输出适配器 */
if ( (fp= pcap_open(argv[1], 100, PCAP_OPENFLAG_PROMISCUOUS, 1000, NULL, errbuf) ) == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr,"nUnable to open adapter %s.n", errbuf);
return;
}
/* 不用关心掩码,在这个过滤器中,它不会被使用 */
netmask=0xffffff;
// 编译过滤器
if (pcap_compile(fp, &fcode, "tcp", 1, netmask) <0 )
{
fprintf(stderr,"nUnable to compile the packet filter. Check the syntax.n");
/* 释放设备列表 */
return;
}
//设置过滤器
if (pcap_setfilter(fp, &fcode)<0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"nError setting the filter.n");
pcap_close(fp);
/* 释放设备列表 */
return;
}
/* 将接口设置为统计模式 */
if (pcap_setmode(fp, MODE_STAT)<0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"nError setting the mode.n");
pcap_close(fp);
/* 释放设备列表 */
return;
}
printf("TCP traffic summary:n");
/* 开始主循环 */
pcap_loop(fp, 0, dispatcher_handler, (PUCHAR)&st_ts);
pcap_close(fp);
return;
}
void dispatcher_handler(u_char *state, const struct pcap_pkthdr *header, const u_char *pkt_data)
{
struct timeval *old_ts = (struct timeval *)state;
u_int delay;
LARGE_INTEGER Bps,Pps;
struct tm *ltime;
char timestr[16];
time_t local_tv_sec;
/* 以毫秒计算上一次采样的延迟时间 */
/* 这个值通过采样到的时间戳获得 */
delay=(header->ts.tv_sec - old_ts->tv_sec) * 1000000 - old_ts->tv_usec + header->ts.tv_usec;
/* 获取每秒的比特数b/s */
Bps.QuadPart=(((*(LONGLONG*)(pkt_data + 8)) * 8 * 1000000) / (delay));
/* ^ ^
| |
| |
| |
将字节转换成比特 -- |
|
延时是以毫秒表示的 --
*/
/* 得到每秒的数据包数量 */
Pps.QuadPart=(((*(LONGLONG*)(pkt_data)) * 1000000) / (delay));
/* 将时间戳转化为可识别的格式 */
local_tv_sec = header->ts.tv_sec;
ltime=localtime(&local_tv_sec);
strftime( timestr, sizeof timestr, "%H:%M:%S", ltime);
/* 打印时间戳*/
printf("%s ", timestr);
/* 打印采样结果 */
printf("BPS=%I64u ", Bps.QuadPart);
printf("PPS=%I64un", Pps.QuadPart);
//存储当前的时间戳
old_ts->tv_sec=header->ts.tv_sec;
old_ts->tv_usec=header->ts.tv_usec;
}
void usage()
{
printf("nShows the TCP traffic load, in bits per second and packets per second.nCopyright (C) 2002 Loris Degioanni.n");
printf("nUsage:n");
printf("t tcptop adaptern");
printf("t You can use "WinDump -D" if you don't know the name of your adapters.n");
exit(0);
}
在启动统计模式前,用户需要设置一个过滤器,以定义要监听的数据流。详细内容请参考 过滤表达式语法 。如果没有设置过滤器,那么,所有的数据流量都将会被监听
过程
- 设置过滤器
- 调用 pcap_setmode()
- 回调函数通过 pcap_loop()被启动
接口描述符(the interface descriptor)开始工作在统计模式下。注意 pcap_open() 函数的第4个参数( to_ms ):它定义了统计残阳的时间间隔。回调函数将在每一个to_ms时间,收到由驱动发来的计算好的采样数据。这些采样数据将通过回调函数的第2个和第3个参数传递,如下所示
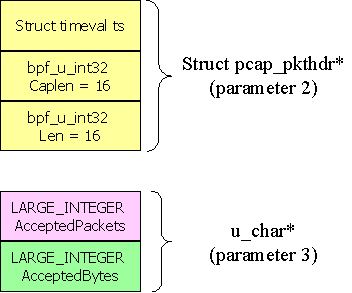
它提供了两个64位的计数器,分别记录在最后一个时间间隔内,收到的数据包的数量和字节总数。
在这个范例中,适配器打开后的超时时间设置为1000毫秒。这就意味着dispatcher_handler()每隔1秒就会被调用一次。这里的过滤器被设置为只监视TCP包。然后, pcap_setmode() 和 pcap_loop() 被调用。注意,一个指向timeval结构的指针,作为user参数传递给函数 pcap_loop() 。这个结构体会被用来存储时间戳,以便计算两次采样的时间间隔。 dispatcher_handler() 会使用这个时间间隔来获得每秒的比特数(bps)以及每秒的数据包数量(pps),并将它们的值打印在屏幕上。
最后,我们想说,这个范例程序比传统的捕获和统计流量的程序都要高效,因为传统的程序都在用户层进行。静态模式需要最小的数据包拷贝和上下文交换,因此,CPU的性能会最优,而且,内存的需求量也会很少。

