debug
A tiny JavaScript debugging utility modelled after Node.js core's debuggingtechnique. Works in Node.js and web browsers.
Installation
$ npm install debug
Usage
debug exposes a function; simply pass this function the name of your module, and it will return a decorated version of console.error for you to pass debug statements to. This will allow you to toggle the debug output for different parts of your module as well as the module as a whole.
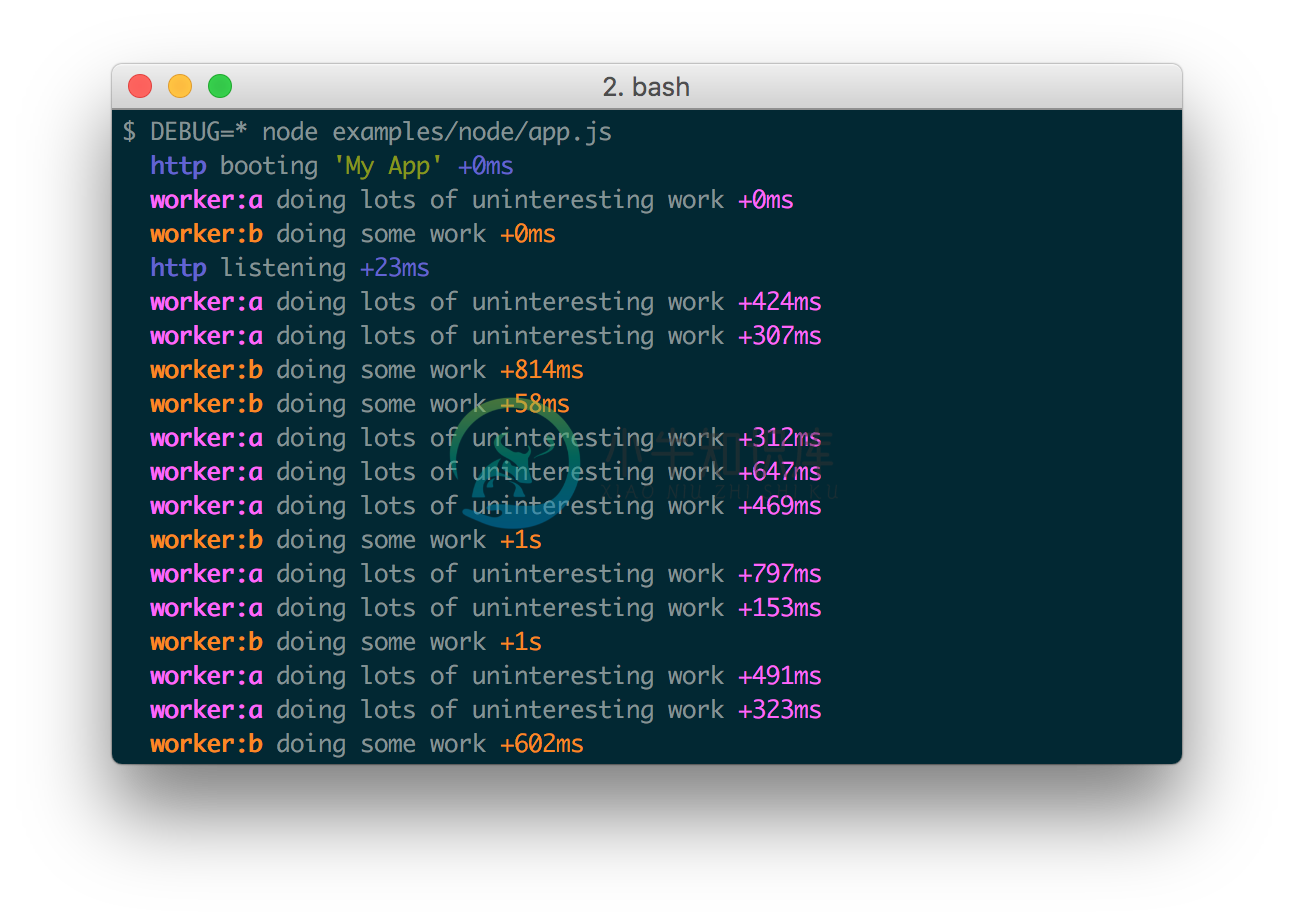
Example app.js:
var debug = require('debug')('http')
, http = require('http')
, name = 'My App';
// fake app
debug('booting %o', name);
http.createServer(function(req, res){
debug(req.method + ' ' + req.url);
res.end('hello\n');
}).listen(3000, function(){
debug('listening');
});
// fake worker of some kind
require('./worker');
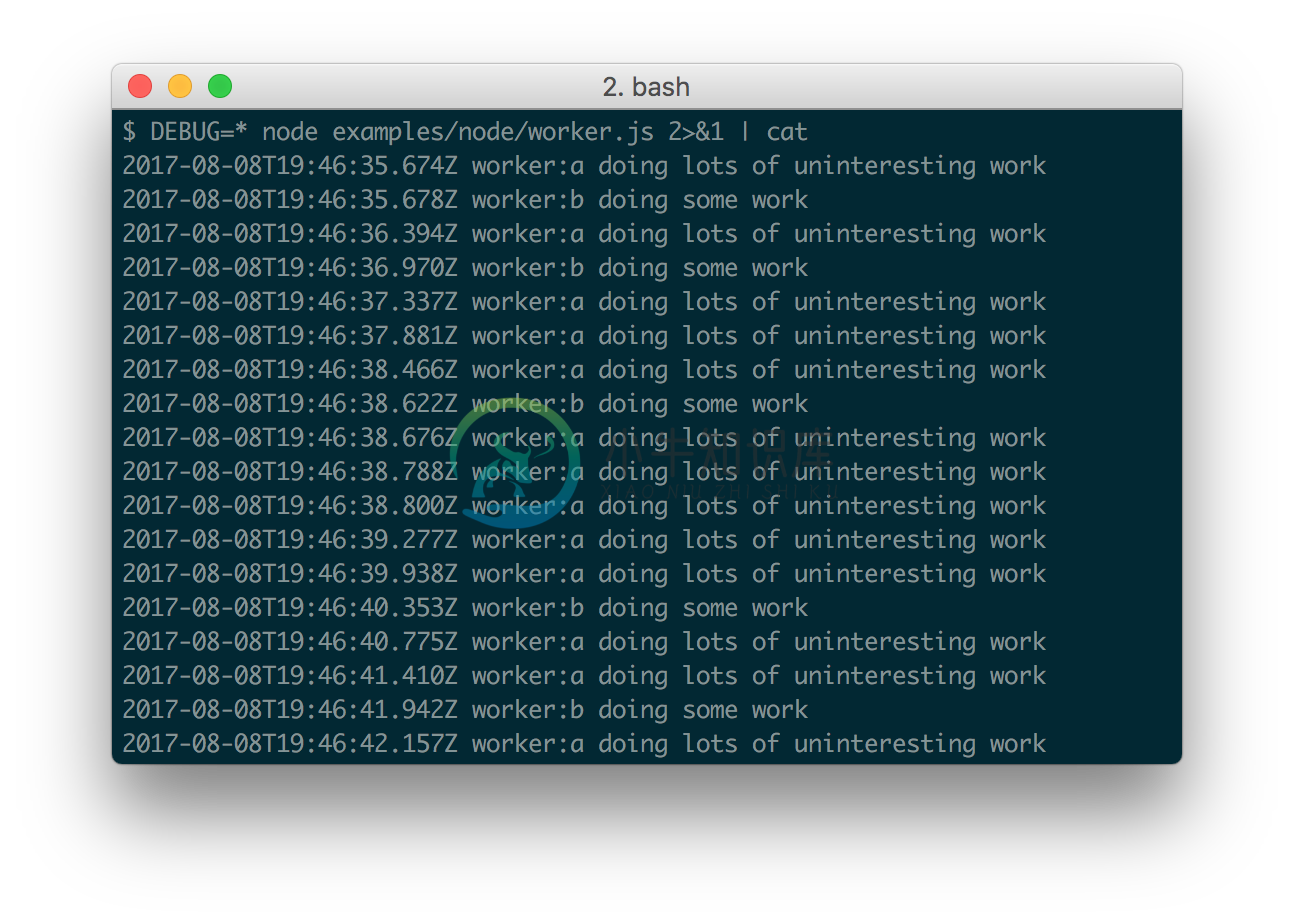
Example worker.js:
var a = require('debug')('worker:a')
, b = require('debug')('worker:b');
function work() {
a('doing lots of uninteresting work');
setTimeout(work, Math.random() * 1000);
}
work();
function workb() {
b('doing some work');
setTimeout(workb, Math.random() * 2000);
}
workb();
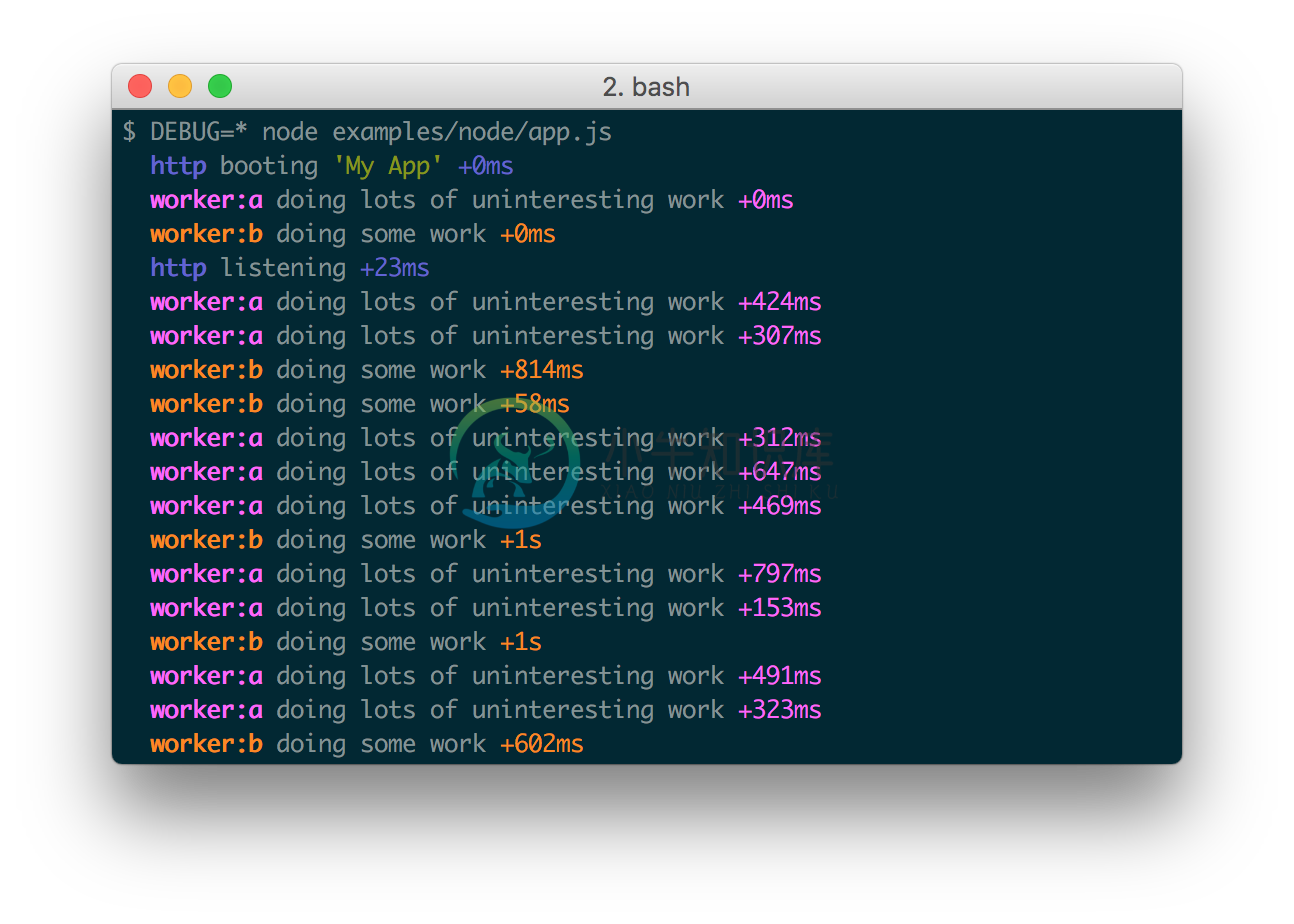
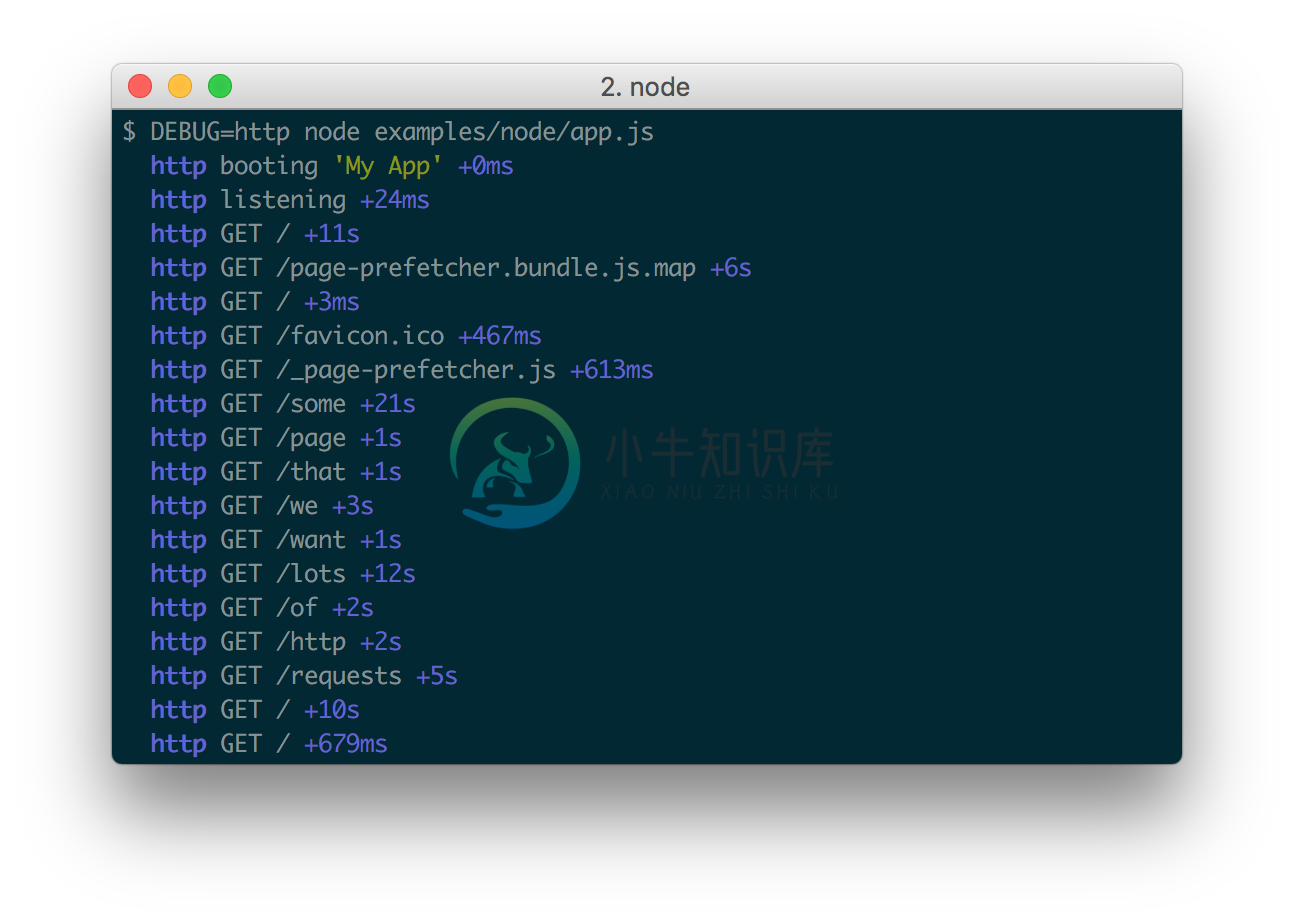
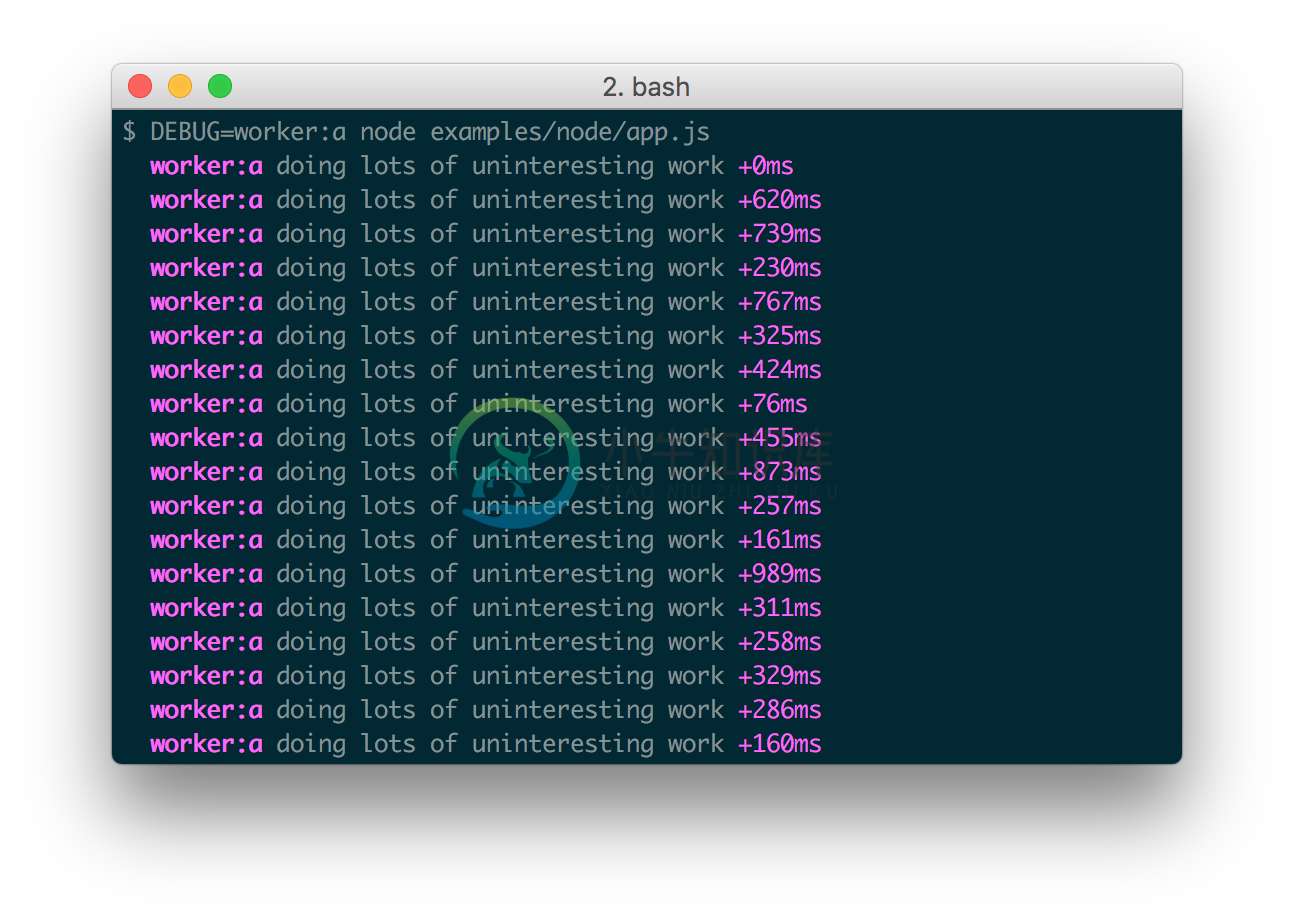
The DEBUG environment variable is then used to enable these based on space orcomma-delimited names.
Here are some examples:
Windows command prompt notes
CMD
On Windows the environment variable is set using the set command.
set DEBUG=*,-not_this
Example:
set DEBUG=* & node app.js
PowerShell (VS Code default)
PowerShell uses different syntax to set environment variables.
$env:DEBUG = "*,-not_this"
Example:
$env:DEBUG='app';node app.js
Then, run the program to be debugged as usual.
npm script example:
"windowsDebug": "@powershell -Command $env:DEBUG='*';node app.js",
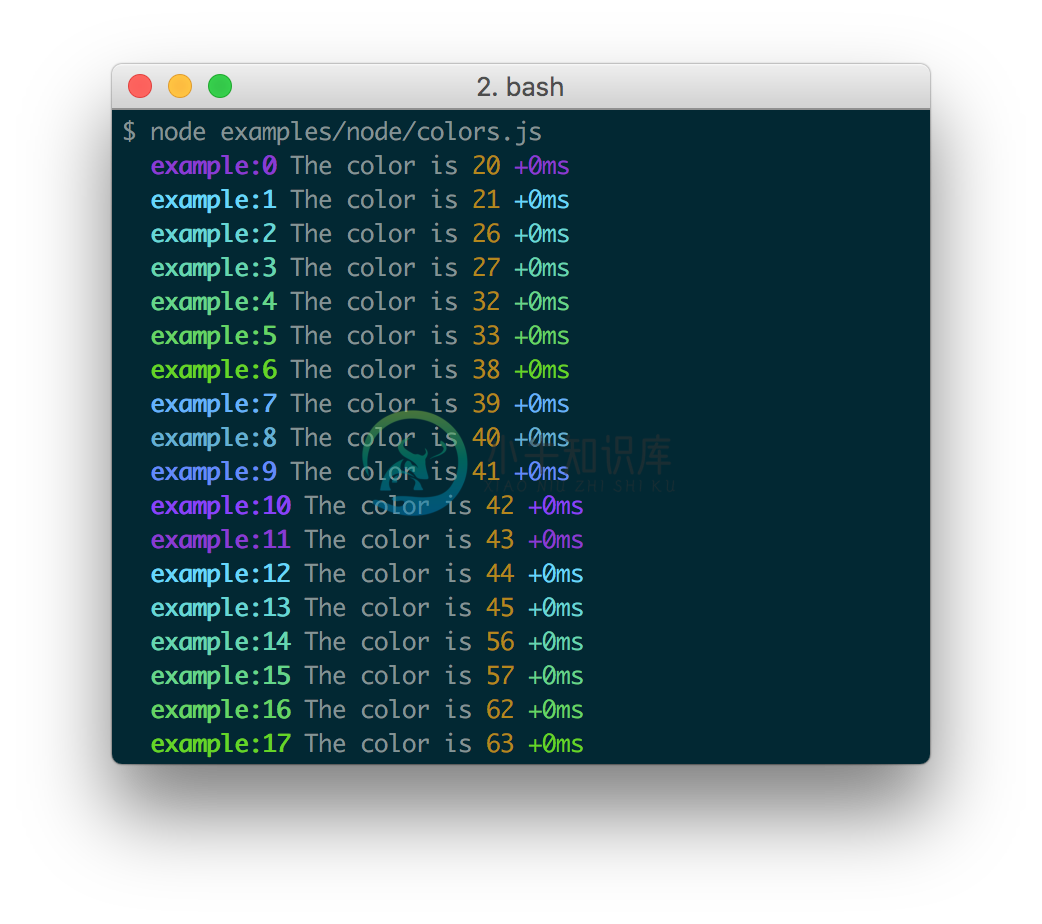
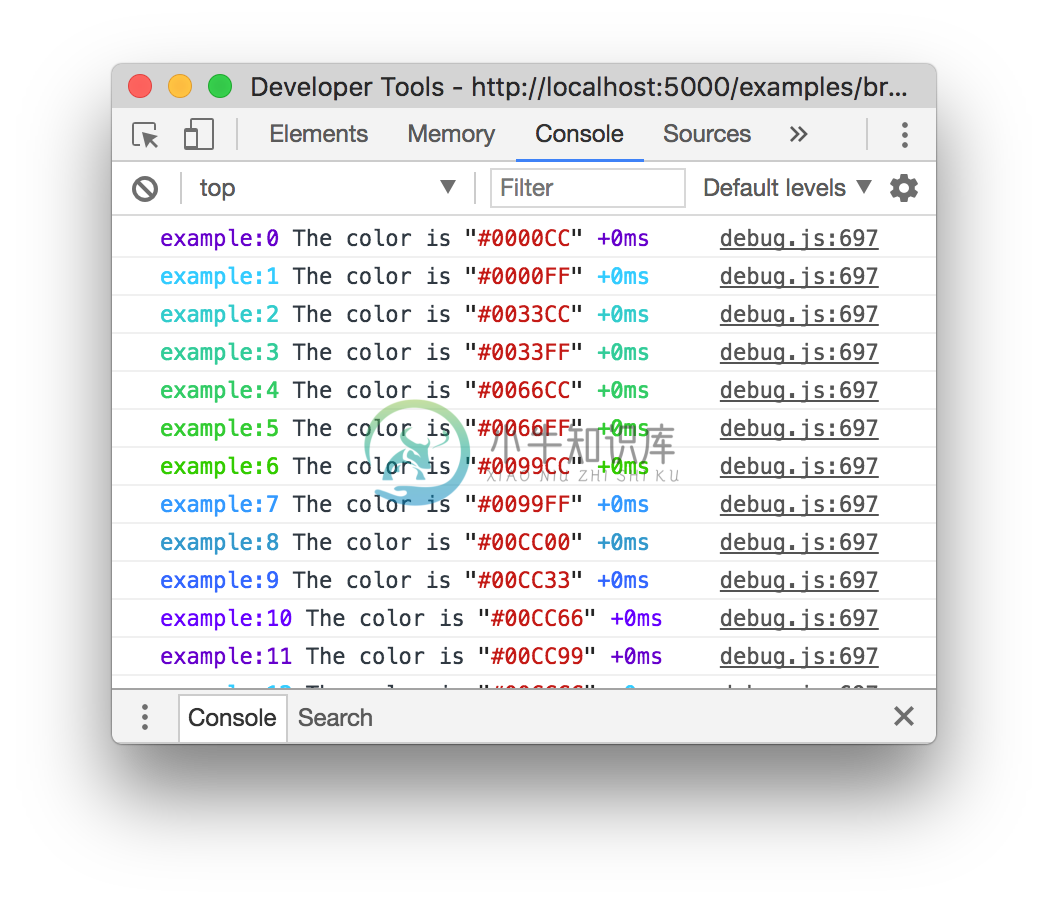
Namespace Colors
Every debug instance has a color generated for it based on its namespace name.This helps when visually parsing the debug output to identify which debug instancea debug line belongs to.
Node.js
In Node.js, colors are enabled when stderr is a TTY. You also should installthe supports-color module alongside debug,otherwise debug will only use a small handful of basic colors.
Web Browser
Colors are also enabled on "Web Inspectors" that understand the %c formattingoption. These are WebKit web inspectors, Firefox (since version31)and the Firebug plugin for Firefox (any version).
Millisecond diff
When actively developing an application it can be useful to see when the time spent between one debug() call and the next. Suppose for example you invoke debug() before requesting a resource, and after as well, the "+NNNms" will show you how much time was spent between calls.
When stdout is not a TTY, Date#toISOString() is used, making it more useful for logging the debug information as shown below:
Conventions
If you're using this in one or more of your libraries, you should use the name of your library so that developers may toggle debugging as desired without guessing names. If you have more than one debuggers you should prefix them with your library name and use ":" to separate features. For example "bodyParser" from Connect would then be "connect:bodyParser". If you append a "*" to the end of your name, it will always be enabled regardless of the setting of the DEBUG environment variable. You can then use it for normal output as well as debug output.
Wildcards
The * character may be used as a wildcard. Suppose for example your library hasdebuggers named "connect:bodyParser", "connect:compress", "connect:session",instead of listing all three withDEBUG=connect:bodyParser,connect:compress,connect:session, you may simply doDEBUG=connect:*, or to run everything using this module simply use DEBUG=*.
You can also exclude specific debuggers by prefixing them with a "-" character.For example, DEBUG=*,-connect:* would include all debuggers except thosestarting with "connect:".
Environment Variables
When running through Node.js, you can set a few environment variables that willchange the behavior of the debug logging:
| Name | Purpose |
|---|---|
DEBUG |
Enables/disables specific debugging namespaces. |
DEBUG_HIDE_DATE |
Hide date from debug output (non-TTY). |
DEBUG_COLORS |
Whether or not to use colors in the debug output. |
DEBUG_DEPTH |
Object inspection depth. |
DEBUG_SHOW_HIDDEN |
Shows hidden properties on inspected objects. |
Note: The environment variables beginning with DEBUG_ end up beingconverted into an Options object that gets used with %o/%O formatters.See the Node.js documentation forutil.inspect()for the complete list.
Formatters
Debug uses printf-style formatting.Below are the officially supported formatters:
| Formatter | Representation |
|---|---|
%O |
Pretty-print an Object on multiple lines. |
%o |
Pretty-print an Object all on a single line. |
%s |
String. |
%d |
Number (both integer and float). |
%j |
JSON. Replaced with the string '[Circular]' if the argument contains circular references. |
%% |
Single percent sign ('%'). This does not consume an argument. |
Custom formatters
You can add custom formatters by extending the debug.formatters object.For example, if you wanted to add support for rendering a Buffer as hex with%h, you could do something like:
const createDebug = require('debug')
createDebug.formatters.h = (v) => {
return v.toString('hex')
}
// …elsewhere
const debug = createDebug('foo')
debug('this is hex: %h', new Buffer('hello world'))
// foo this is hex: 68656c6c6f20776f726c6421 +0ms
Browser Support
You can build a browser-ready script using browserify,or just use the browserify-as-a-service build,if you don't want to build it yourself.
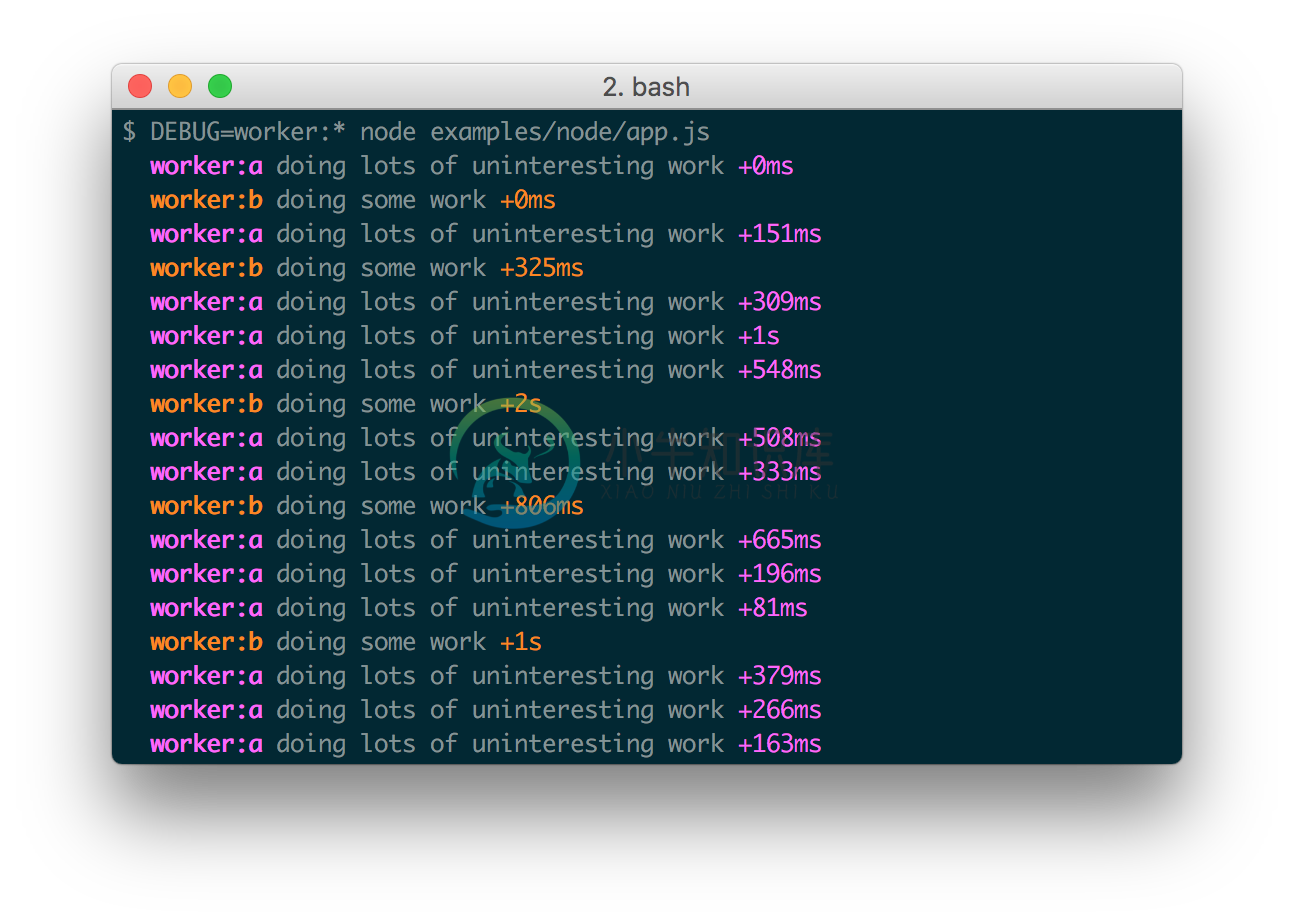
Debug's enable state is currently persisted by localStorage.Consider the situation shown below where you have worker:a and worker:b,and wish to debug both. You can enable this using localStorage.debug:
localStorage.debug = 'worker:*'
And then refresh the page.
a = debug('worker:a');
b = debug('worker:b');
setInterval(function(){
a('doing some work');
}, 1000);
setInterval(function(){
b('doing some work');
}, 1200);
Output streams
By default debug will log to stderr, however this can be configured per-namespace by overriding the log method:
Example stdout.js:
var debug = require('debug');
var error = debug('app:error');
// by default stderr is used
error('goes to stderr!');
var log = debug('app:log');
// set this namespace to log via console.log
log.log = console.log.bind(console); // don't forget to bind to console!
log('goes to stdout');
error('still goes to stderr!');
// set all output to go via console.info
// overrides all per-namespace log settings
debug.log = console.info.bind(console);
error('now goes to stdout via console.info');
log('still goes to stdout, but via console.info now');
Extend
You can simply extend debugger
const log = require('debug')('auth');
//creates new debug instance with extended namespace
const logSign = log.extend('sign');
const logLogin = log.extend('login');
log('hello'); // auth hello
logSign('hello'); //auth:sign hello
logLogin('hello'); //auth:login hello
Set dynamically
You can also enable debug dynamically by calling the enable() method :
let debug = require('debug');
console.log(1, debug.enabled('test'));
debug.enable('test');
console.log(2, debug.enabled('test'));
debug.disable();
console.log(3, debug.enabled('test'));
print :
1 false
2 true
3 false
Usage :enable(namespaces)namespaces can include modes separated by a colon and wildcards.
Note that calling enable() completely overrides previously set DEBUG variable :
$ DEBUG=foo node -e 'var dbg = require("debug"); dbg.enable("bar"); console.log(dbg.enabled("foo"))'
=> false
disable()
Will disable all namespaces. The functions returns the namespaces currentlyenabled (and skipped). This can be useful if you want to disable debuggingtemporarily without knowing what was enabled to begin with.
For example:
let debug = require('debug');
debug.enable('foo:*,-foo:bar');
let namespaces = debug.disable();
debug.enable(namespaces);
Note: There is no guarantee that the string will be identical to the initialenable string, but semantically they will be identical.
Checking whether a debug target is enabled
After you've created a debug instance, you can determine whether or not it isenabled by checking the enabled property:
const debug = require('debug')('http');
if (debug.enabled) {
// do stuff...
}
You can also manually toggle this property to force the debug instance to beenabled or disabled.
Usage in child processes
Due to the way debug detects if the output is a TTY or not, colors are not shown in child processes when stderr is piped. A solution is to pass the DEBUG_COLORS=1 environment variable to the child process.
For example:
worker = fork(WORKER_WRAP_PATH, [workerPath], {
stdio: [
/* stdin: */ 0,
/* stdout: */ 'pipe',
/* stderr: */ 'pipe',
'ipc',
],
env: Object.assign({}, process.env, {
DEBUG_COLORS: 1 // without this settings, colors won't be shown
}),
});
worker.stderr.pipe(process.stderr, { end: false });
Authors
- TJ Holowaychuk
- Nathan Rajlich
- Andrew Rhyne
Backers
Support us with a monthly donation and help us continue our activities. [Become a backer]
Sponsors
Become a sponsor and get your logo on our README on Github with a link to your site. [Become a sponsor]
License
(The MIT License)
Copyright (c) 2014-2017 TJ Holowaychuk <tj@vision-media.ca>
Permission is hereby granted, free of charge, to any person obtaininga copy of this software and associated documentation files (the'Software'), to deal in the Software without restriction, includingwithout limitation the rights to use, copy, modify, merge, publish,distribute, sublicense, and/or sell copies of the Software, and topermit persons to whom the Software is furnished to do so, subject tothe following conditions:
The above copyright notice and this permission notice shall beincluded in all copies or substantial portions of the Software.
THE SOFTWARE IS PROVIDED 'AS IS', WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,EXPRESS OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO THE WARRANTIES OFMERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT.IN NO EVENT SHALL THE AUTHORS OR COPYRIGHT HOLDERS BE LIABLE FOR ANYCLAIM, DAMAGES OR OTHER LIABILITY, WHETHER IN AN ACTION OF CONTRACT,TORT OR OTHERWISE, ARISING FROM, OUT OF OR IN CONNECTION WITH THESOFTWARE OR THE USE OR OTHER DEALINGS IN THE SOFTWARE.
-
在大型项目中,哪种方法更好,为什么使用: #if DEBUG public void SetPrivateValue(int value) { ... } #endif 要么 [System.Diagnostics.Conditional("DEBUG")] public void SetPrivateValue(int value) { ... } #1楼 我有一个SOAP
-
问题内容: 我正在寻找一种方法,在我调试的应用程序结束后,可以返回到Eclipse中的标准Java视图。 有可能做到这一点吗?这是某些其他IDE(例如Visual Studio)的默认行为,我更希望采用这种方式。不得不手动再次将视图切换到初始视图很无聊:( 谢谢 问题答案: Eclipse是一个通用平台,您可以在其中使用多种类型的不同启动配置,因此,良好且可用的此功能的“通用”实现并非易事。 但是
-
问题内容: 我尝试用Selenium 抓取此网站。 我想单击“下一页”按钮,为此,我这样做: 它适用于许多页面,但不适用于所有页面,我收到此错误 始终为此页面 我尝试了这个 但是我遇到了同样的错误 问题答案: 另一个元素覆盖了您要单击的元素。您可以使用它来单击。
-
问题内容: 我正在开发一个简单的桌面应用程序(不是webapp)。 这是我的: 如你所见,为了消除控制台中的Spring日志消息,我尝试了以下解决方案: 当我从代码中调用log4j记录器时,记录消息是根据上面指定的模式进行的(这很好)。 但是,最糟糕的是-我仍然从Spring进入控制台的DEBUG级别消息…它们看起来像这里: 无法禁用日志记录消息 他们有不同的模式。好像他们忽略了我的设置。 我还尝
-
问题内容: 此代码使用golang的先前版本(1.8.3)进行了编译,但是升级到新的golang(1.9)后无法编译 有任何想法吗 ?实际上,任何golang版本升级都会发生此错误,而不仅仅是我在这里提到的版本。 PS 发行时也会遇到相同的错误:go -v -t。/ … 问题答案: 解决方案:您必须先删除以前的golang安装,然后再安装新的go版本 典型输出: 所以就删除它 在安装新版本之前
-
本文向大家介绍Eclipse Debug模式的开启与关闭问题简析,包括了Eclipse Debug模式的开启与关闭问题简析的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 默认情况下,eclipse中右键debug,当运行到设置的断点时会自动跳到debug模式下。但由于我的eclipse环境,从开始一直用到现在,中间包括装、卸各种插件,更换版本,从英文界面导到中文界面又换回来,可以说现在的环境已经臃肿混乱
-
本文向大家介绍spyder 在控制台(console)执行python文件,debug python程序方式,包括了spyder 在控制台(console)执行python文件,debug python程序方式的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 执行: 在IPython console里先cd到test.py所在的文件夹,再run test.py。注意使用的是命令run 而不是命令pytho
-
本文向大家介绍Node.js利用debug模块打印出调试日志的方法,包括了Node.js利用debug模块打印出调试日志的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 前言 大家都知道在node程序开发中时,经常需要打印调试日志。用的比较多的是debug模块,比如express框架中就用到了。下文简单举几个例子进行说明。文中相关代码示例,可在这里找到。 备注:node在0.11.3版本也加入了ut
-
本文向大家介绍node.js中debug模块的简单介绍与使用,包括了node.js中debug模块的简单介绍与使用的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 前言 相信使用node.js的朋友们都知道,一般在nodejs需要进行调试的时候,可以使用console.log()方法来将调试信息输出到控制台,当发布到生产环境的时候,需要将这些调试信息都注释掉,为了方便切换而不需要改动程序代码,可以使用no