��
react-native-localize
A toolbox for your React Native app localization.
Support
| package name | version | react-native version |
|---|---|---|
| react-native-localize | 2.0.0+ | 0.60.0+ |
| react-native-localize | 1.0.0+ | 0.56.0+ |
Setup
$ npm install --save react-native-localize
# --- or ---
$ yarn add react-native-localize
Don't forget to run pod install after that !
��
Manual linking
Because this package targets React Native 0.60.0+, you will probably don't need to link it manually. Otherwise if it's not the case, follow this additional instructions:
��
See manual linking instructions
iOS
Add this line to your ios/Podfile file, then run pod install.
target 'YourAwesomeProject' do
# …
pod 'RNLocalize', :path => '../node_modules/react-native-localize'
end
Android
- Add the following lines to
android/settings.gradle:
include ':react-native-localize'
project(':react-native-localize').projectDir = new File(rootProject.projectDir, '../node_modules/react-native-localize/android')
- Add the implementation line to the dependencies in
android/app/build.gradle:
dependencies {
// ...
implementation project(':react-native-localize')
}
- Add the import and link the package in
MainApplication.java:
import com.zoontek.rnlocalize.RNLocalizePackage; // <- add the RNLocalizePackage import
public class MainApplication extends Application implements ReactApplication {
// …
@Override
protected List<ReactPackage> getPackages() {
@SuppressWarnings("UnnecessaryLocalVariable")
List<ReactPackage> packages = new PackageList(this).getPackages();
// …
packages.add(new RNLocalizePackage());
return packages;
}
// …
}
Windows Support
Because this RNW package targets React Native 0.63.0+, you probably won't need to link it manually. Otherwise if it's not the case, follow these additional instructions. You also need to manually link the module on Windows when using React Native Windows prior to 0.63:
For more information about autolinking and manual linking. Follow the official guide
Web support
This package supports react-native-web. Follow their official guide to configure webpack.
Basic usage example
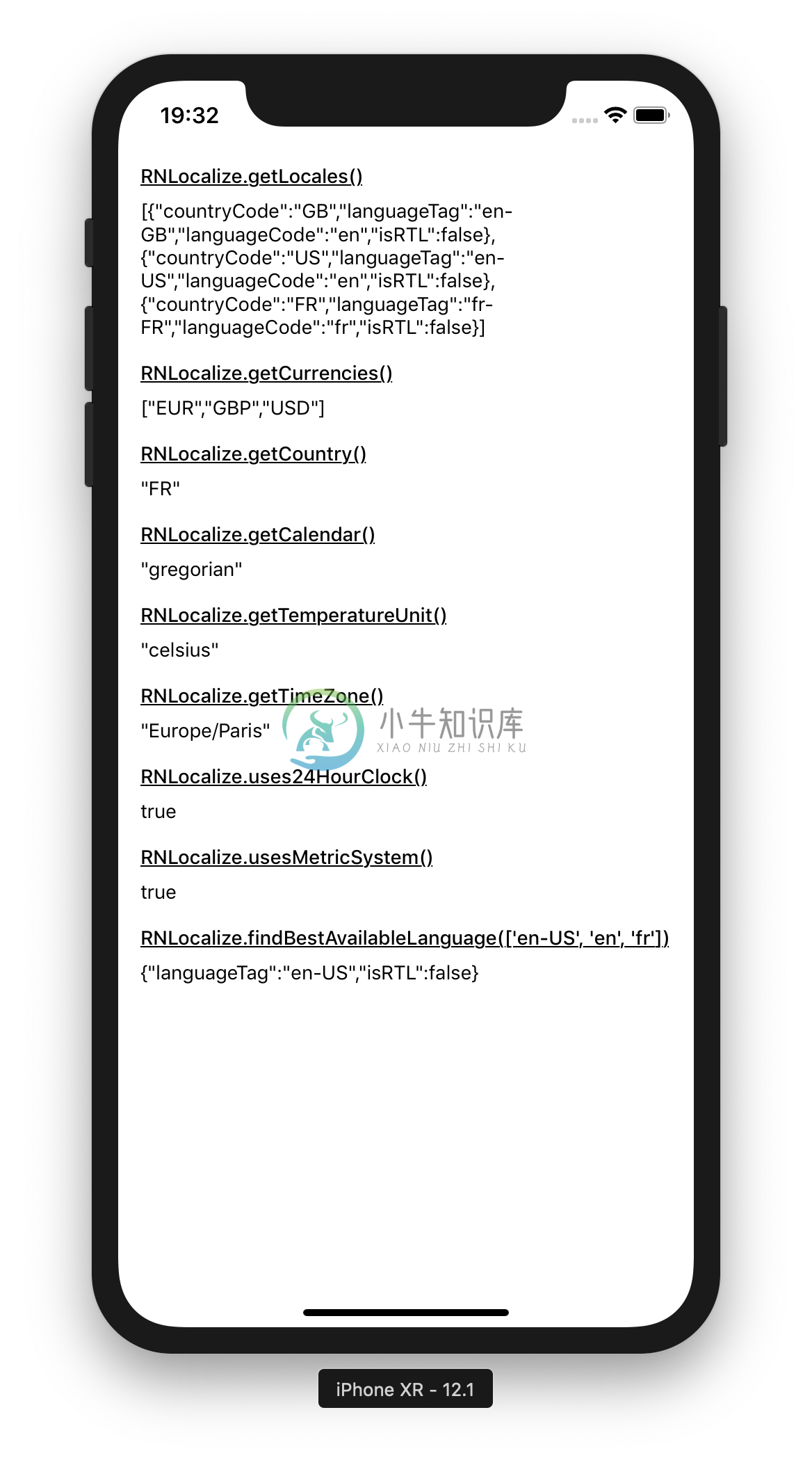
import * as RNLocalize from "react-native-localize";
console.log(RNLocalize.getLocales());
console.log(RNLocalize.getCurrencies());
RNLocalize.addEventListener("change", () => {
// do localization related stuff…
});
API
getLocales()
Returns the user preferred locales, in order.
Method type
type getLocales = () => Array<{
languageCode: string;
scriptCode?: string;
countryCode: string;
languageTag: string;
isRTL: boolean;
}>;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getLocales());
/* -> [
{ countryCode: "GB", languageTag: "en-GB", languageCode: "en", isRTL: false },
{ countryCode: "US", languageTag: "en-US", languageCode: "en", isRTL: false },
{ countryCode: "FR", languageTag: "fr-FR", languageCode: "fr", isRTL: false },
] */
getNumberFormatSettings()
Returns number formatting settings.
Method type
type getNumberFormatSettings = () => {
decimalSeparator: string;
groupingSeparator: string;
};
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getNumberFormatSettings());
/* -> {
decimalSeparator: ".",
groupingSeparator: ",",
} */
getCurrencies()
Returns the user preferred currency codes, in order.
Method type
type getCurrencies = () => Array<string>;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getCurrencies());
// -> ["EUR", "GBP", "USD"]
getCountry()
Returns the user current country code (based on its device locale, not on its position).
Method type
type getCountry = () => string;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getCountry());
// -> "FR"
Note
Devices using Latin American regional settings will return "UN" instead of "419", as the latter is not a standard country code.
getCalendar()
Returns the user preferred calendar format.
Method type
type getCalendar = () => "gregorian" | "japanese" | "buddhist";
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getCalendar());
// -> "gregorian"
getTemperatureUnit()
Returns the user preferred temperature unit.
Method type
type getTemperatureUnit = () => "celsius" | "fahrenheit";
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getTemperatureUnit());
// -> "celsius"
getTimeZone()
Returns the user preferred timezone (based on its device settings, not on its position).
Method type
type getTimeZone = () => string;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.getTimeZone());
// -> "Europe/Paris"
uses24HourClock()
Returns true if the user prefers 24h clock format, false if he prefers 12h clock format.
Method type
type uses24HourClock = () => boolean;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.uses24HourClock());
// -> true
usesMetricSystem()
Returns true if the user prefers metric measure system, false if he prefers imperial.
Method type
type usesMetricSystem = () => boolean;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.usesMetricSystem());
// -> true
usesAutoDateAndTime()
Tells if the automatic date & time setting is enabled on the phone. Android only
Method type
type Option<T> = T | undefined;
type usesAutoDateAndTime = () => Option<boolean>;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.usesAutoDateAndTime()); // true or false
usesAutoTimeZone()
Tells if the automatic time zone setting is enabled on the phone. Android only
Method type
type Option<T> = T | undefined;
type usesAutoTimeZone = () => Option<boolean>;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.usesAutoTimeZone());
addEventListener() / removeEventListener()
Allows you to listen for any localization change.
Methods type
type addEventListener = (type: "change", handler: Function) => void;
type removeEventListener = (type: "change", handler: Function) => void;
Usage example
function handleLocalizationChange() {
console.log(RNLocalize.getLocales());
}
RNLocalize.addEventListener("change", handleLocalizationChange);
// …later (ex: component unmount)
RNLocalize.removeEventListener("change", handleLocalizationChange);
findBestAvailableLanguage()
Returns the best language tag possible and its reading direction (
Method type
type findBestAvailableLanguage = (
languageTags: Array<string>,
) => { languageTag: string; isRTL: boolean } | void;
Usage example
console.log(RNLocalize.findBestAvailableLanguage(["en-US", "en", "fr"]));
// -> { languageTag: "en-US", isRTL: false }
Examples with i18n-js
Browse the files in the /example directory.
How to test your code
Because it's a native module, you might need to mock this package to run your tests flawlessly.
Here is an example for Jest, adapt it to your needs :
// __mocks__/react-native-localize.js
const getLocales = () => [
// you can choose / add the locales you want
{ countryCode: "US", languageTag: "en-US", languageCode: "en", isRTL: false },
{ countryCode: "FR", languageTag: "fr-FR", languageCode: "fr", isRTL: false },
];
// use a provided translation, or return undefined to test your fallback
const findBestAvailableLanguage = () => ({
languageTag: "en-US",
isRTL: false,
});
const getNumberFormatSettings = () => ({
decimalSeparator: ".",
groupingSeparator: ",",
});
const getCalendar = () => "gregorian"; // or "japanese", "buddhist"
const getCountry = () => "US"; // the country code you want
const getCurrencies = () => ["USD", "EUR"]; // can be empty array
const getTemperatureUnit = () => "celsius"; // or "fahrenheit"
const getTimeZone = () => "Europe/Paris"; // the timezone you want
const uses24HourClock = () => true;
const usesMetricSystem = () => true;
const addEventListener = jest.fn();
const removeEventListener = jest.fn();
export {
findBestAvailableLanguage,
getLocales,
getNumberFormatSettings,
getCalendar,
getCountry,
getCurrencies,
getTemperatureUnit,
getTimeZone,
uses24HourClock,
usesMetricSystem,
addEventListener,
removeEventListener,
};
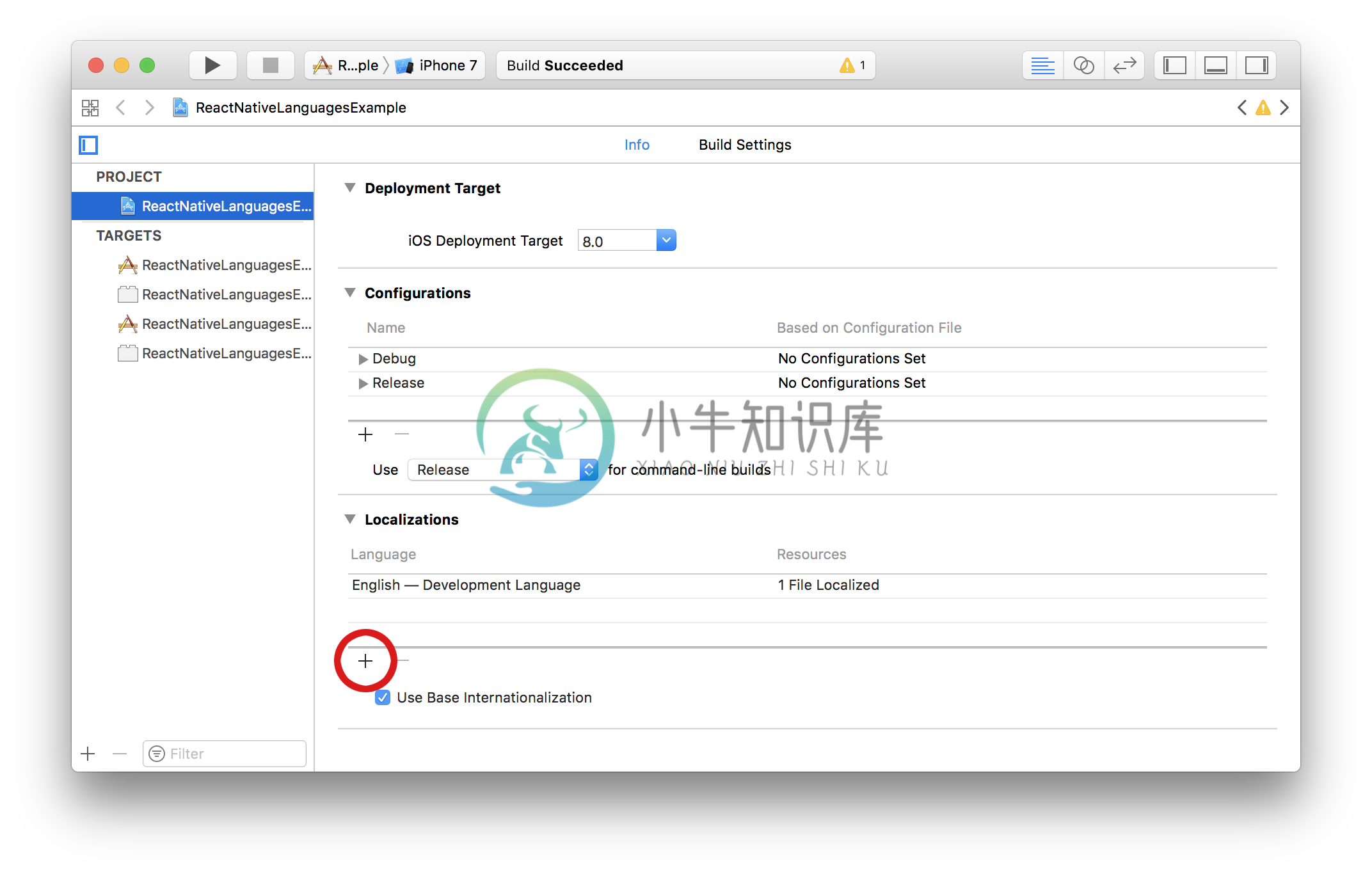
Add project's supported localizations (iOS)
-
React Native多语言切换应该是一个比较常见的需求,具体可以分为两种方式: 1. 识别手机系统语言,app自动加载相应的语言文件; 2. 允许用户在App内手动切换语言,这种情况并不需要保证App语言与手机系统语言一致; 下面就来介绍一下这两种方式如何完成,在介绍之前先声明一下本人目前开发所使用的react native版本是0.61.5,且使用的是react hook语法进行组件的编写。
-
本文向大家介绍react-native 启动React Native Packager,包括了react-native 启动React Native Packager的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 示例 在最新版本的React Native上,无需运行打包程序。它将自动运行。 默认情况下,这将在端口8081上启动服务器。要指定服务器所在的端口
-
百度移动统计SDK支持使用react native框架的H5页面统计,封装好的插件已经在github上开源,相关用法具体请参考:https://github.com/BaiduMobileAnalysis/baidumobstat-react-native。
-
The React Native environment has a lot of little quirks, so this documentation is aimed at helping smooth those over. Please feel free to create issues on GitHub for recommendations and additions to t
-
React Native 可以基于目前大热的开源JavaScript库React.js来开发iOS和Android原生App。而且React Native已经用于生产环境——Facebook Groups iOS 应用就是基于它开发的。 React Native的原理是在JavaScript中用React抽象操作系统原生的UI组件,代替DOM元素来渲染,比如以<View>取代<div>,以<Ima
-
本文向大家介绍react-native setState,包括了react-native setState的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 示例 要在应用程序中更改视图,可以使用setState-这将重新渲染您的组件及其任何子组件。setState在新状态和先前状态之间执行浅表合并,并触发组件的重新呈现。 setState 接受键值对象或返回键值对象的函数 键值对象 功能 使用函数对于基于
-
诸葛io移动统计支持React Native插件,以下为集成方法。 1. 环境准备 1.1. iOS环境 iOS 8.0+ 代码支持iOS8.0的系统 pod 1.0+ iOS系统的集成依赖于cocoaPod工具 1.2. Android环境 Android SDK 16+ 代码支持Android 16+ 1.3. React Native环境 react-native 0.50+ react-n