AWS 2 Tier Architecture setup with AWS CLI - Wordpress application on AWS RDS running MySQL
There are two parts to the setup,
- Part 1 - Setting up the network infrastructure (VPC, Subnets, Security Groups)
- Part 2 - Create & Configure the Database, Web & Load Balancer Instances
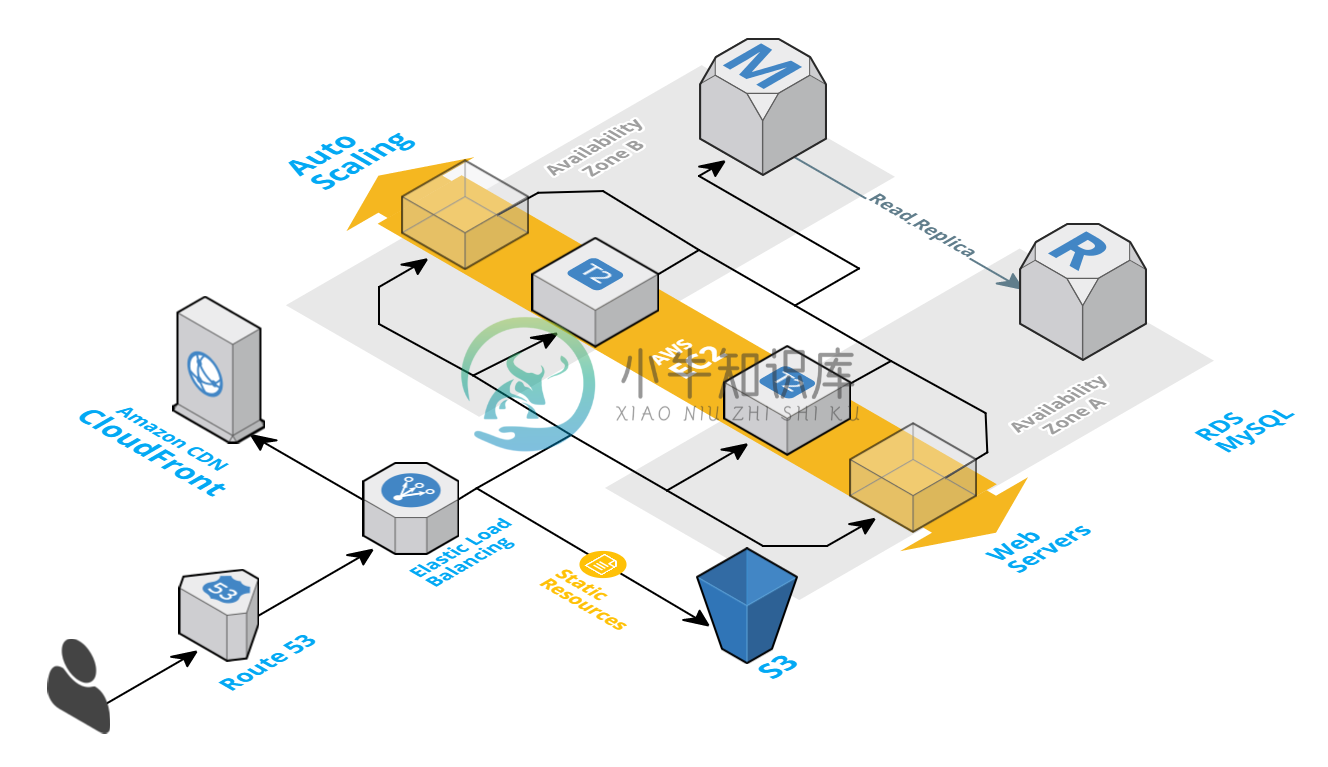 Assuming you have already setup your AWS CLI for Region
Assuming you have already setup your AWS CLI for Region US East (N. Virginia). Lets move forward;
Part 1 - Create VPC, Subnet, Security Group
Setting the AWS Region
export AWS_DEFAULT_REGION=us-east-1
Creating a VPC
Lets create a Virtual Private Cloud - VPC for our setup with /20 range and get our VPC ID using the query parameter and set the output format to text. Its is a good practice to give meaningful name to the AWS resources, Lets call our VPC tmpVPC
vpcID=$(aws ec2 create-vpc \
--cidr-block 10.0.0.0/20 \
--query 'Vpc.VpcId' \
--output text)
Tag the VPC
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$vpcID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=tmpVPC'
Instances launched inside a VPC are invisible to the rest of the internet by default. AWS therefore does not bother assigning them a public DNS name. This can be changed easily by enabling the DNS support as shown below,
aws ec2 modify-vpc-attribute --vpc-id "$vpcID" --enable-dns-support "{\"Value\":true}"
aws ec2 modify-vpc-attribute --vpc-id "$vpcID" --enable-dns-hostnames "{\"Value\":true}"
Check if internet gateway is set. If it wasn't there then do these,
internetGatewayId=$(aws ec2 create-internet-gateway \
--query 'InternetGateway.InternetGatewayId' \
--output text) && echo "$internetGatewayId"
aws ec2 attach-internet-gateway --internet-gateway-id "$internetGatewayId" --vpc-id "$vpcID"
Tag the Internet Gateway
aws ec2 create-tags --resources $internetGatewayId --tags 'Key=Name,Value=tmpVPC-Internet-Gateway'
I have chosen /20 CIDR deliberately to allow us to create different subnets for our db, web instances and reserve some for the future. You might want to choose something else that works better for you. Important: AWS reserves both the first four and the last IP address in each subnet's CIDR block. They're not available for use. The smallest subnet (and VPC) you can create uses a /28 netmask (16 IP addresses), and the largest uses a /16 netmask (65,536 IP addresses). Excellent resources to understand CIDR blocks here & here & my quick help gist
Subnet Reservation for the Database, Web Servers & future
Lets reserve the IP Range to spread across multiple availability zones.
| VPC Range | Availability Zone | Reservation Purpose | IP Ranges | IP Ranges | IP Ranges |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10.0.0.0/20 | |||||
| AZ1 | US-East-1b | 10.0.0.0/21 | |||
| AZ1 | Private - DB Subnet | 10.0.0.0/22 | |||
| AZ1 | 10.0.4.0/22 | ||||
| AZ1 | Web Subnet | 10.0.4.0/23 | |||
| AZ1 | Spare Subnet | 10.0.6.0/23 | |||
| AZ2 | US-East-1c | 10.0.8.0/21 | |||
| AZ2 | Private - DB Subnet | 10.0.8.0/22 | |||
| AZ2 | 10.0.12.0/22 | ||||
| AZ2 | Web Subnet | 10.0.12.0/23 | |||
| AZ2 | Spare Subnet | 10.0.14.0/23 |
After creating all the subnets, It should look something like this,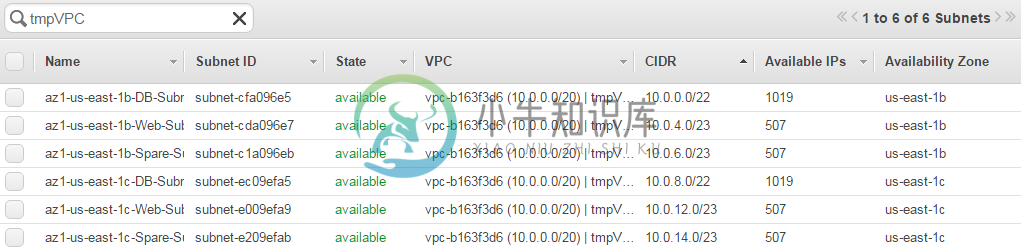
Creating subnets for the DB & Web Servers in AZ1
USEast1b_DbSubnetID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id "$vpcID" --cidr-block 10.0.0.0/22 --availability-zone us-east-1b --query 'Subnet.SubnetId' --output text)
USEast1b_WebSubnetID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id "$vpcID" --cidr-block 10.0.4.0/23 --availability-zone us-east-1b --query 'Subnet.SubnetId' --output text)
USEast1b_SpareSubnetID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id "$vpcID" --cidr-block 10.0.6.0/23 --availability-zone us-east-1b --query 'Subnet.SubnetId' --output text)
Tag the subnet ID's for AZ1
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$USEast1b_DbSubnetID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=az1-us-east-1b-DB-Subnet'
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$USEast1b_WebSubnetID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=az1-us-east-1b-Web-Subnet'
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$USEast1b_SpareSubnetID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=az1-us-east-1b-Spare-Subnet'
Creating subnets for the DB & Web Servers in AZ2
USEast1c_DbSubnetID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id "$vpcID" --cidr-block 10.0.8.0/22 --availability-zone us-east-1c --query 'Subnet.SubnetId' --output text)
USEast1c_WebSubnetID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id "$vpcID" --cidr-block 10.0.12.0/23 --availability-zone us-east-1c --query 'Subnet.SubnetId' --output text)
USEast1c_SpareSubnetID=$(aws ec2 create-subnet --vpc-id "$vpcID" --cidr-block 10.0.14.0/23 --availability-zone us-east-1c --query 'Subnet.SubnetId' --output text)
Tag the subnet ID's for AZ2
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$USEast1c_DbSubnetID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=az1-us-east-1c-DB-Subnet'
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$USEast1c_WebSubnetID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=az1-us-east-1c-Web-Subnet'
aws ec2 create-tags --resources "$USEast1c_SpareSubnetID" --tags 'Key=Name,Value=az1-us-east-1c-Spare-Subnet'
Configuring the Route Table
Each subnet needs to have a route table associated with it to specify the routing of its outbound traffic. By default every subnet inherits the default VPC route table which allows for intra-VPC communication only.
The following adds a route table to our subnet that allows traffic not meant for an instance inside the VPC to be routed to the internet through our earlier created internet gateway.
routeTableID=$(aws ec2 create-route-table --vpc-id "$vpcID" --query 'RouteTable.RouteTableId' --output text)
aws ec2 create-route --route-table-id "$routeTableID" --destination-cidr-block 0.0.0.0/0 --gateway-id "$internetGatewayId"
aws ec2 associate-route-table --route-table-id "$routeTableID" --subnet-id "$USEast1b_WebSubnetID"
aws ec2 associate-route-table --route-table-id "$routeTableID" --subnet-id "$USEast1c_WebSubnetID"
Creating a security group for the Web Servers
- Group Name -
webSecGrp - Description -
My Web Security Group
webSecGrpID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group --group-name webSecGrp \
--description "Security Group for Web servers" \
--vpc-id "$vpcID" \
--output text)
Add a rule that allows inbound SSH, HTTP, HTTP traffic ( from any source )
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id "$webSecGrpID" --protocol tcp --port 22 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id "$webSecGrpID" --protocol tcp --port 80 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress --group-id "$webSecGrpID" --protocol tcp --port 443 --cidr 0.0.0.0/0
Interesting reading here about why we need to use security group ID instead of name; AWS Documentation & Github Bug Report
When you specify a security group for a nondefault VPC to the CLI or the API actions, you must use the security group ID and not the security group name to identify the security group.
Part 2 - Create & Configure the Database, Web & Load Balancer Instances
Creating the RDS Instance
Pre-Requisites
- DB Subnet - The RDS instances requires the db subnet group to span across (atleast two) availability zones
- DB Security Group - Security group all allows other EC2 instances to connect with this RDS instance
Create the DB Subnet
Creates a new DB subnet group. DB subnet groups must contain at least one subnet in at least two AZs in the region.
aws rds create-db-subnet-group \
--db-subnet-group-name "mysqlDBSubnet" \
--db-subnet-group-description "Subnet group for my databases instances" \
--subnet-ids "$USEast1b_DbSubnetID" "$USEast1c_DbSubnetID"
Creating a Security Group for RDS Database (running MySQL)
- Group Name -
dbSecGrp - Description -
My Database Security Group
dbSecGrpID=$(aws ec2 create-security-group \
--group-name dbSecGrp \
--description "Security Group for database servers" \
--vpc-id "$vpcID" \
--output text)
Add a rule that allows inbound MySQL from Webservers (in our Web Security Group)
aws ec2 authorize-security-group-ingress \
--group-id "$dbSecGrpID" \
--protocol tcp \
--port 3306 \
--source-group \
"$webSecGrpID"
Create a DB parameter group to monitor CRUD
aws rds create-db-parameter-group \
--db-parameter-group-name myParamGrp \
--db-parameter-group-family MySQL5.6 \
--description "My new parameter group"
aws rds modify-db-parameter-group --db-parameter-group-name myParamGrp --parameters "ParameterName=general_log, ParameterValue=ON, Description=logParameter,ApplyMethod=immediate"
Start the RDS - MySQL Instance
rdsInstID=rds-mysql-inst01
aws rds create-db-instance \
--db-instance-identifier "$rdsInstID" \
--allocated-storage 5 \
--db-instance-class db.t2.micro \
--no-multi-az \
--no-auto-minor-version-upgrade \
--availability-zone us-east-1b \
--vpc-security-group-ids "$dbSecGrpID" \
--db-subnet-group-name "mysqldbsubnet" \
--engine mysql \
--port 3306 \
--master-username dbuser \
--master-user-password dbuserpass \
--db-parameter-group-name myParamGrp \
--db-name wpdb \
--backup-retention-period 3
aws rds modify-db-instance --db-instance-identifier "$rdsInstID" --db-parameter-group-name myParamGrp
Refer:
- [1] https://www.linux.com/blog/introduction-aws-command-line-tool-part-2
- [2] http://docs.aws.amazon.com/cli/latest/reference/rds/create-db-instance.html
- [3] Cloning RDS Instances for Testing
Create the Web Servers
Create the SSH Keys & boot-strap the binaries
aws ec2 create-key-pair --key-name webKey --query 'KeyMaterial' --output text > webKey.pem
chmod 400 webKey.pem
cat >> userDataScript <<EOF
#!/bin/bash
set -e -x
# Setting up the HTTP server
yum update -y
yum install -y httpd php php-mysql mysql
service httpd start
chkconfig httpd on
groupadd www
usermod -a -G www ec2-user
# Download wordpress site & move to http
cd /var/www/
curl -O https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz && tar -zxf latest.tar.gz
rm -rf /var/www/html
mv wordpress /var/www/html
# Set the permissions
chown -R root:www /var/www
chmod 2775 /var/www
find /var/www -type d -exec chmod 2775 {} +
find /var/www -type f -exec chmod 0664 {} +
# SE Linux permissive
# needed to make wp connect to DB over newtork
setsebool -P httpd_can_network_connect=1
setsebool httpd_can_network_connect_db on
systemctl restart httpd
# Remove below file after testing
echo "<?php phpinfo(); ?>" > /var/www/html/phpinfo.php
EOF
Start the Web Instance
instanceID=$(aws ec2 run-instances \
--image-id ami-2051294a \
--count 1 \
--instance-type t2.micro \
--key-name wpKey \
--security-group-ids "$webSecGrpID" \
--subnet-id "$webSubnetID" \
--user-data file://userDataScript \
--associate-public-ip-address \
--query 'Instances[0].InstanceId' \
--output text)
instanceUrl=$(aws ec2 describe-instances \
--instance-ids "$instanceID" \
--query 'Reservations[0].Instances[0].PublicDnsName' \
--output text)
# Get the IP address of the running instance:
ip_address=$(aws ec2 describe-instances \
--instance-ids "$instanceID" \
--output text --query 'Reservations[*].Instances[*].PublicIpAddress')
Create the Elastic Load Balancer
Ref: https://aws.amazon.com/articles/1636185810492479
aws elb create-load-balancer \
--load-balancer-name my-load-balancer \
--listeners "Protocol=HTTP,LoadBalancerPort=80,InstanceProtocol=HTTP,InstancePort=80" \
--subnets "$USEast1c_WebSubnetID" \
--security-groups "$webSecGrpID"
Apache Workbench Results
[root@ip-172-31-55-78 ec2-user]# ab -n 20000 -c 30 -k http://xx.xx.xx.xx/
This is ApacheBench, Version 2.3 <$Revision: 1430300 $>
Copyright 1996 Adam Twiss, Zeus Technology Ltd, http://www.zeustech.net/
Licensed to The Apache Software Foundation, http://www.apache.org/
Benchmarking xx.xx.xx.xx (be patient)
Completed 2000 requests
Completed 4000 requests
Completed 6000 requests
Completed 8000 requests
Completed 10000 requests
Completed 12000 requests
Completed 14000 requests
Completed 16000 requests
Completed 18000 requests
Completed 20000 requests
Finished 20000 requests
Server Software: Apache/2.4.6
Server Hostname: xx.xx.xx.xx
Server Port: 80
Document Path: /
Document Length: 11951 bytes
Concurrency Level: 30
Time taken for tests: 4684.053 seconds
Complete requests: 20000
Failed requests: 5641
(Connect: 0, Receive: 0, Length: 5641, Exceptions: 0)
Write errors: 0
Keep-Alive requests: 0
Total transferred: 349703793 bytes
HTML transferred: 344441217 bytes
Requests per second: 4.27 [#/sec] (mean)
Time per request: 7026.079 [ms] (mean)
Time per request: 234.203 [ms] (mean, across all concurrent requests)
Transfer rate: 72.91 [Kbytes/sec] received
Connection Times (ms)
min mean[+/-sd] median max
Connect: 1 2 49.6 1 7014
Processing: 356 7013 3842.2 5067 43302
Waiting: 0 6040 3317.2 4332 40634
Total: 357 7014 3842.9 5069 43303
Percentage of the requests served within a certain time (ms)
50% 5069
66% 7997
75% 9596
80% 10332
90% 12134
95% 13574
98% 16122
99% 18490
100% 43303 (longest request)
[root@ip-172-31-55-78 ec2-user]#
-
我想知道使用AWS OpsWorks与AWS Beanstalk和AWS CloudFormation的优缺点是什么? 我感兴趣的是一个可以自动伸缩的系统,它可以处理任意数量的并发web请求(从每分钟1000个请求到1000万rpm),包括一个可以自动伸缩的数据库层。 理想情况下,我希望有效地共享一些硬件资源,而不是为每个应用程序提供单独的实例。在过去,我主要使用EC2实例RDS Cloudtop
-
介绍如何在AWS上获取在云联壹云平台需要使用的配置参数。 获取AWS的访问密钥 使用AWS主账号(或拥有AdministratorAccess管理权限的子账号)登录AWS管理控制台,单击 “IAM” 菜单项,进入IAM控制面板页面。 单击左侧菜单栏 “用户” 菜单项,进入用户管理列表,单击用户名名称项,进入指定用户详情页面。注意需要选择有足够管理权限的用户。 单击“安全证书”页签。 单击 “创建访
-
AWS Global Infrastructure AWS Global Cloud - A single global cloud, is made up of devices and Services in many regions. AWS Region - A physical location around the world where Amazon have equipment(de
-
A collection of bash shell scripts for automating various tasks with Amazon Web Services using the AWS CLI and jq. https://github.com/swoodford/aws Table of contents Why Getting Started What's Include
-
我使用的是AWS SQS服务,很难定义SQS队列上的权限。在我的设置中,我使用的是AWS Lambda服务,当一个对象被推到S3存储桶上时会触发该服务。 然而,让我简短地提问,这是我想要实现的: 对象被推送到S3存储桶中 正如您可以从前面的用例中看到的,我希望我的AWS Lambda方法是唯一可以向SQS队列发送消息的应用程序。我试图设置一个原则和一个条件“sourceArn”。但是它们都不起作用
-
我有一个Powershell Lambda,我希望通过AWS CDK部署它,但在运行时遇到问题。 通过手动发布AWSPowerShellLambda部署Powershell可以: 但是,与CDK一起部署的同一脚本不会记录到CloudWatch日志,即使它具有以下权限: powershell脚本当前仅包含以下行,在CLI上由Publish AWSPowerShellLambda部署时可以工作: 注意

