NAME
svsh - Process supervision shell for daemontools/perp/s6/runit
SYNOPSIS
# from the command line
$ svsh --suite perp --basedir /etc/services
# run one specific command and exit
$ svsh --suite runit --basedir /var/services restart nginx
DESCRIPTION
svsh is a command line shell for process supervision suites of the daemontools family. Currently, it supportsdaemontools, perp, s6and runit. It provides a unified interface allowing easy inspectionand manipulation of services (i.e. processes) managed by supported supervision suites.
svsh does not require any configurations or changes to your suite's service directories;just point it at a base directory and you immediately get a usable shell, listing allservices and their statuses, and accepting commands to perform on them.
The shell provides a very simple syntax that is easy to remember, far simpler than theparticular syntax of the underlying supervision suite. Instead of having to executeperpctl -b /services q nginx to restart an nginx service running from /services/nginx,just execute restart nginx. Couldn't be simpler. Want to send a HUP signal to allservices whose names begin with "worker"? just execute signal hup worker*.
svsh is inspired by supervisord's supervisorctl shell. I'veattempted to provide a similar syntax and feature set.
OPTIONS
-s, --suite
The supervision suite managing the base directory. Either daemontools, perp,s6 or runit. If not provided, the SVSH_SUITE environment variable willbe checked. An error will be raised if no suite is defined.
-d, --basedir
Base directory of services supervised by the supervision suite. If not provided,the SVSH_BASE environment variable will be checked, and if not set, the defaultbase directory of the selected suite will be used. Check the documentation ofthe specific suite class for its default directory. If no directory is found,an error will be raised.
-b, --bindir
If the supervision suite's tools are not in the environment PATH variable,you can provide the directory where they are located (e.g. /usr/local/bin).
-c, --collapse
Collapse multi-process services to one line in status. See "COLLAPSE"for more details. This can be changed from inside the shell too.
COMMANDS
The following commands are provided by svsh. Note that some suites do notsupport all commands.
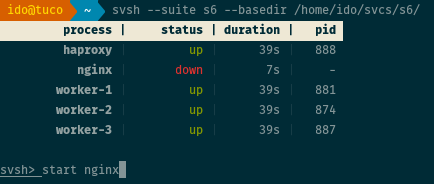
status
Prints a list of all services, their statuses (up, down, etc.), uptimes (ordowntimes) and process IDs. This command is automatically executed uponinitialization of the shell.
start service, ...
Starts a list of one or more services, if they are not already up.
svsh> start nginx haproxy
stop service, ...
Stops a list of one or more services. The services stopped will not be restarted.
svsh> stop nginx haproxy
restart service, ...
Restarts a list of one or more services. Generally, this means sending a QUIT signalto the services, which should cause them to shutdown and be restarted by thesupervisor.
svsh> restart nginx haproxy
signal sig service, ...
Send a UNIX signal to a list of one or more services. The name of the signal canbe lowercase or uppercase, and may include the prefix "SIG".
svsh> signal term nginx
svsh> signal SIGUSR1 haproxy
rescan
Alias: update.
Causes the supervision suite to rescan the base directory for new or removed services.
fg service
"Moves" a service to the foreground, so that its output streams (at least standard output,possibly standard error) are printed on screen. In reality, it determines where the process'log file is located, and tails it with tail -f. See "LOG INSPECTION" for more details, as thisis a complicated subject.
svsh> fg nginx
terminate
Alias: shutdown.
Terminate the supervision suite. This will cause all services managed by the supervisor toterminate as well.
toggle option
Toggles a shell option on or off. Currently, only the collapse option is supported. Thestatus command will be automatically called after toggling the option.
svsh> toggle collapse
help [ command ]
Prints help information. Can also provide information about specific commands.
svsh> help signal
quit
Alias: exit.
Quits the shell.
ADVANCED FEATURES AND IMPORTANT INFORMATION
LOG INSPECTION
All of the supported supervision suites do not enforce a logging scheme on managedservices. While all of them provide a logging tool (daemontools provides multilog,perp provides tinylog and sissylog; s6 provides s6-log; runitprovides svlogd), none of them enforce their usage. It is actually not uncommonamong users of these suites to use a logging tool provided by one suite for servicesmanaged by another one. This means it is hard for an external program such as svshto determine where log files are stored, if at all.
Currently, svsh will attempt to find the log file of a service by checking thepid of the associated log process, and if (and only if) that process is one of thesupported loggers (multilog, tinylog, s6-log or svlogd), it will try to find thefile descriptor used by that process under /proc/<pid>/fd. As long as your servicesare being logged by one of these tools, svsh should be able to tail their logfiles when the fg command is used. However, if the log file is being rotatedwhile it is being tailed, behavior is currently undefined (will probably stop working untilthe command is run again).
HISTORY
svsh provides bash-like history so you can use your up arrow key to cycle back throughpast commands, or use Ctrl+R to search your history. The history file is saved underthe name .svsh_history under the home directory of the running user (~/.svsh_history).
Note that history is saved only when the shell is properly terminated, such as with thequit command. Ctrl+C will not trigger history saving.
It is highly recommended to install Term::ReadLine::Gnu for proper history support.
AUTOCOMPLETION
svsh provides autocompletion for all its commands. Tap the tab key at any moment whiletyping in commands and arguments, and svsh will attempt to autocomplete your currentword, or display a list if multiple options are available. Again, Term::ReadLine::Gnuis recommended for better autocompletion.
WILDCARDS
svsh makes it easy to manipulate multiple services at once. Wildcards are supportedby the start, stop, restart and signal commands. If, for example, you haveseveral services whose names start with "worker", you can stop them all by executingstop worker*. Wildcards are also supported at the beginning of the name, sosignal term *d will send a TERM signal to all services whose names end with "d".
svsh> status
process | status | duration | pid
worker-1 | up | 9813s | 25984
worker-2 | up | 9813s | 25976
worker-3 | up | 4393s | 2990
svsh> stop worker*
svsh> status
process | status | duration | pid
worker-1 | down | 2s | -
worker-2 | down | 2s | -
worker-3 | down | 2s | -
COLLAPSE
Often times you would like to run a certain service with X number of identical processes.None of the supervision suites have any mechanism to allow this (none that Iknow of at least), apart from creating identical copies of a service directory for everyprocess needed. While svsh can't help you with that, it provides a nice feature for collapsingthese identical services in the output of the "status" command to just one line. This canbe very useful with lots of multi-process services.
Currently, svsh determines multi-process services if their names are postfixed with a dashand a number. For example, if you have a service called worker that you need 3 processesof which to run, you can create worker-1, worker-2 and worker-3 service directories.If the collapse option is on, svsh will collapse all of these intojust one line, under the name status.
svsh> status
process | status | duration | pid
worker-1 | up | 9813s | 25984
worker-2 | up | 9813s | 25976
worker-3 | up | 4393s | 2990
svsh> toggle collapse
process | status | duration | pid
worker | 3 up | 9850s | -
This feature combines well with the "WILDCARDS" feature.
Hopefully, future versions will find a more generic way of identifying multi-process services.
CONFIGURATION AND ENVIRONMENT
svsh requires no configuration files or environment variables.
DEPENDENCIES
svsh depends on the following modules:
For proper history and autocompletion support, and generally a betterworking shell, it is recommended to install Term::ReadLine::Gnu.
INCOMPATIBILITIES
None reported.
BUGS AND LIMITATIONS
No bugs have been reported.
Please report any bugs or feature requests tobug-Svsh@rt.cpan.org, or through the web interface athttp://rt.cpan.org/NoAuth/ReportBug.html?Queue=Svsh.
SUPPORT
You can find documentation for this module with the perldoc command.
perldoc svsh
You can also look for information at:
RT: CPAN's request tracker
AnnoCPAN: Annotated CPAN documentation
CPAN Ratings
Search CPAN
AUTHOR
Ido Perlmuter .
Thanks to the guys at the supervision mailing list,especially Colin Booth, for helping out with suggestions and information.
LICENSE AND COPYRIGHT
Copyright (c) 2015, Ido Perlmuter ido at ido50 dot net.
This module is free software; you can redistribute it and/ormodify it under the same terms as Perl itself, either version5.8.1 or any later version. See perlartisticand perlgpl.
The full text of the license can be found in theLICENSE file included with this module.
DISCLAIMER OF WARRANTY
BECAUSE THIS SOFTWARE IS LICENSED FREE OF CHARGE, THERE IS NO WARRANTYFOR THE SOFTWARE, TO THE EXTENT PERMITTED BY APPLICABLE LAW. EXCEPT WHENOTHERWISE STATED IN WRITING THE COPYRIGHT HOLDERS AND/OR OTHER PARTIESPROVIDE THE SOFTWARE "AS IS" WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EITHEREXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, BUT NOT LIMITED TO, THE IMPLIEDWARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY AND FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. THEENTIRE RISK AS TO THE QUALITY AND PERFORMANCE OF THE SOFTWARE IS WITHYOU. SHOULD THE SOFTWARE PROVE DEFECTIVE, YOU ASSUME THE COST OF ALLNECESSARY SERVICING, REPAIR, OR CORRECTION.
IN NO EVENT UNLESS REQUIRED BY APPLICABLE LAW OR AGREED TO IN WRITINGWILL ANY COPYRIGHT HOLDER, OR ANY OTHER PARTY WHO MAY MODIFY AND/ORREDISTRIBUTE THE SOFTWARE AS PERMITTED BY THE ABOVE LICENCE, BELIABLE TO YOU FOR DAMAGES, INCLUDING ANY GENERAL, SPECIAL, INCIDENTAL,OR CONSEQUENTIAL DAMAGES ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USETHE SOFTWARE (INCLUDING BUT NOT LIMITED TO LOSS OF DATA OR DATA BEINGRENDERED INACCURATE OR LOSSES SUSTAINED BY YOU OR THIRD PARTIES OR AFAILURE OF THE SOFTWARE TO OPERATE WITH ANY OTHER SOFTWARE), EVEN IFSUCH HOLDER OR OTHER PARTY HAS BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OFSUCH DAMAGES.
-
Virus.Win32.AutoRun.cp(SVSH0ST.EXE)病毒的分析解决 作者:佚名 来源:不详 发布时间:2007-7-19 20:32:48 添加项禁止修改主页 [HKCU\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Internet Explorer\Control Panel] "HomePage"=dword:00000001 其他行为: 修改 .