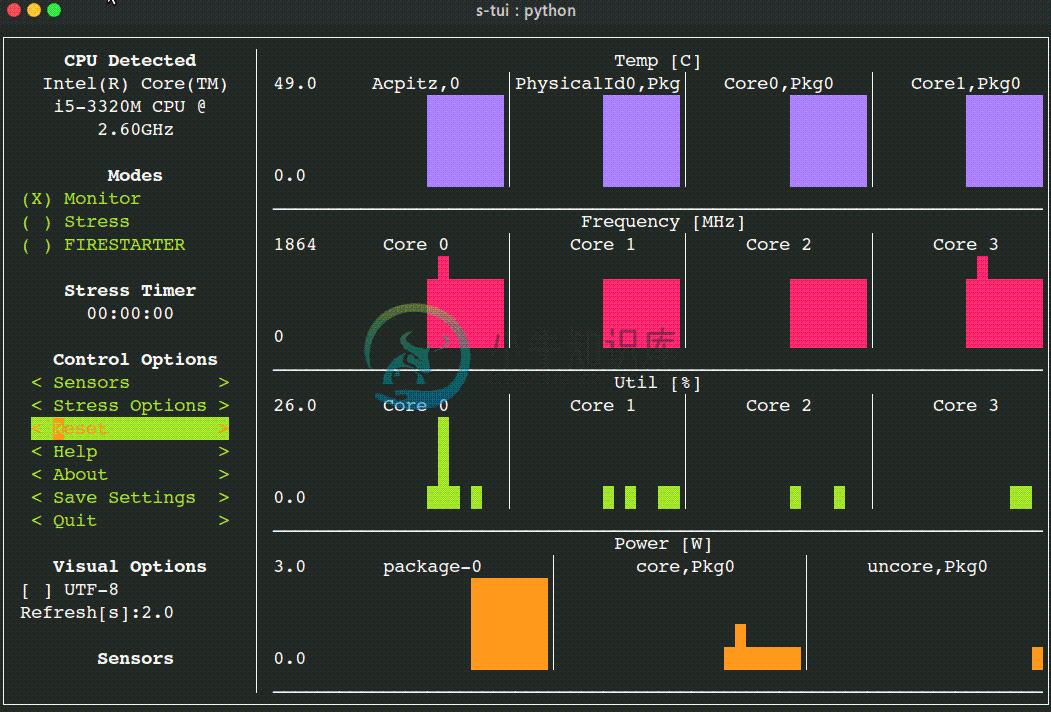
The Stress Terminal UI: s-tui
Stress-Terminal UI, s-tui, monitors CPU temperature, frequency, power and utilization in a graphical way from the terminal.
Screenshot
Table of Contents
- The Stress Terminal UI: s-tui
What it does
- Monitoring your CPU temperature/utilization/frequency/power
- Shows performance dips caused by thermal throttling
- Requires no X-server
- Built in options for stressing the CPU (stress/stress-ng/FIRESTARTER)
Usage
s-tui
Simple installation
pip (x86 + ARM)
The most up to date version of s-tui is available with pip.
Install with:
pip install s-tui --user
(This usuall creates an executable in ~/.local/bin/ dir. Make sure it is in your PATH)
To install as root
sudo pip install s-tui
You might need to install python-dev first
Installation in virtualenv with pipsi:
pipsi install s-tui
More installation methods
Ubuntu (18.10 and newer)
sudo apt install s-tui
Ubuntu (18.04, 16.04)
A PPA is available but is not up to date
sudo add-apt-repository ppa:amanusk/python-s-tui
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-s-tui
Arch Linux, Manjaro
s-tui is in the Arch repository:
sudo pacman -S s-tui
s-tui-git follows the master branch, maintained by @MauroMombelli
Install it with:yay -S s-tui-git
OpenSUSE
sudo zypper install s-tui
Fedora
s-tui is in the Fedora repository:
sudo dnf install s-tui
Options
TUI interface:
The side bar houses the controls for the displayed graphs.
At the bottom, all sensors reading are presented in text form.
* Use the arrow keys or 'hjkl' to navigate the side bar
* Toggle between stressed and regular operation using the radio buttons in 'Modes'.
* If you wish to alternate stress defaults, you can do it in <Stress options>
* Select graphs to display in the <Graphs> menu
* Select summaries to display in the <Summaries> menu
* Use the <Reset> button to reset graphs and statistics
* If your system supports it, you can use the UTF-8 button to get a smoother graph
* Save your current configuration with the <Save Settings> button
* Press 'q' or the <Quit> button to quit
* Run `s-tui --help` to get this message and additional cli options
optional arguments:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-d, --debug Output debug log to _s-tui.log
--debug-file DEBUG_FILE
Use a custom debug file. Default: _s-tui.log
-dr, --debug_run Run for 5 seconds and quit
-c, --csv Save stats to csv file
--csv-file CSV_FILE Use a custom CSV file. Default: s-tui_log_<TIME>.csv
-t, --terminal Display a single line of stats without tui
-j, --json Display a single line of stats in JSON format
-nm, --no-mouse Disable Mouse for TTY systems
-v, --version Display version
-tt T_THRESH, --t_thresh T_THRESH
High Temperature threshold. Default: 80
Dependencies
s-tui is a great for monitoring. If you would like to stress your system, install stress. Stress options will then show up in s-tui (optional)
sudo apt-get install stress
Configuration
s-tui is a self-contained application which can run out-of-the-box and doesn't need config files to drive its core features. However, additional features like running scripts when a certain threshold has been exceeded (e.g. CPU temperature) does necessitate creating a config directory. This directory will be made in ~/.config/s-tui by default.
Saving a configuration
Selecting <Save Settings> will save the current configuration to ~/.config/s-tui/s-tui.conf. If you would like to restore defaults, simply remove the file.
Adding threshold scripts
s-tui gives you the ability to run arbitrary shell scripts when a certain threshold is surpassed, like your CPU temperature. You can define this custom behaviour by adding a shell file to the directory ~/.config/s-tui/hooks.d with one of the following names, depending on what threshold you're interesting in reacting to:
tempsource.sh: triggered when the CPU temperature threshold is exceeded
If s-tui finds a script in the hooks directory with the name of a source it supports, it will run that script every 30 seconds as long as the current value of the source remains above the threshold.
Note that at the moment only CPU temperature threshold hooks are supported.
Run from source code
Start by cloning the repository
git clone https://github.com/amanusk/s-tui.git
cd s-tui
Install required dependencies as [root] or as (local user)
[sudo] pip install urwid (--user)
[sudo] pip install psutil (--user)
Install stress (optional)
sudo apt-get install stress
Run the .py file
python -m s_tui.s_tui
OPTIONAL integration of FIRESTARTER (via submodule, does not work on all systems)
FIRESTARTER is a great tool to stress your system to the extreme.If you would like, you can integrate FIRESTARTER submodule into s-tui.
To build FIRESTARTER:
git submodule init
git submodule update
cd ./FIRESTARTER
./code-generator.py
make
Once you have completed these steps, you can either:
- Install FIRESTARTER to make it accessible to s-tui, e.g make a soft-link to FIRESTARTER in /usr/local/bin.
- Run s-tui from the main project directory with
python -m s_tui.s_tui
An option to run FIRESTARTER will then be available in s-tui
Compatibility
s-tui uses psutil to probe hardware information. If your hardware is not supported, you might not see all the information.
s-tui uses urwid as a graphical engine. urwid only works with UNIX-like systems
- Power read is supported on Intel Core CPUs of the second generation and newer (Sandy Bridge)and on AMD Family 17h CPUs through the amd_energy driver.
- s-tui tested to run on Raspberry-Pi 4,3,2,1
FAQ
Q: How is this different from htop?
A: s-tui is not a processes monitor like htop. The purpose is to monitor your CPU statistics and have an option to test the system under heavy load. (Think AIDA64 stress test, not task manager).
Q: I am using the TTY with no X server and s-tui crashes on start
A: By default, s-tui is handles mouse inputs. This causes some systems to crash. Try running s-tui --no-mouse
Q: I am not seeing all the stats in the sidebar.
A: The sidebar is scrollable, you can scroll down with DOWN or j or scroll to the bottom with PG-DN or G. You might consider also decreasing the size of the font that you use in your terminal.:)
Contributing
New issues and Pull Requests are welcome :)
If you notice a bug, please report it as a new issue, using the provided template.
To open a Pull Request, please see CONTRIBUTING for more information.
Tip
If you like this work, please star in on GitHub.
BTC: 1PPhYgecwvAN7utN2EotgTfy2mmLqzF8m3
ETH: 0xc169699A825066f2F07E0b29C4082094b32A3F3e
-
gdb tui命令汇总 1.启动gdb时开启tui gdb -tui 2.切换tui模式 C-x a或C-x C-a 3.tui模式下切换窗口焦点 C-x o 下一窗口 focus src 或fs s 源码窗 focus cmd 或fs c 命令窗 focus asm 或fs a 汇编窗 focus regs或fs r 寄存器窗 focus src 或fs s
-
下载脚本安装pip wget https://bootstrap.pypa.io/get-pip.py python3 get-pip.py 安装s-tui yum install python-pip stress pip install --upgrade pip yum install -y python-devel pip install s-tui
-
描述 (Description) 这不是一个功能。 这是正则表达式替换运算符。 根据PATTERN中指定的正则表达式,数据将替换为REPLACE。 与m //一样,分隔符由s后面的第一个字符定义。 语法 (Syntax) 以下是此函数的简单语法 - s/PATTERN/REPLACE/ 返回值 (Return Value) 此函数在失败时返回0,并在成功时返回替换次数。 例子 (Example)
-
描述 (Description) 字符类\S匹配任何非空白字符。 例子 (Example) 以下示例显示了预定义字符类匹配的用法。 package com.wenjiangs; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class PredefinedCharacterClassDemo {
-
描述 (Description) 字符类\s匹配任何空格字符。 例子 (Example) 以下示例显示了预定义字符类匹配的用法。 package com.wenjiangs; import java.util.regex.Matcher; import java.util.regex.Pattern; public class PredefinedCharacterClassDemo { p
-
问题内容: 在我上大学的这个Java项目中,我遇到一种情况,当前正在使用 其中msgs是一个链接的阻止队列,通过 但是,我想使用一个ObjectInputStream和一个ObjectOutputStream。我已经在构造函数中初始化了它们,并在构造它后刷新了ObjectOutputStream,我读到某个地方必须这样做。 我想同时发送Strings和另一个Object类型,通过网络将其称为gam
-
_ _ _____ | | | |/ ____|| | __ _ _ __ __ ___ _____| | (___ | | / _` | '__/ _` \ \ / / _ \ |\___ \ | |___| (_| | | | (_| |\ V / __/
-
引言 MVC时代:在MVC模型里,更关注的Model的不变,业务需求通常是Model不变,同时有多个对Model的不同显示,即View。所以,在MVC模型里,Model不依赖于View,但是View是依赖于Model的。不仅如此,因为有一些业务逻辑在View里实现了,导致要更改View也是比较困难的,至少那些业务逻辑是无法重用的。 MVP时代:在MVP里,Presenter完全把Model和Vie