Junit4 参数化测试
精华
小牛编辑
105浏览
2023-03-14
1 参数化测试的介绍
自定义流道参数化实现参数化测试。运行参数化测试类时,将为测试方法和测试数据元素的叉积创建实例。
例如,要测试斐波那契函数,请编写:
例如,要测试斐波那契函数,请编写:
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
/**
* 小牛知识库网: https://www.xnip.cn
*/
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
private int fInput;
private int fExpected;
public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected) {
this.fInput = input;
this.fExpected = expected;
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(fExpected, Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
}
/**
* 小牛知识库网: https://www.xnip.cn
*/
public class Fibonacci {
public static int compute(int n) {
int result = 0;
if (n <= 1) {
result = n;
} else {
result = compute(n - 1) + compute(n - 2);
}
return result;
}
}
FibonacciTest的每个实例都将使用二元参数构造函数和方法中的数据值构造 @Parameters 。
2 使用@Parameter进行字段注入而不是构造函数
也可以将数据值直接注入字段中,而无需使用@Parameter批注的构造函数,如下所示:
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameter;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
/**
* 小牛知识库网: https://www.xnip.cn
*/
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameters
public static Collection<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
@Parameter // first data value (0) is default
public /* NOT private */ int fInput;
@Parameter(1)
public /* NOT private */ int fExpected;
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(fExpected, Fibonacci.compute(fInput));
}
}
public class Fibonacci {
...
}
3 使用单个参数进行测试
(自4.12-beta-3开始)
如果您的测试仅需要单个参数,则不必用数组包装它。相反,您可以提供Iterable或对象数组。
@Parameters
public static Iterable<? extends Object> data() {
return Arrays.asList("first test", "second test");
}
或者
@Parameters
public static Object[] data() {
return new Object[] { "first test", "second test" };
}
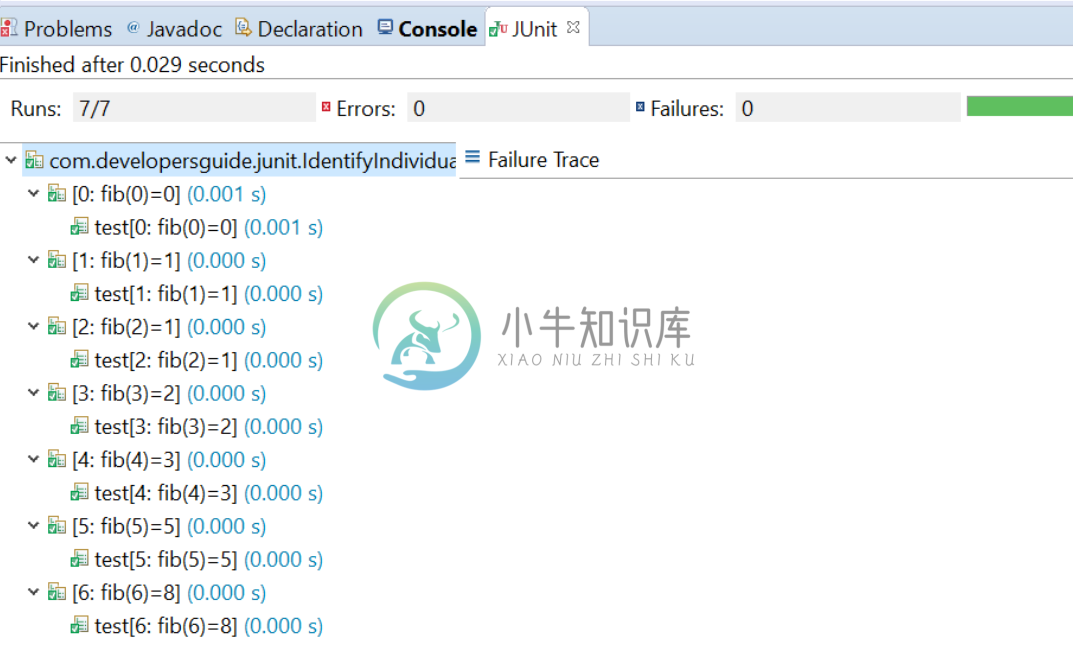
4 识别单个测试用例
为了在Parameterized测试中轻松识别各个测试用例,可以使用@Parameters注解提供名称。该名称允许包含在运行时替换的占位符:
- {index}:当前参数索引
- {0}, {1}, …:第一个,第二个,依此类推,参数值。注意:单引号 ' 应转义为两个单引号 ''。
4.1 范例
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
import java.util.Arrays;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized;
import org.junit.runners.Parameterized.Parameters;
/**
* 小牛知识库网: https://www.xnip.cn
*/
@RunWith(Parameterized.class)
public class FibonacciTest {
@Parameters(name = "{index}: fib({0})={1}")
public static Iterable<Object[]> data() {
return Arrays.asList(new Object[][] {
{ 0, 0 }, { 1, 1 }, { 2, 1 }, { 3, 2 }, { 4, 3 }, { 5, 5 }, { 6, 8 }
});
}
private int input;
private int expected;
public FibonacciTest(int input, int expected) {
this.input = input;
this.expected = expected;
}
@Test
public void test() {
assertEquals(expected, Fibonacci.compute(input));
}
}
public class Fibonacci {
...
}
在上面给出的示例中,参数化运行器创建的名称类似[3:fib(3)= 2]。如果未指定名称,则默认情况下将使用当前参数索引。
4.2 输出