Python搭建Keras CNN模型破解网站验证码的实现
在本项目中,将会用Keras来搭建一个稍微复杂的CNN模型来破解以上的验证码。验证码如下:

利用Keras可以快速方便地搭建CNN模型,本项目搭建的CNN模型如下:
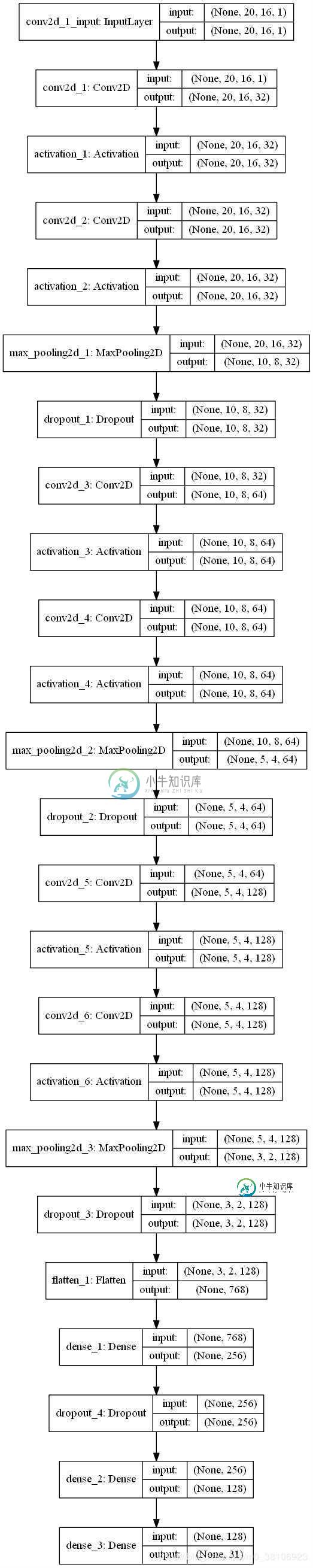
将数据集分为训练集和测试集,占比为8:2,该模型训练的代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from matplotlib import pyplot as plt
from keras.utils import np_utils, plot_model
from keras.models import Sequential
from keras.layers.core import Dense, Dropout, Activation, Flatten
from keras.callbacks import EarlyStopping
from keras.layers import Conv2D, MaxPooling2D
# 读取数据
df = pd.read_csv('./data.csv')
# 标签值
vals = range(31)
keys = ['1','2','3','4','5','6','7','8','9','A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','J','K','L','N','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','X','Y','Z']
label_dict = dict(zip(keys, vals))
x_data = df[['v'+str(i+1) for i in range(320)]]
y_data = pd.DataFrame({'label':df['label']})
y_data['class'] = y_data['label'].apply(lambda x: label_dict[x])
# 将数据分为训练集和测试集
X_train, X_test, Y_train, Y_test = train_test_split(x_data, y_data['class'], test_size=0.3, random_state=42)
x_train = np.array(X_train).reshape((1167, 20, 16, 1))
x_test = np.array(X_test).reshape((501, 20, 16, 1))
# 对标签值进行one-hot encoding
n_classes = 31
y_train = np_utils.to_categorical(Y_train, n_classes)
y_val = np_utils.to_categorical(Y_test, n_classes)
input_shape = x_train[0].shape
# CNN模型
model = Sequential()
# 卷积层和池化层
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3), input_shape=input_shape, padding='same'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(32, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), padding='same'))
# Dropout层
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(64, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), padding='same'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(Conv2D(128, kernel_size=(3, 3), padding='same'))
model.add(Activation('relu'))
model.add(MaxPooling2D(pool_size=(2, 2), padding='same'))
model.add(Dropout(0.25))
model.add(Flatten())
# 全连接层
model.add(Dense(256, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dropout(0.5))
model.add(Dense(128, activation='relu'))
model.add(Dense(n_classes, activation='softmax'))
model.compile(loss='categorical_crossentropy', optimizer='adam', metrics=['accuracy'])
# plot model
##plot_model(model, to_file=r'./model.png', show_shapes=True)
# 模型训练
callbacks = [EarlyStopping(monitor='val_acc', patience=5, verbose=1)]
batch_size = 64
n_epochs = 100
history = model.fit(x_train, y_train, batch_size=batch_size, epochs=n_epochs, \
verbose=1, validation_data=(x_test, y_val), callbacks=callbacks)
mp = './verifycode_Keras.h5'
model.save(mp)
# 绘制验证集上的准确率曲线
val_acc = history.history['val_acc']
plt.plot(range(len(val_acc)), val_acc, label='CNN model')
plt.title('Validation accuracy on verifycode dataset')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('accuracy')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
在上述代码中,训练模型的时候采用了early stopping技巧。early stopping是用于提前停止训练的callbacks。具体地,可以达到当训练集上的loss不在减小(即减小的程度小于某个阈值)的时候停止继续训练。
运行上述模型训练代码,输出的结果如下:
......(忽略之前的输出) Epoch 22/100 64/1167 [>.............................] - ETA: 3s - loss: 0.0399 - acc: 1.0000 128/1167 [==>...........................] - ETA: 3s - loss: 0.1195 - acc: 0.9844 192/1167 [===>..........................] - ETA: 2s - loss: 0.1085 - acc: 0.9792 256/1167 [=====>........................] - ETA: 2s - loss: 0.1132 - acc: 0.9727 320/1167 [=======>......................] - ETA: 2s - loss: 0.1045 - acc: 0.9750 384/1167 [========>.....................] - ETA: 2s - loss: 0.1006 - acc: 0.9740 448/1167 [==========>...................] - ETA: 2s - loss: 0.1522 - acc: 0.9643 512/1167 [============>.................] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.1450 - acc: 0.9648 576/1167 [=============>................] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.1368 - acc: 0.9653 640/1167 [===============>..............] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.1353 - acc: 0.9641 704/1167 [=================>............] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.1280 - acc: 0.9659 768/1167 [==================>...........] - ETA: 1s - loss: 0.1243 - acc: 0.9674 832/1167 [====================>.........] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1577 - acc: 0.9639 896/1167 [======================>.......] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1488 - acc: 0.9665 960/1167 [=======================>......] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1488 - acc: 0.9656 1024/1167 [=========================>....] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1427 - acc: 0.9668 1088/1167 [==========================>...] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1435 - acc: 0.9669 1152/1167 [============================>.] - ETA: 0s - loss: 0.1383 - acc: 0.9688 1167/1167 [==============================] - 4s 3ms/step - loss: 0.1380 - acc: 0.9683 - val_loss: 0.0835 - val_acc: 0.9760 Epoch 00022: early stopping
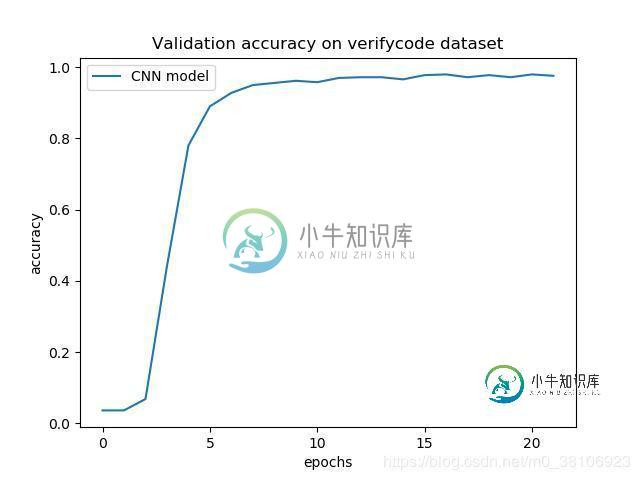
可以看到,花费几分钟,一共训练了21次,最近一次的训练后,在测试集上的准确率为96.83%。在测试集的准确率曲线如下图:
模型训练完后,我们对新的验证码进行预测。新的100张验证码如下图:

使用训练好的CNN模型,对这些新的验证码进行预测,预测的Python代码如下:
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*- import os import cv2 import html" target="_blank">numpy as np def split_picture(imagepath): # 以灰度模式读取图片 gray = cv2.imread(imagepath, 0) # 将图片的边缘变为白色 height, width = gray.shape for i in range(width): gray[0, i] = 255 gray[height-1, i] = 255 for j in range(height): gray[j, 0] = 255 gray[j, width-1] = 255 # 中值滤波 blur = cv2.medianBlur(gray, 3) #模板大小3*3 # 二值化 ret,thresh1 = cv2.threshold(blur, 200, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 提取单个字符 chars_list = [] image, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(thresh1, 2, 2) for cnt in contours: # 最小的外接矩形 x, y, w, h = cv2.boundingRect(cnt) if x != 0 and y != 0 and w*h >= 100: chars_list.append((x,y,w,h)) sorted_chars_list = sorted(chars_list, key=lambda x:x[0]) for i,item in enumerate(sorted_chars_list): x, y, w, h = item cv2.imwrite('test_verifycode/%d.jpg'%(i+1), thresh1[y:y+h, x:x+w]) def remove_edge_picture(imagepath): image = cv2.imread(imagepath, 0) height, width = image.shape corner_list = [image[0,0] < 127, image[height-1, 0] < 127, image[0, width-1]<127, image[ height-1, width-1] < 127 ] if sum(corner_list) >= 3: os.remove(imagepath) def resplit_with_parts(imagepath, parts): image = cv2.imread(imagepath, 0) os.remove(imagepath) height, width = image.shape file_name = imagepath.split('/')[-1].split(r'.')[0] # 将图片重新分裂成parts部分 step = width//parts # 步长 start = 0 # 起始位置 for i in range(parts): cv2.imwrite('./test_verifycode/%s.jpg'%(file_name+'-'+str(i)), \ image[:, start:start+step]) start += step def resplit(imagepath): image = cv2.imread(imagepath, 0) height, width = image.shape if width >= 64: resplit_with_parts(imagepath, 4) elif width >= 48: resplit_with_parts(imagepath, 3) elif width >= 26: resplit_with_parts(imagepath, 2) # rename and convert to 16*20 size def convert(dir, file): imagepath = dir+'/'+file # 读取图片 image = cv2.imread(imagepath, 0) # 二值化 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) img = cv2.resize(thresh, (16, 20), interpolation=cv2.INTER_AREA) # 保存图片 cv2.imwrite('%s/%s' % (dir, file), img) # 读取图片的数据,并转化为0-1值 def Read_Data(dir, file): imagepath = dir+'/'+file # 读取图片 image = cv2.imread(imagepath, 0) # 二值化 ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(image, 127, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY) # 显示图片 bin_values = [1 if pixel==255 else 0 for pixel in thresh.ravel()] return bin_values def predict(VerifyCodePath): dir = './test_verifycode' files = os.listdir(dir) # 清空原有的文件 if files: for file in files: os.remove(dir + '/' + file) split_picture(VerifyCodePath) files = os.listdir(dir) if not files: print('查看的文件夹为空!') else: # 去除噪声图片 for file in files: remove_edge_picture(dir + '/' + file) # 对黏连图片进行重分割 for file in os.listdir(dir): resplit(dir + '/' + file) # 将图片统一调整至16*20大小 for file in os.listdir(dir): convert(dir, file) # 图片中的字符代表的向量 files = sorted(os.listdir(dir), key=lambda x: x[0]) table = np.array([Read_Data(dir, file) for file in files]).reshape(-1,20,16,1) # 模型保存地址 mp = './verifycode_Keras.h5' # 载入模型 from keras.models import load_model cnn = load_model(mp) # 模型预测 y_pred = cnn.predict(table) predictions = np.argmax(y_pred, axis=1) # 标签字典 keys = range(31) vals = ['1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9', 'A', 'B', 'C', 'D', 'E', 'F', 'G', 'H', 'J', 'K', 'L', 'N', 'P', 'Q', 'R', 'S', 'T', 'U', 'V', 'X', 'Y', 'Z'] label_dict = dict(zip(keys, vals)) return ''.join([label_dict[pred] for pred in predictions]) def main(): dir = './VerifyCode/' correct = 0 for i, file in enumerate(os.listdir(dir)): true_label = file.split('.')[0] VerifyCodePath = dir+file pred = predict(VerifyCodePath) if true_label == pred: correct += 1 print(i+1, (true_label, pred), true_label == pred, correct) total = len(os.listdir(dir)) print('\n总共图片:%d张\n识别正确:%d张\n识别准确率:%.2f%%.'\ %(total, correct, correct*100/total)) main()
以下是该CNN模型的预测结果:
Using TensorFlow backend.
2018-10-25 15:13:50.390130: I C: f_jenkinsworkspace
el-winMwindowsPY35 ensorflowcoreplatformcpu_feature_guard.cc:140] Your CPU supports instructions that this TensorFlow binary was not compiled to use: AVX2
1 ('ZK6N', 'ZK6N') True 1
2 ('4JPX', '4JPX') True 2
3 ('5GP5', '5GP5') True 3
4 ('5RQ8', '5RQ8') True 4
5 ('5TQP', '5TQP') True 5
6 ('7S62', '7S62') True 6
7 ('8R2Z', '8R2Z') True 7
8 ('8RFV', '8RFV') True 8
9 ('9BBT', '9BBT') True 9
10 ('9LNE', '9LNE') True 10
11 ('67UH', '67UH') True 11
12 ('74UK', '74UK') True 12
13 ('A5T2', 'A5T2') True 13
14 ('AHYV', 'AHYV') True 14
15 ('ASEY', 'ASEY') True 15
16 ('B371', 'B371') True 16
17 ('CCQL', 'CCQL') True 17
18 ('CFD5', 'GFD5') False 17
19 ('CJLJ', 'CJLJ') True 18
20 ('D4QV', 'D4QV') True 19
21 ('DFQ8', 'DFQ8') True 20
22 ('DP18', 'DP18') True 21
23 ('E3HC', 'E3HC') True 22
24 ('E8VB', 'E8VB') True 23
25 ('DE1U', 'DE1U') True 24
26 ('FK1R', 'FK1R') True 25
27 ('FK91', 'FK91') True 26
28 ('FSKP', 'FSKP') True 27
29 ('FVZP', 'FVZP') True 28
30 ('GC6H', 'GC6H') True 29
31 ('GH62', 'GH62') True 30
32 ('H9FQ', 'H9FQ') True 31
33 ('H67Q', 'H67Q') True 32
34 ('HEKC', 'HEKC') True 33
35 ('HV2B', 'HV2B') True 34
36 ('J65Z', 'J65Z') True 35
37 ('JZCX', 'JZCX') True 36
38 ('KH5D', 'KH5D') True 37
39 ('KXD2', 'KXD2') True 38
40 ('1GDH', '1GDH') True 39
41 ('LCL3', 'LCL3') True 40
42 ('LNZR', 'LNZR') True 41
43 ('LZU5', 'LZU5') True 42
44 ('N5AK', 'N5AK') True 43
45 ('N5Q3', 'N5Q3') True 44
46 ('N96Z', 'N96Z') True 45
47 ('NCDG', 'NCDG') True 46
48 ('NELS', 'NELS') True 47
49 ('P96U', 'P96U') True 48
50 ('PD42', 'PD42') True 49
51 ('PECG', 'PEQG') False 49
52 ('PPZF', 'PPZF') True 50
53 ('PUUL', 'PUUL') True 51
54 ('Q2DN', 'D2DN') False 51
55 ('QCQ9', 'QCQ9') True 52
56 ('QDB1', 'QDBJ') False 52
57 ('QZUD', 'QZUD') True 53
58 ('R3T5', 'R3T5') True 54
59 ('S1YT', 'S1YT') True 55
60 ('SP7L', 'SP7L') True 56
61 ('SR2K', 'SR2K') True 57
62 ('SUP5', 'SVP5') False 57
63 ('T2SP', 'T2SP') True 58
64 ('U6V9', 'U6V9') True 59
65 ('UC9P', 'UC9P') True 60
66 ('UFYD', 'UFYD') True 61
67 ('V9NJ', 'V9NH') False 61
68 ('V35X', 'V35X') True 62
69 ('V98F', 'V98F') True 63
70 ('VD28', 'VD28') True 64
71 ('YGHE', 'YGHE') True 65
72 ('YNKD', 'YNKD') True 66
73 ('YVXV', 'YVXV') True 67
74 ('ZFBS', 'ZFBS') True 68
75 ('ET6X', 'ET6X') True 69
76 ('TKVC', 'TKVC') True 70
77 ('2UCU', '2UCU') True 71
78 ('HNBK', 'HNBK') True 72
79 ('X8FD', 'X8FD') True 73
80 ('ZGNX', 'ZGNX') True 74
81 ('LQCU', 'LQCU') True 75
82 ('JNZY', 'JNZVY') False 75
83 ('RX34', 'RX34') True 76
84 ('811E', '811E') True 77
85 ('ETDX', 'ETDX') True 78
86 ('4CPR', '4CPR') True 79
87 ('FE91', 'FE91') True 80
88 ('B7XH', 'B7XH') True 81
89 ('1RUA', '1RUA') True 82
90 ('UBCX', 'UBCX') True 83
91 ('KVT5', 'KVT5') True 84
92 ('HZ3A', 'HZ3A') True 85
93 ('3XLR', '3XLR') True 86
94 ('VC7T', 'VC7T') True 87
95 ('7PG1', '7PQ1') False 87
96 ('4F21', '4F21') True 88
97 ('3HLJ', '3HLJ') True 89
98 ('1KT7', '1KT7') True 90
99 ('1RHE', '1RHE') True 91
100 ('1TTA', '1TTA') True 92
总共图片:100张
识别正确:92张
识别准确率:92.00%.
可以看到,该训练后的CNN模型,其预测新验证的准确率在90%以上。
Demo及数据集下载网站:CNN_4_Verifycode_jb51.rar
到此这篇关于Python搭建Keras CNN模型破解网站验证码的实现的文章就介绍到这了,更多相关Python Keras CNN破解网站验证码内容请搜索小牛知识库以前的文章或继续浏览下面的相关文章希望大家以后多多支持小牛知识库!
-
本文向大家介绍利用Python破解验证码实例详解,包括了利用Python破解验证码实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一、前言 本实验将通过一个简单的例子来讲解破解验证码的原理,将学习和实践以下知识点: Python基本知识 PIL模块的使用 二、实例详解 安装 pillow(PIL)库: 下载实验用的文件: 这是我们实验使用的验证码 captcha.gif
-
本文向大家介绍Python网站验证码识别,包括了Python网站验证码识别的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 0x00 识别涉及技术 验证码识别涉及很多方面的内容。入手难度大,但是入手后,可拓展性又非常广泛,可玩性极强,成就感也很足。 验证码图像处理 验证码图像识别技术主要是操作图片内的像素点,通过对图片的像素点进行一系列的操作,最后输出验证码图像内的每个字符的文本矩阵。 读取图片 图片降噪
-
网站搭建这一块实际上原理是大同小异的,国光这里只写几个网站的安装方法,给大家提供一个思路。 DVWA DVWA 是一个用来搞 Web 安全从业者入门使用的一个练习靶场,用来学习掌握基本的漏洞原理使用的,如果你对 Web 安全不感兴趣的话可以直接跳过这一个小节。 国光建议 DVWA 练习的时候 要结合源码去分析漏洞 不要直接把网上攻击流程走一步就草草了之了 不看源码的学习 等于啥都没有学 环境准备
-
为什么要验证网站 搜索资源平台推荐站长添加主站(您网站的链接也许会使用www 和非 www 两种网址,建议添加用户能够真实访问到的网址),添加并验证后,可证明您是该域名的拥有者,可以快捷批量添加子站点,查看所有子站数据,无需再一一验证您的子站点。 如何验证网站 百度搜索资源平台提供三种验证方式(百度统计的导入方式已下线):文件验证、html标签验证、CNAME验证。 1.文件验证:您需要下载验证文
-
常见验证码的弱点与验证码识别
-
本文向大家介绍使用puppeteer破解极验的滑动验证码,包括了使用puppeteer破解极验的滑动验证码的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 基本的流程: 1. 打开前端网,点击登录。 2. 填写账号,密码。 3. 点解验证按钮,通过滑动验证,最后成功登陆。 代码实现: github上可以checkout。 具体代码如下所示: run.js 运行 1. 将这个两个文件保存到文件夹下面,终端切

