Spring Cloud Ribbon负载均衡器处理方法
接下来撸一撸负载均衡器的内部,看看是如何获取服务实例,获取以后做了哪些处理,处理后又是如何选取服务实例的。
分成三个部分来撸:
- 配置
- 获取服务
- 选择服务
配置
在上一篇《撸一撸Spring Cloud Ribbon的原理》的配置部分可以看到默认的负载均衡器是ZoneAwareLoadBalancer。
看一看配置类。
位置:
spring-cloud-netflix-core-1.3.5.RELEASE.jar org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon RibbonClientConfiguration.class
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
//Order is important here, last should be the default, first should be optional
// see https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/2086#issuecomment-316281653
@Import({OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class, RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class})
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {
// 略
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
// 略
}
在实例化ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的时候注入了,config、rule、ping、serverList、serverListFilter、serverListUpdater实例。
config:配置实例。
rule:负载均衡策略实例。
ping:ping实例。
serverList:获取和更新服务的实例。
serverListFilter:服务过滤实例。
serverListUpdater:服务列表信息更新实例。
@SuppressWarnings("deprecation")
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties
//Order is important here, last should be the default, first should be optional
// see https://github.com/spring-cloud/spring-cloud-netflix/issues/2086#issuecomment-316281653
@Import({OkHttpRibbonConfiguration.class, RestClientRibbonConfiguration.class, HttpClientRibbonConfiguration.class})
public class RibbonClientConfiguration {
// 略
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IClientConfig ribbonClientConfig() {
DefaultClientConfigImpl config = new DefaultClientConfigImpl();
config.loadProperties(this.name);
return config;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IRule ribbonRule(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IRule.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IRule.class, config, name);
}
ZoneAvoidanceRule rule = new ZoneAvoidanceRule();
rule.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return rule;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, name);
}
return new DummyPing();
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerList<Server> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, name);
}
ConfigurationBasedServerList serverList = new ConfigurationBasedServerList();
serverList.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return serverList;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerListUpdater ribbonServerListUpdater(IClientConfig config) {
return new PollingServerListUpdater(config);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ILoadBalancer ribbonLoadBalancer(IClientConfig config,
ServerList<Server> serverList, ServerListFilter<Server> serverListFilter,
IRule rule, IPing ping, ServerListUpdater serverListUpdater) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ILoadBalancer.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ILoadBalancer.class, config, name);
}
return new ZoneAwareLoadBalancer<>(config, rule, ping, serverList,
serverListFilter, serverListUpdater);
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public ServerListFilter<Server> ribbonServerListFilter(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerListFilter.class, name)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerListFilter.class, config, name);
}
ZonePreferenceServerListFilter filter = new ZonePreferenceServerListFilter();
filter.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return filter;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public RibbonLoadBalancerContext ribbonLoadBalancerContext(
ILoadBalancer loadBalancer, IClientConfig config, RetryHandler retryHandler) {
return new RibbonLoadBalancerContext(loadBalancer, config, retryHandler);
}
// 略
}
在这里配置相关的实例
config:DefaultClientConfigImpl。
rule:ZoneAvoidanceRule。
ping:DummyPing。
serverList:ConfigurationBasedServerList,基于配置的服务列表实例。
serverListFilter:ZonePreferenceServerListFilter。
serverListUpdater:PollingServerListUpdater。
要注意的是,在这里serverList的实例是ConfigurationBasedServerList,这是在未使用Eureka时获取服务信息的实例,是从配置文件中获取。
那么在和Eureka配合使用时,需要从 Eureka Server获取服务信息,那该是哪个实例来做这件事情呢。
在启用Eureka服务发现时,会首先会采用EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration配置类。
位置:
spring-cloud-netflix-eureka-client-1.3.5.RELEASE.jar org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration.class
@Configuration
@CommonsLog
public class EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration {
// 略
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public IPing ribbonPing(IClientConfig config) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(IPing.class, serviceId)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(IPing.class, config, serviceId);
}
NIWSDiscoveryPing ping = new NIWSDiscoveryPing();
ping.initWithNiwsConfig(config);
return ping;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public ServerList<?> ribbonServerList(IClientConfig config, Provider<EurekaClient> eurekaClientProvider) {
if (this.propertiesFactory.isSet(ServerList.class, serviceId)) {
return this.propertiesFactory.get(ServerList.class, config, serviceId);
}
DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList discoveryServerList = new DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList(
config, eurekaClientProvider);
DomainExtractingServerList serverList = new DomainExtractingServerList(
discoveryServerList, config, this.approximateZoneFromHostname);
return serverList;
}
// 略
}
在首先采用了EurekaRibbonClientConfiguration配置后,实际上各实例变成了
config:DefaultClientConfigImpl。
rule:ZoneAvoidanceRule。
ping:NIWSDiscoveryPing。
serverList:DomainExtractingServerList,内部是DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList,实际上是通过服务发现获取服务信息列表。
serverListFilter:ZonePreferenceServerListFilter。
serverListUpdater:PollingServerListUpdater。
获取服务
在找到获取服务信息入口前,先把负载均衡器的类继承关系撸一下。
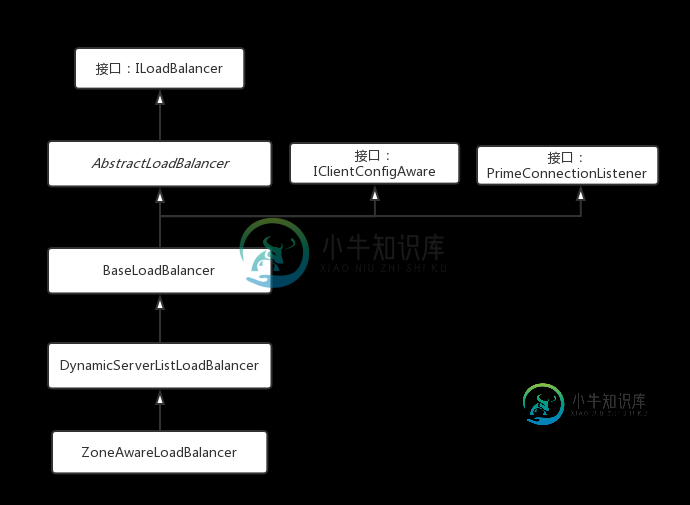
在ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的构造中调用了父类DynamicServerListLoadBalancer构造。
位置:
ribbon-loadbalancer-2.2.2.jar
com.netflix.loadbalancer
ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.class
在DynamicServerListLoadBalancer的构造中,调用了restOfInit函数。
ribbon-loadbalancer-2.2.2.jar
com.netflix.loadbalancer
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer.class
void restOfInit(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
boolean primeConnection = this.isEnablePrimingConnections();
// turn this off to avoid duplicated asynchronous priming done in BaseLoadBalancer.setServerList()
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(false);
enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature();
updateListOfServers();
if (primeConnection && this.getPrimeConnections() != null) {
this.getPrimeConnections()
.primeConnections(getReachableServers());
}
this.setEnablePrimingConnections(primeConnection);
LOGGER.info("DynamicServerListLoadBalancer for client {} initialized: {}", clientConfig.getClientName(), this.toString());
}
先是通过调用enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature方法启动定时更新服务列表,然后立即调用updateListOfServers函数马上获取并更新服务列表信息。
先看下enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature方法,实际上是调用了服务列表信息更新实例的start方法启动定时更新功能。
/**
* Feature that lets us add new instances (from AMIs) to the list of
* existing servers that the LB will use Call this method if you want this
* feature enabled
*/
public void enableAndInitLearnNewServersFeature() {
LOGGER.info("Using serverListUpdater {}", serverListUpdater.getClass().getSimpleName());
serverListUpdater.start(updateAction);
}
这里的服务列表信息更新实例就是配置阶段配置的PollingServerListUpdater实例,看一下这个类的构造和start方法。
public class PollingServerListUpdater implements ServerListUpdater {
// 略
private static long LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_UPDATE_DELAY = 1000; // msecs;
private static int LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_REPEAT_INTERVAL = 30 * 1000; // msecs;
// 略
private final AtomicBoolean isActive = new AtomicBoolean(false);
private volatile long lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
private final long initialDelayMs;
private final long refreshIntervalMs;
// 略
public PollingServerListUpdater(IClientConfig clientConfig) {
this(LISTOFSERVERS_CACHE_UPDATE_DELAY, getRefreshIntervalMs(clientConfig));
}
public PollingServerListUpdater(final long initialDelayMs, final long refreshIntervalMs) {
this.initialDelayMs = initialDelayMs;
this.refreshIntervalMs = refreshIntervalMs;
}
@Override
public synchronized void start(final UpdateAction updateAction) {
if (isActive.compareAndSet(false, true)) {
final Runnable wrapperRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
if (!isActive.get()) {
if (scheduledFuture != null) {
scheduledFuture.cancel(true);
}
return;
}
try {
updateAction.doUpdate();
lastUpdated = System.currentTimeMillis();
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("Failed one update cycle", e);
}
}
};
scheduledFuture = getRefreshExecutor().scheduleWithFixedDelay(
wrapperRunnable,
initialDelayMs,
refreshIntervalMs,
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS
);
} else {
logger.info("Already active, no-op");
}
}
// 略
}
从构造和常量定义看出来,延迟一秒执行,默认每隔30秒执行更新,可以通过配置修改间隔更新的时间。
从start方法看,就是开了一个定时执行的schedule,定时执行 updateAction.doUpdate()。
回到start方法调用方DynamicServerListLoadBalancer类中看一下UpdateAction实例的定义。
protected final ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction updateAction = new ServerListUpdater.UpdateAction() {
@Override
public void doUpdate() {
updateListOfServers();
}
};
实际上就是调用了DynamicServerListLoadBalancer类的updateListOfServers方法,这跟启动完定时更新后立即更新服务信息列表的路径是一致的。
继续看updateListOfServers方法。
public void updateListOfServers() {
List<T> servers = new ArrayList<T>();
if (serverListImpl != null) {
servers = serverListImpl.getUpdatedListOfServers();
LOGGER.debug("List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
if (filter != null) {
servers = filter.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
LOGGER.debug("Filtered List of Servers for {} obtained from Discovery client: {}",
getIdentifier(), servers);
}
}
updateAllServerList(servers);
}
1.通过ServerList实例获取服务信息列表。
2.通过ServerListFilter 实例对获取到的服务信息列表进行过滤。
3.将过滤后的服务信息列表保存到LoadBalancerStats中作为状态保持。
接下分别看一下。
1.通过ServerList实例获取服务信息列表。
ServerList实例就是配置阶段生成的DomainExtractingServerList,获取服务信息都是委托给DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList。
public class DiscoveryEnabledNIWSServerList extends AbstractServerList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>{
// 略
@Override
public List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> getInitialListOfServers(){
return obtainServersViaDiscovery();
}
@Override
public List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> getUpdatedListOfServers(){
return obtainServersViaDiscovery();
}
private List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> obtainServersViaDiscovery() {
List<DiscoveryEnabledServer> serverList = new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>();
if (eurekaClientProvider == null || eurekaClientProvider.get() == null) {
logger.warn("EurekaClient has not been initialized yet, returning an empty list");
return new ArrayList<DiscoveryEnabledServer>();
}
EurekaClient eurekaClient = eurekaClientProvider.get();
if (vipAddresses!=null){
for (String vipAddress : vipAddresses.split(",")) {
// if targetRegion is null, it will be interpreted as the same region of client
List<InstanceInfo> listOfInstanceInfo = eurekaClient.getInstancesByVipAddress(vipAddress, isSecure, targetRegion);
for (InstanceInfo ii : listOfInstanceInfo) {
if (ii.getStatus().equals(InstanceStatus.UP)) {
if(shouldUseOverridePort){
if(logger.isDebugEnabled()){
logger.debug("Overriding port on client name: " + clientName + " to " + overridePort);
}
// copy is necessary since the InstanceInfo builder just uses the original reference,
// and we don't want to corrupt the global eureka copy of the object which may be
// used by other clients in our system
InstanceInfo copy = new InstanceInfo(ii);
if(isSecure){
ii = new InstanceInfo.Builder(copy).setSecurePort(overridePort).build();
}else{
ii = new InstanceInfo.Builder(copy).setPort(overridePort).build();
}
}
DiscoveryEnabledServer des = new DiscoveryEnabledServer(ii, isSecure, shouldUseIpAddr);
des.setZone(DiscoveryClient.getZone(ii));
serverList.add(des);
}
}
if (serverList.size()>0 && prioritizeVipAddressBasedServers){
break; // if the current vipAddress has servers, we dont use subsequent vipAddress based servers
}
}
}
return serverList;
}
// 略
}
可以看到其实就是通过Eureka客户端从Eureka服务端获取所有服务实例信息并把上线的包装成DiscoveryEnabledServer实例,带有zone信息,做到服务列表中。
2.通过ServerListFilter 实例对获取到的服务信息列表进行过滤。
serverListFilte实例就是配置阶段生成的ZonePreferenceServerListFilter,通过调用该实例的getFilteredListOfServers方法进行过滤。
@Data
@EqualsAndHashCode(callSuper = false)
public class ZonePreferenceServerListFilter extends ZoneAffinityServerListFilter<Server> {
private String zone;
@Override
public void initWithNiwsConfig(IClientConfig niwsClientConfig) {
super.initWithNiwsConfig(niwsClientConfig);
if (ConfigurationManager.getDeploymentContext() != null) {
this.zone = ConfigurationManager.getDeploymentContext().getValue(
ContextKey.zone);
}
}
@Override
public List<Server> getFilteredListOfServers(List<Server> servers) {
List<Server> output = super.getFilteredListOfServers(servers);
if (this.zone != null && output.size() == servers.size()) {
List<Server> local = new ArrayList<Server>();
for (Server server : output) {
if (this.zone.equalsIgnoreCase(server.getZone())) {
local.add(server);
}
}
if (!local.isEmpty()) {
return local;
}
}
return output;
}
}
在getFilteredListOfServers方法里面,一上来是调用父类的同名方法先过滤,其实父类也是把和消费端同区域的服务给过滤出来使用,不仅如此,增加了些智能的判定,保证在故障/负载较高时或者可用实例较少时不进行同区域的过滤。
但是在ZonePreferenceServerListFilter.getFilteredListOfServers这里,就算父类没做过过滤,这里依然要把同zone的服务给滤出来使用,谁叫这里的类是ZonePreference的呢。
这是比较怪异的地方,感觉父类的智能判定没什么作用。
还是看看ZoneAffinityServerListFilter.getFilteredListOfServers做的辛苦工作吧。
public class ZoneAffinityServerListFilter<T extends Server> extends
AbstractServerListFilter<T> implements IClientConfigAware {
// 略
private boolean shouldEnableZoneAffinity(List<T> filtered) {
if (!zoneAffinity && !zoneExclusive) {
return false;
}
if (zoneExclusive) {
return true;
}
LoadBalancerStats stats = getLoadBalancerStats();
if (stats == null) {
return zoneAffinity;
} else {
logger.debug("Determining if zone affinity should be enabled with given server list: {}", filtered);
ZoneSnapshot snapshot = stats.getZoneSnapshot(filtered);
double loadPerServer = snapshot.getLoadPerServer();
int instanceCount = snapshot.getInstanceCount();
int circuitBreakerTrippedCount = snapshot.getCircuitTrippedCount();
if (((double) circuitBreakerTrippedCount) / instanceCount >= blackOutServerPercentageThreshold.get()
|| loadPerServer >= activeReqeustsPerServerThreshold.get()
|| (instanceCount - circuitBreakerTrippedCount) < availableServersThreshold.get()) {
logger.debug("zoneAffinity is overriden. blackOutServerPercentage: {}, activeReqeustsPerServer: {}, availableServers: {}",
new Object[] {(double) circuitBreakerTrippedCount / instanceCount, loadPerServer, instanceCount - circuitBreakerTrippedCount});
return false;
} else {
return true;
}
}
}
@Override
public List<T> getFilteredListOfServers(List<T> servers) {
if (zone != null && (zoneAffinity || zoneExclusive) && servers !=null && servers.size() > 0){
List<T> filteredServers = Lists.newArrayList(Iterables.filter(
servers, this.zoneAffinityPredicate.getServerOnlyPredicate()));
if (shouldEnableZoneAffinity(filteredServers)) {
return filteredServers;
} else if (zoneAffinity) {
overrideCounter.increment();
}
}
return servers;
}
// 略
}
首先会将与消费端相同的zone的服务过滤出来,然后通过shouldEnableZoneAffinity(filteredServers)来判定是否可以采纳同zone的服务,还是采用所有的服务。
在shouldEnableZoneAffinity方法内,对相同zone的服务做了一次snapshot,获取这些服务的实例数量,平均负载,断路的实例数进行计算判定。
可以看一下initWithNiwsConfig方法中关键指标的值。
判定条件:
断路实例百分比>=0.8(断路的实例数/服务的实例数量)
平均负载>=0.6
可用实例数<2(实例数量-断路的实例数)
如果达到判定条件,那么就使用全部的服务,保证可用性。
但,上面也说了,因为ZonePreferenceServerListFilter本身总是会选用和消费端zone一致的服务,所以ZoneAffinityServerListFilter.getFilteredListOfServers中做的智能操作并没什么用。
不过,当然可以通过自定义配置来采用ZoneAffinityServerListFilter实例。
3.将过滤后的服务信息列表保存到LoadBalancerStats中作为状态保持。
跟进updateAllServerList(servers);去,一步步深入,会发现,实际上是保存到LoadBalancerStats中,并且这时候的服务是按照zone分组以HashMap<String, List<Server>>结构保存的,key是zone。
选择服务
实现了ILoadBalancer接口的负载均衡器,是通过实现chooseServer方法来进行服务的选择,选择后的服务做为目标请求服务。
看一下ZoneAwareLoadBalancer.chooseServer方法。
@Override
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) {
logger.debug("Zone aware logic disabled or there is only one zone");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
Server server = null;
try {
LoadBalancerStats lbStats = getLoadBalancerStats();
Map<String, ZoneSnapshot> zoneSnapshot = ZoneAvoidanceRule.createSnapshot(lbStats);
logger.debug("Zone snapshots: {}", zoneSnapshot);
if (triggeringLoad == null) {
triggeringLoad = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".triggeringLoadPerServerThreshold", 0.2d);
}
if (triggeringBlackoutPercentage == null) {
triggeringBlackoutPercentage = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".avoidZoneWithBlackoutPercetage", 0.99999d);
}
Set<String> availableZones = ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones(zoneSnapshot, triggeringLoad.get(), triggeringBlackoutPercentage.get());
logger.debug("Available zones: {}", availableZones);
if (availableZones != null && availableZones.size() < zoneSnapshot.keySet().size()) {
String zone = ZoneAvoidanceRule.randomChooseZone(zoneSnapshot, availableZones);
logger.debug("Zone chosen: {}", zone);
if (zone != null) {
BaseLoadBalancer zoneLoadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(zone);
server = zoneLoadBalancer.chooseServer(key);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error choosing server using zone aware logic for load balancer={}", name, e);
}
if (server != null) {
return server;
} else {
logger.debug("Zone avoidance logic is not invoked.");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
}
注意这里有两种用法:
1.通过配置ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer.enabled=false关闭区域感知负载均衡,或者zone的个数<=1个。
2.采用区域感知,或者zone的个数>1。
一个个来看一下
1.通过配置ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer.enabled=false关闭区域感知负载均衡,或者zone的个数<=1个。
这种情况下,调用了父类BaseLoadBalancer.chooseServer方法。
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (counter == null) {
counter = createCounter();
}
counter.increment();
if (rule == null) {
return null;
} else {
try {
return rule.choose(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.warn("LoadBalancer [{}]: Error choosing server for key {}", name, key, e);
return null;
}
}
}
这里使用的负载均衡策略rule实际上就是构造ZoneAwareLoadBalancer时传进来的,在配置阶段生成的ZoneAvoidanceRule策略实例。
public void setRule(IRule rule) {
if (rule != null) {
this.rule = rule;
} else {
/* default rule */
this.rule = new RoundRobinRule();
}
if (this.rule.getLoadBalancer() != this) {
this.rule.setLoadBalancer(this);
}
}
假设,如果没有配置,默认用的是RoundRobinRule策略实例。
2.采用区域感知,或者zone的个数>1。
public Server chooseServer(Object key) {
if (!ENABLED.get() || getLoadBalancerStats().getAvailableZones().size() <= 1) {
logger.debug("Zone aware logic disabled or there is only one zone");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
Server server = null;
try {
LoadBalancerStats lbStats = getLoadBalancerStats();
Map<String, ZoneSnapshot> zoneSnapshot = ZoneAvoidanceRule.createSnapshot(lbStats);
logger.debug("Zone snapshots: {}", zoneSnapshot);
if (triggeringLoad == null) {
triggeringLoad = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".triggeringLoadPerServerThreshold", 0.2d);
}
if (triggeringBlackoutPercentage == null) {
triggeringBlackoutPercentage = DynamicPropertyFactory.getInstance().getDoubleProperty(
"ZoneAwareNIWSDiscoveryLoadBalancer." + this.getName() + ".avoidZoneWithBlackoutPercetage", 0.99999d);
}
Set<String> availableZones = ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones(zoneSnapshot, triggeringLoad.get(), triggeringBlackoutPercentage.get());
logger.debug("Available zones: {}", availableZones);
if (availableZones != null && availableZones.size() < zoneSnapshot.keySet().size()) {
String zone = ZoneAvoidanceRule.randomChooseZone(zoneSnapshot, availableZones);
logger.debug("Zone chosen: {}", zone);
if (zone != null) {
BaseLoadBalancer zoneLoadBalancer = getLoadBalancer(zone);
server = zoneLoadBalancer.chooseServer(key);
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
logger.error("Error choosing server using zone aware logic for load balancer={}", name, e);
}
if (server != null) {
return server;
} else {
logger.debug("Zone avoidance logic is not invoked.");
return super.chooseServer(key);
}
}
在这种情况下默认使用ZoneAvoidanceRule负载均衡策略。
获取zone的snapshot信息。
获取可用的zone,通过观察ZoneAvoidanceRule.getAvailableZones定义,不是可用zone的条件是:
- 所属实例数==0。
- 故障率>0.99999或者平均负载<0。
- 如果不是上面两种情况,就选择负载最高的一个去除不作为可用的zone。
可用zone都获取后,随机选一个。
并从该zone中,通过ZoneAwareLoadBalancer的父类BaseLoadBalancer.chooseServer选取服务,上面整理过,BaseLoadBalancer里如果没有传入rule,那么默认使用RoundRobinRule策略轮寻一个服务。
其实,还是上面获取服务中ZonePreferenceServerListFilter过滤器的问题,实际上过滤出来的只有一个和消费端相同的一个zone的服务,所以第2.部分的从可用zone中选取服务的功能是走不到,要走到就得把过滤器给换掉。
总结:
配置的负载均衡器会启动schedule获取服务信息,在使用了Eureka客户端时,会从Eureka服务获取所有服务实例信息,通过过滤器过滤出可以使用的服务,过滤器默认只过滤出与消费端相同zone的服务,如果要保证高可用可配置ZoneAffinityServerListFilter过滤器,过滤后的服务列表,通过实现了IRule接口的负载均衡策略选取对应的服务,如果是使用zone感知的策略,可以从负载情况良好的zone中选取合适的服务。
-
负载均衡(Load balancing)是一种计算机网络技术,用来在多个计算机(计算机集群)、网络连接、CPU、磁盘驱动器或其他资源中分配负载,以达到最佳化资源使用、最大化吞吐率、最小化响应时间、同时避免过载的目的。 使用带有负载均衡的多个服务器组件,取代单一的组件,可以通过冗余提高可靠性。负载均衡服务通常是由专用软体和硬件来完成。 负载均衡最重要的一个应用是利用多台服务器提供单一服务,这种方案有
-
负载均衡包括负载均衡实例、访问控制及证书。 实例 负载均衡实例是一个运行的负载均衡服务,通过设置的虚拟IP接收流量并将其转发分配给后端服务器。 访问控制 访问控制用于设置访问负载均衡的IP白名单或IP黑名单。 证书 当在负载均衡实例上配置HTTPS监听转发来自HTTPS协议的请求时,需要配置证书。
-
一个简单的负载均衡的示例,把www.domain.com均衡到本机不同的端口,也可以改为均衡到不同的地址上。> http { : upstream myproject { : server 127.0.0.1:8000 weight=3; : server 127.0.0.1:8001; : server 127.0.0.1:8002; : server 127.0.0.1:8003; : }
-
SOFARPC 提供多种负载均衡算法,目前支持以下五种: 类型 名称 描述 random 随机算法 默认负载均衡算法。 localPref 本地优先算法 优先发现是否本机发布了该服务,如果没有再采用随机算法。 roundRobin 轮询算法 方法级别的轮询,各个方法间各自轮询,互不影响。 consistentHash 一致性hash算法 同样的方法级别的请求会路由到同样的节点。 weightRou
-
tcp_proxy_server 主要是为需要负载均衡的场景准备的。 它既能做四层tcp负载均衡,也能作七层http负载均衡。内置负载均衡算法为轮询法。 HTTP 七层负载均衡 来看一个http反向代理的例子: #include <unistd.h> #include <sys/wait.h> #include <sys/signal.h> #include <sys/prctl.h> #in
-
本节将会讨论常见的分布式系统负载均衡手段。 6.5.1 常见的负载均衡思路 如果我们不考虑均衡的话,现在有n个服务节点,我们完成业务流程实际上只需要从这n个中挑出其中的一个。有几种思路: 按顺序挑: 例如上次选了第一台,那么这次就选第二台,下次第三台,如果已经到了最后一台,那么下一次从第一台开始。这种情况下我们可以把服务节点信息都存储在数组中,每次请求完成下游之后,将一个索引后移即可。在移到尽头时

