详解SpringBoot优雅编码之Lombok加持
本文介绍了SpringBoot优雅编码之Lombok加持,分享给大家,具体如下:

概述
Lombok 通过提供简单的语法注解形式来帮助简化消除一些必须有但显得很臃肿的 java 代码。典型的是对于 POJO对象的简化(如自动帮我们生成Setter和Getter等),有了Lombok的加持,开发人员可以免去很多重复且臃肿的操作,极大地提高java代码的信噪比,因此我们必须尝试并应用起来!
IntelliJ IDEA上配置
方法一:直接在IDEA界面中配置
首先进入Plugins界面:
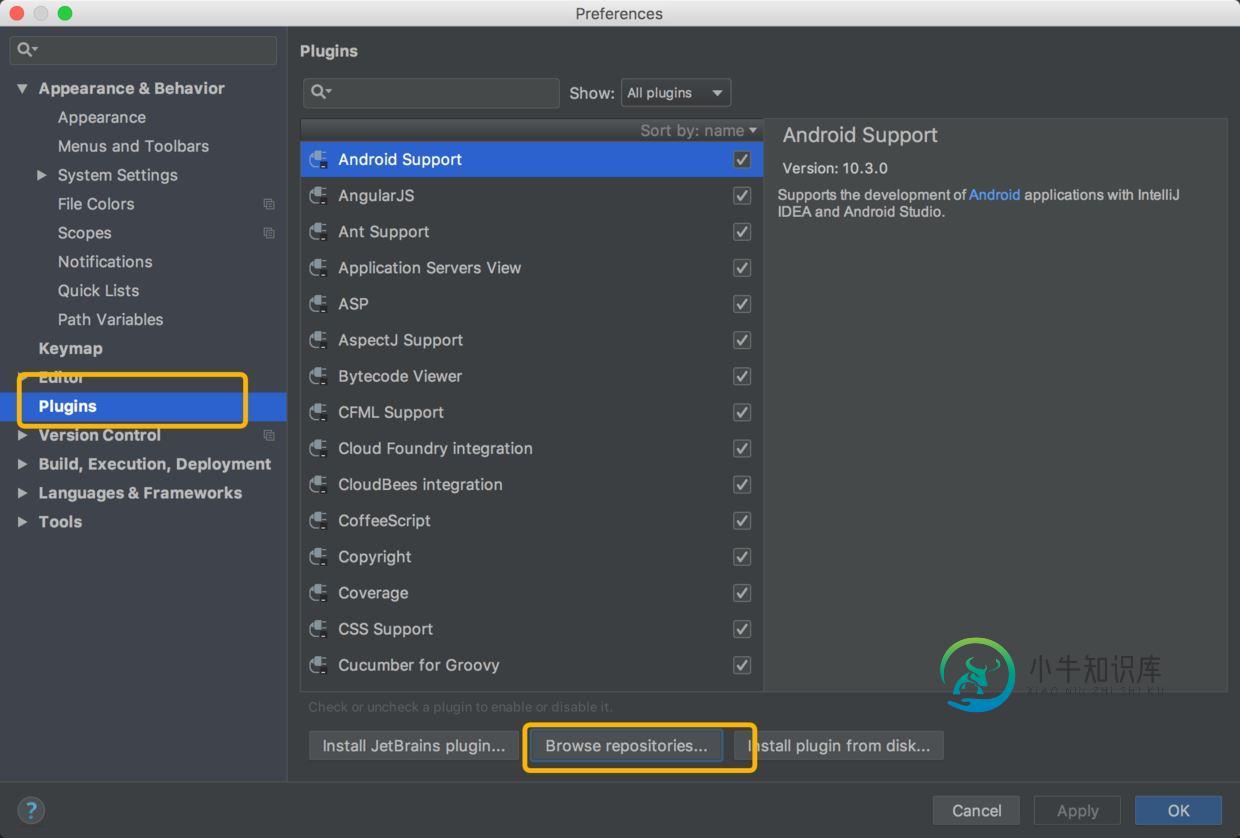
然后搜索并安装Lombok插件:

最后不要忘了开启Annotation Processors的Enable选项:
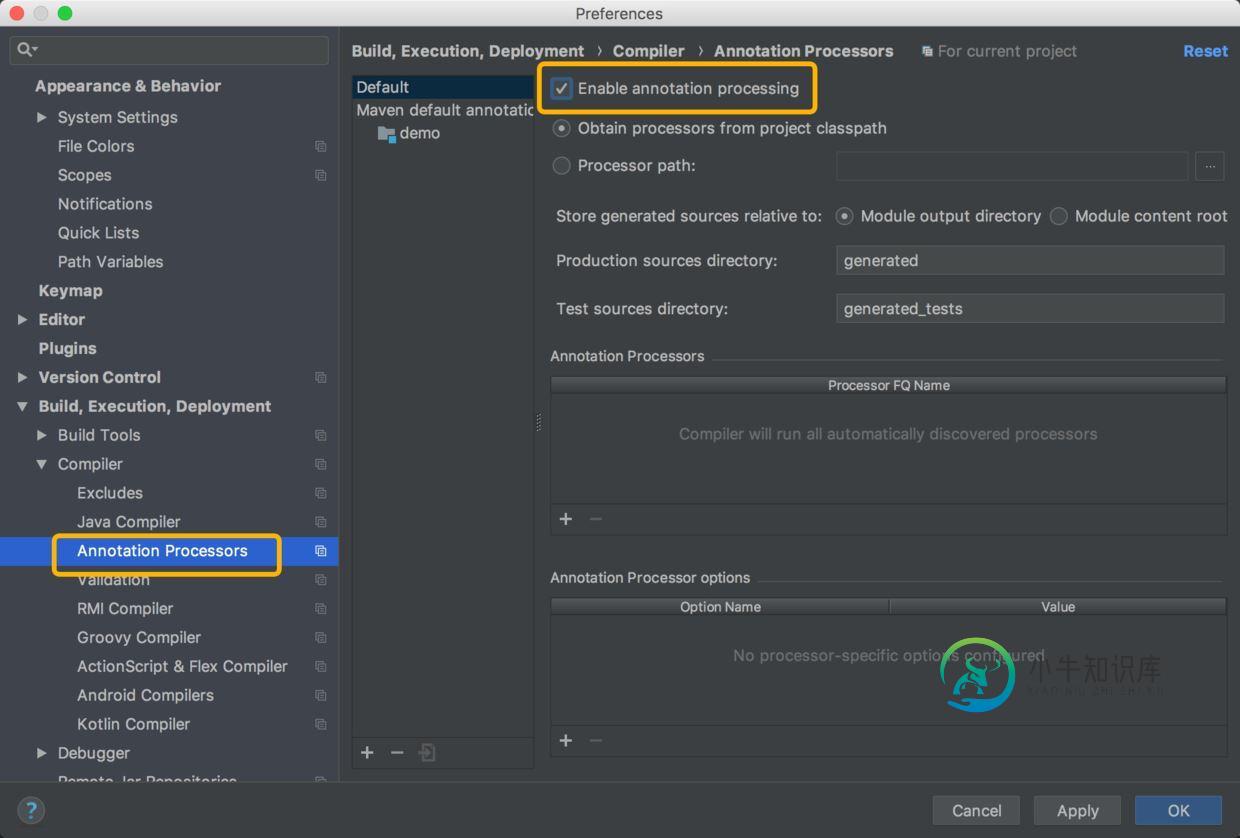
上述安装完成以后需要重启IDEA生效!
方法二:手动下载Lombok插件安装
有时由于网络原因,上面方法一这种方式安装失败,因此只能手动下载安装
下载lombok插件:
https://github.com/mplushnikov/lombok-intellij-plugin/releases
Plugins -> Install plugin from disk... 选择下载的zip包安装
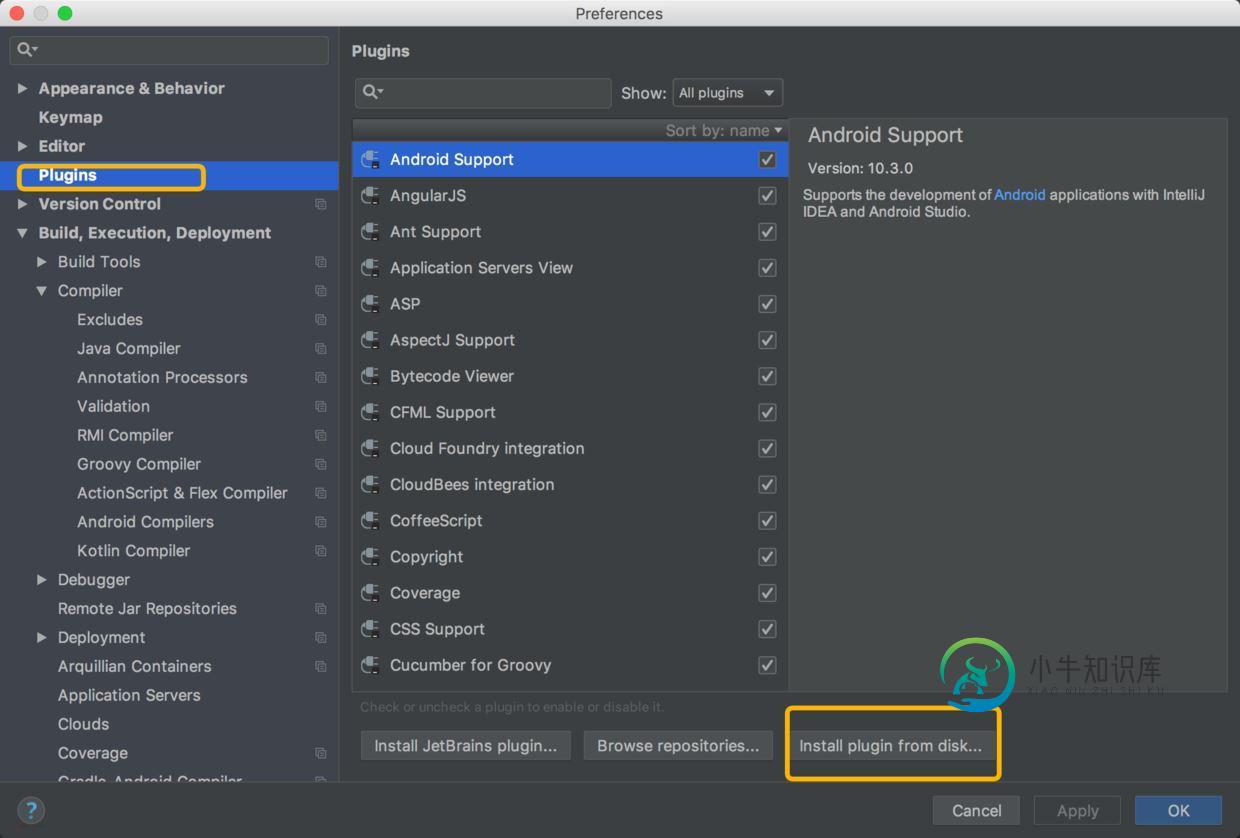
重启idea即可
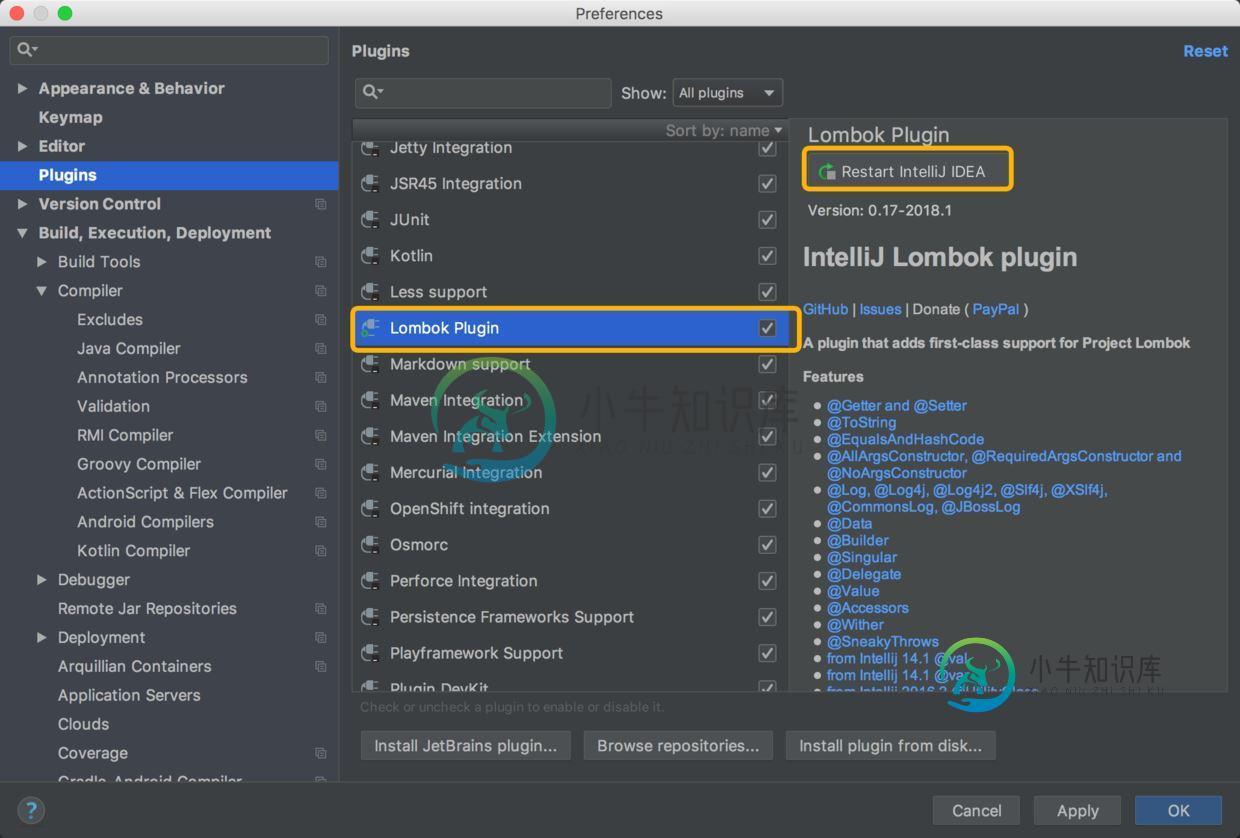
IDE中设置完成以后需要在pom.xml中添加如下所示的lombok依赖才能使用
<dependency> <groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId> <artifactId>lombok</artifactId> <version>1.16.16</version> </dependency>
Lombok主要注解
- @Getter and @Setter / 自动为属性提供 Set和Get 方法
- @ToString / 该注解的作用是为类自动生成toString()方法
- @EqualsAndHashCode / 为对象字段自动生成hashCode和equals实现
- @AllArgsConstructor, @RequiredArgsConstructor and @NoArgsConstructor / 顾名思义,为类自动生成对应参数的constructor
- @Log, @Log4j, @Log4j2, @Slf4j, @XSlf4j, @CommonsLog, @JBossLog / 自动为类添加对应的log支持
- @Data / 自动为所有字段添加@ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, @Getter,为非final字段添加@Setter,和@RequiredArgsConstructor,本质上相当于几个注解的综合效果
- @NonNull / 自动帮助我们避免空指针。作用在方法参数上的注解,用于自动生成空值参数检查
- @Cleanup / 自动帮我们调用close()方法。作用在局部变量上,在作用域结束时会自动调用close方法释放资源
下文就Lombok中用的最为频繁的@Data和@Log注解进行代码实战!
@Data注解使用
官网关于@Data注解的解释如下:
All together now: A shortcut for @ToString, @EqualsAndHashCode, @Getter on all fields, @Setter on all non-final fields, and @RequiredArgsConstructor!
不难理解,其可以看成是多个Lombok注解的集成,因此使用很方便!
先来创建一个POJO实体UserLombok,普通的写法如下:
public class UserLombok {
private final String name;
private int age;
private double score;
private String[] tags;
public UserLombok(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {
return this.age;
}
public void setScore(double score) {
this.score = score;
}
public double getScore() {
return this.score;
}
public String[] getTags() {
return this.tags;
}
public void setTags(String[] tags) {
this.tags = tags;
}
@Override public String toString() {
return "DataExample(" + this.getName() + ", " + this.getAge() + ", " + this.getScore() + ", " + Arrays.deepToString(this.getTags()) + “)”;
}
protected boolean canEqual(Object other) {
return other instanceof DataExample;
}
@Override public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this) return true;
if (!(o instanceof DataExample)) return false;
DataExample other = (DataExample) o;
if (!other.canEqual((Object)this)) return false;
if (this.getName() == null ? other.getName() != null : !this.getName().equals(other.getName())) return false;
if (this.getAge() != other.getAge()) return false;
if (Double.compare(this.getScore(), other.getScore()) != 0) return false;
if (!Arrays.deepEquals(this.getTags(), other.getTags())) return false;
return true;
}
@Override public int hashCode() {
final int PRIME = 59;
int result = 1;
final long temp1 = Double.doubleToLongBits(this.getScore());
result = (result*PRIME) + (this.getName() == null ? 43 : this.getName().hashCode());
result = (result*PRIME) + this.getAge();
result = (result*PRIME) + (int)(temp1 ^ (temp1 >>> 32));
result = (result*PRIME) + Arrays.deepHashCode(this.getTags());
return result;
}
}
Lombok加持后,写法可简化为:
@Data
public class UserLombok {
private final String name;
private int age;
private double score;
private String[] tags;
}
在IDEA中使用时,Lombok的注解会自动补全,如下图所示:
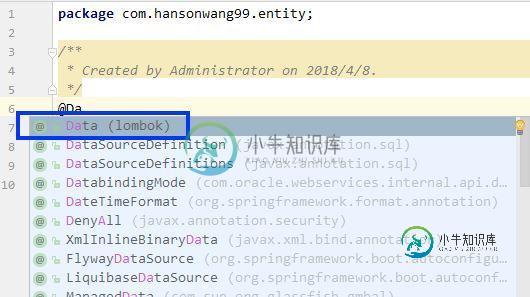
我们来写POJO的测试代码
public static void main( String[] args ) {
UserLombok userLombok = new UserLombok("hansonwang99”);
userLombok.setAge(18);
String[] array = new String[]{"apple","juice”};
userLombok.setTags( array );
userLombok.setScore( 99.0 );
System.out.println(userLombok);
}
由下图我们可以看到IDEA依然可以自动为我们补全由Lombok自动生成的代码:
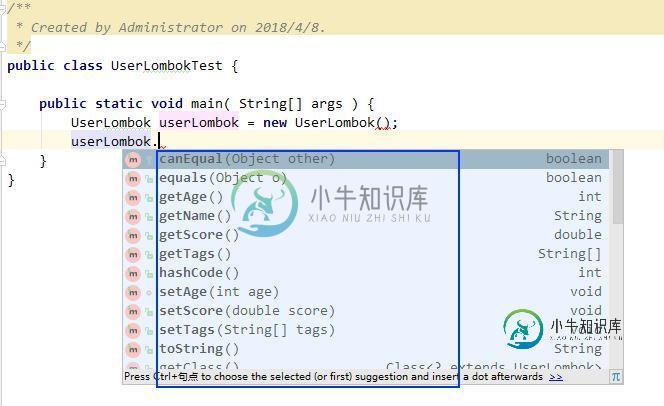
结果打印
由于Lombok为我们自动生成了toString方法,因此对象的打印结果如下:
UserLombok(name=hansonwang99, age=18, score=99.0, tags=[apple, juice])
@Log注解实战
在我的文章 Spring Boot日志框架实践 一文中,我们使用Log4j2来作为日志对象,其写法如下:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/testlogging”)
public class LoggingTestController {
private final Logger logger = LogManager.getLogger(this.getClass());
@GetMapping("/hello”)
public String hello() {
for(int i=0;i<10_0000;i++){
logger.info("info execute index method”);
logger.warn("warn execute index method”);
logger.error("error execute index method”);
}
return "My First SpringBoot Application”;
}
}
若改用Lombok后,写法变得更加简洁,我们只需要引入对应的@Log注解即可完成log对象的生成:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/testloggingwithlombok”)
@Log4j2
public class LoggingTestControllerLombok {
@GetMapping("/hello”)
public String hello() {
for(int i=0;i<10_0000;i++){
log.info("info execute index method”);
log.warn("warn execute index method”);
log.error("error execute index method”);
}
return "My First SpringBoot Application”;
}
}
怎么样,是不是一切都是那么地优雅!
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
本文向大家介绍详解Springboot 优雅停止服务的几种方法,包括了详解Springboot 优雅停止服务的几种方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在使用Springboot的时候,都要涉及到服务的停止和启动,当我们停止服务的时候,很多时候大家都是kill -9 直接把程序进程杀掉,这样程序不会执行优雅的关闭。而且一些没有执行完的程序就会直接退出。 我们很多时候都需要安全的将服务停止,
-
本文向大家介绍SpringBoot如何优雅地处理全局异常详解,包括了SpringBoot如何优雅地处理全局异常详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 前言 之前用springboot的时候,只知道捕获异常使用try{}catch,一个接口一个try{}catch,这也是大多数开发人员异常处理的常用方式,虽然屡试不爽,但会造成一个问题,就是一个Controller下面,满屏幕的try{}cat
-
本文向大家介绍Java编码辅助工具Lombok用法详解,包括了Java编码辅助工具Lombok用法详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 前言 在项目开发过程中,经常会涉及到一些调整很少但又必不可少的环节,比如实体类的Getter/Setter方法,ToString方法等。这时可以使用Lombok来避免这种重复的操作,减少非核心代码的臃肿,提高编码效率。 如何在IntelliJ IDEA中引
-
本文向大家介绍shiro编码和加密代码详解,包括了shiro编码和加密代码详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 涉及到密码存储问题上,应该加密/生成密码摘要存储,而不是存储明文密码。比如之前的600w csdn账号泄露对用户可能造成很大损失,因此应加密/生成不可逆的摘要方式存储。 编码/解码 Shiro提供了base64和16进制字符串编码/解码的API支持,方便一些编码解码操作。Shi
-
本文向大家介绍golang的httpserver优雅重启方法详解,包括了golang的httpserver优雅重启方法详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 前言 去年在做golangserver的时候,内部比较头疼的就是在线服务发布的时候,大量用户的请求在发布时候会被重连,在那时候也想了n多的方法,最后还是落在一个github上的项目,facebook的一个golang项目grace,那时
-
本文向大家介绍详解SpringBoot之集成Spring AOP,包括了详解SpringBoot之集成Spring AOP的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在开始之前,我们先把需要的jar包添加到工程里。新增Maven依赖如下: 接下来,我们进入正题。这里的涉及的通知类型有:前置通知、后置最终通知、后置返回通知、后置异常通知、环绕通知,下面我们就具体的来看一下怎么在SpringBoot中

