Android小程序实现个人信息管理系统
本文实例为大家分享了Android实现个人信息管理系统的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下
要求:使用SQLite实现个人信息管理系统,个人信息包括姓名,年龄,性别以及学历
(1)DBHelper.java代码如下:
package com.example.system;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Context;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteOpenHelper;
public class DBHelper extends SQLiteOpenHelper{
private static final String DB_NAME ="people.db";
private static final String TBL_NAME="Message";
private SQLiteDatabase db;
public DBHelper(Context c){
super(c,DB_NAME,null,2);
}
@Override
public void onCreate(SQLiteDatabase db){
this.db=db;
String CREATE_TBL="create table Message(_id integer primary key autoincrement,name text,age text,sex text,edu text)";
db.execSQL(CREATE_TBL);
}
public void insert(ContentValues values){
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
db.insert(TBL_NAME, null, values);
db.close();
}
public Cursor query(){
SQLiteDatabase db=getWritableDatabase();
Cursor c=db.query(TBL_NAME, null, null, null, null, null, null);
return c;
}
@Override
public void onUpgrade(SQLiteDatabase arg0, int arg1, int arg2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
}
}
(2)MainActivity.java代码如下:
package com.example.system;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.MenuItem;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private TextView textview;
private Button btn1,btn2;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
textview = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textview);
btn1 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn1);
btn2 = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btn2);
//添加监听器
btn1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,AddActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
btn2.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this,QueryActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
对应布局文件如下:
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="90dp" android:gravity="center" android:text="个人信息管理系统" android:textSize="40dp" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignBaseline="@+id/btn1" android:layout_alignBottom="@+id/btn1" android:layout_alignParentRight="true" android:layout_marginRight="60dp" android:text="查询" /> <Button android:id="@+id/btn1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_alignParentLeft="true" android:layout_below="@+id/textview" android:layout_marginLeft="60dp" android:layout_marginTop="100dp" android:text="添加" /> </RelativeLayout>
(3)AddActivity.java代码如下:
package com.example.system;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.ContentValues;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class AddActivity extends Activity {
//声明组件
private EditText name,age,sex,edu;
private Button add;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_add);
name=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.name);
age=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.age);
sex=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.sex);
edu=(EditText)findViewById(R.id.edu);
add=(Button)findViewById(R.id.ButtonAdd);
//根据ID 获取组件
add.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String name1=name.getText().toString();
String age1=age.getText().toString();
String sex1=sex.getText().toString();
String edu1=edu.getText().toString();
//封装信息
ContentValues values=new ContentValues();
values.put("name", name1);
values.put("age", age1);
values.put("sex", sex1);
values.put("edu", edu1);
DBHelper helper=new DBHelper(getApplicationContext());
helper.insert(values);
Intent intent = new Intent(AddActivity.this,MainActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
}
}
对应布局文件如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:orientation="vertical" android:padding="10dp"> <TableLayout android:id="@+id/TableLayout" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:stretchColumns="1"> <TableRow android:id="@+id/TableRow01" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="姓名"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/name" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=""/> </TableRow> <TableRow android:id="@+id/TableRow02" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="年龄"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/age" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=""/> </TableRow> <TableRow android:id="@+id/TableRow03" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="性别"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/sex" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=""/> </TableRow> <TableRow android:id="@+id/TableRow04" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/textview4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="学历"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/edu" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text=""/> </TableRow> <Button android:id="@+id/ButtonAdd" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="添加"/> </TableLayout> </LinearLayout>
(4)QueryActivity.java代码如下:
package com.example.system;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.app.ListActivity;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.widget.AdapterView;
import android.widget.AdapterView.OnItemClickListener;
import android.widget.ListView;
import android.widget.SimpleCursorAdapter;
public class QueryActivity extends ListActivity{
private ListView listview=null;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState){
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
this.setTitle("浏览信息");
listview=getListView();
final DBHelper helper=new DBHelper(this);
Cursor c=helper.query();
String[] from={"_id","name","age","sex","edu"};
int[] to={R.id.text0,R.id.text1,R.id.text2,R.id.text3,R.id.text4};
SimpleCursorAdapter adapter=new SimpleCursorAdapter(this, R.layout.activity_query, c, from, to);
listview.setAdapter(adapter);
}
}
对应布局文件如下:
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/text0" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text3" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/text4" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
实现效果如下:

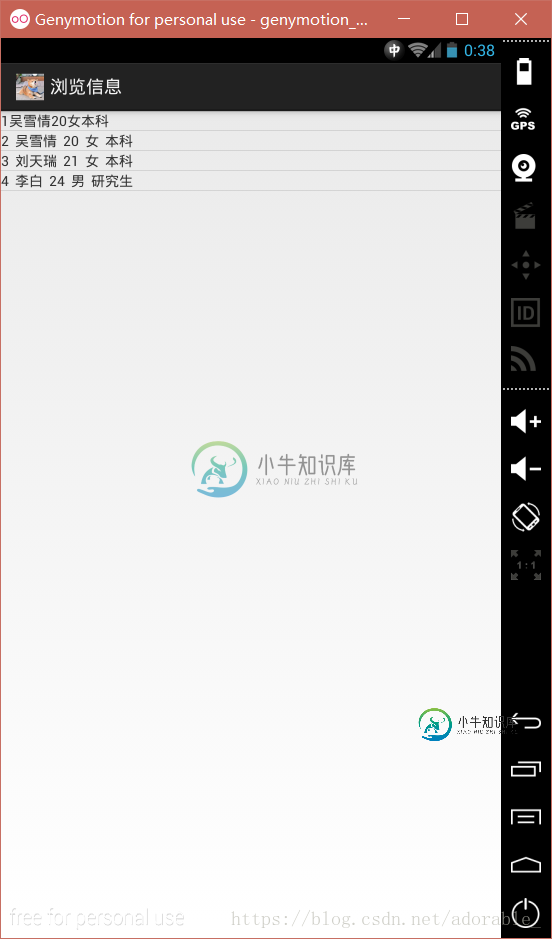
更多学习资料请关注专题《管理系统开发》。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
本文向大家介绍java实现商品信息管理系统,包括了java实现商品信息管理系统的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 超市商品管理系统,供大家参考,具体内容如下 题目要求 超市中商品分为四类,分别是食品、化妆品、日用品和饮料。每种商品都包含商品名称、价格、库存量和生产厂家、品牌等信息。主要完成对商品的销售、统计和简单管理。这个题目相对简单,可以用一张表实现信息的保存和处理,因此不再给出数据库设计
-
本文向大家介绍C#实现学员信息管理系统,包括了C#实现学员信息管理系统的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 新手写一段学员信息管理系统,有代码冗余的情况请谅解,代码如下,请大神指点 以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持呐喊教程。
-
本文向大家介绍python3.6实现学生信息管理系统,包括了python3.6实现学生信息管理系统的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 简单版本学生信息管理系统,用python基础语法实现,基于python 3.6 容错率很高的代码,做了很多异常处理功能,出错也不会丢失信息 启动时自动从文件中读取已有学生信息,退出时自动保存 程序分3个模块: Menu:进行菜单管理 Student_manag
-
本文向大家介绍JSP实现客户信息管理系统,包括了JSP实现客户信息管理系统的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了JSP实现客户信息管理系统的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 项目示意图大概这样吧。我自己画的 登录界面代码 index.jsp: 完全没技术含量的,直接调用一个servlet控制的是否登录 控制登录的 LoginServlet 进来之后就到我们的主页后点击添加
-
本文向大家介绍C++实现景区信息管理系统,包括了C++实现景区信息管理系统的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例为大家分享了C++实现景区信息管理系统的具体代码,供大家参考,具体内容如下 1.1 建立主程序应用菜单选项 主程序应用菜单选项包含所实现的所有功能,并且对选项采用数字标识进行选择,对其他错误输入可以进行判别,提示输入错误。 1.2 导游线路图的创建级景区分布图的输出 用邻接
-
本文向大家介绍用java实现学生信息管理系统,包括了用java实现学生信息管理系统的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 用java写的学生信息管理系统,供大家参考,具体内容如下 使用到了集合类ArrayLisat 来对Student类的对象进行存储。 StudentManagerTest为主类,Student类里面进行了相应数据的封装。里面用了很多循环来写,并且运用了很多标记来进行判断是否退出

