Linux编程之PING实现
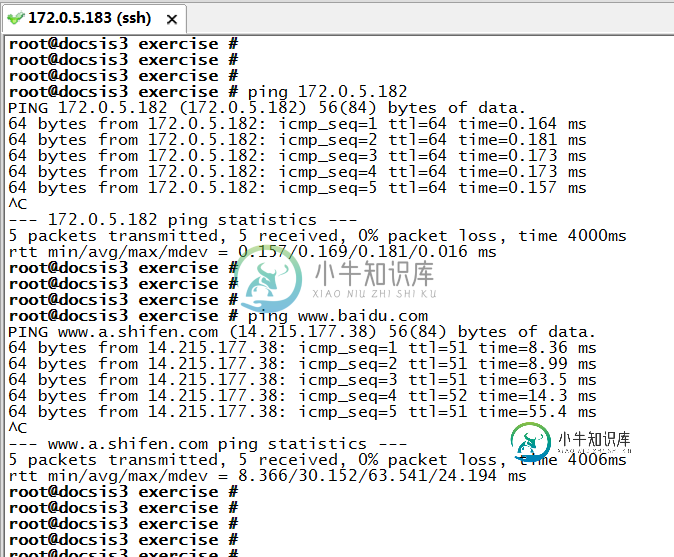
PING(Packet InterNet Groper)中文名为因特网包探索器,是用来查看网络上另一个主机系统的网络连接是否正常的一个工具。ping命令的工作原理是:向网络上的另一个主机系统发送ICMP报文,如果指定系统得到了报文,它将把回复报文传回给发送者,这有点象潜水艇声纳系统中使用的发声装置。所以,我们想知道我这台主机能不能和另一台进行通信,我们首先需要确认的是我们两台主机间的网络是不是通的,也就是我说的话能不能传到你那里,这是双方进行通信的前提。在Linux下使用指令ping的方法和现象如下:
PING的实现看起来并不复杂,我想自己写代码实现这个功能,需要些什么知识储备?我简单罗列了一下:
·ICMP协议的理解
·RAW套接字
·网络封包和解包技能
搭建这么一个ping程序的步骤如下:
1、ICMP包的封装和解封
2、创建一个线程用于ICMP包的发送
3、创建一个线程用于ICMP包的接收
4、原始套接字编程
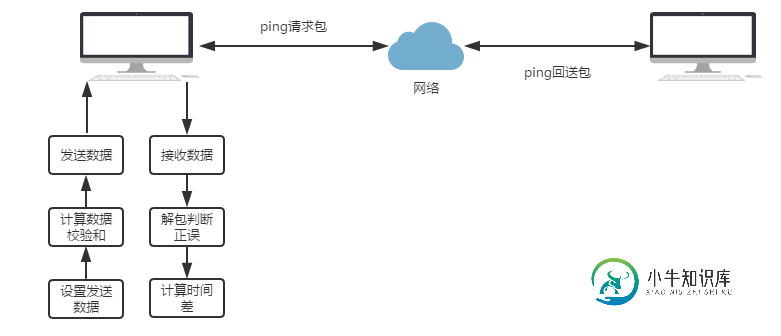
PING的流程如下:
一、ICMP包的封装和解封
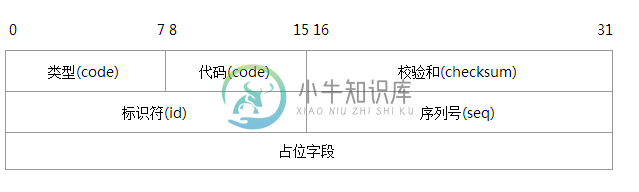
(1) ICMP协议理解要进行PING的开发,我们首先需要知道PING的实现是基于ICMP协议来开发的。要进行ICMP包的封装和解封,我们首先需要理解ICMP协议。ICMP位于网络层,允许主机或者路由器报告差错情况和提供有关异常情况的报告。ICMP报文是封装在IP数据报中,作为其中的数据部分。ICMP报文作为IP层数据报的数据,加上数据报头,组成IP数据报发送出去。ICMP报文格式如下:
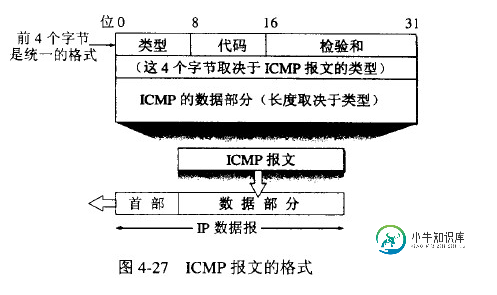
ICMP报文的种类有两种,即ICMP差错报告报文和ICMP询问报文。PING程序使用的ICMP报文种类为ICMP询问报文。注意一下上面说到的ICMP报文格式中的“类型”字段,我们在组包的时候可以向该字段填写不同的值来标定该ICMP报文的类型。下面列出的是几种常用的ICMP报文类型。
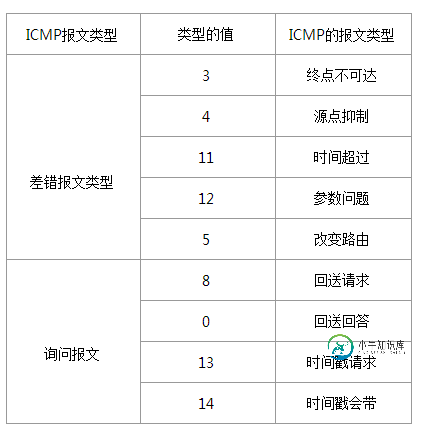
我们的PING程序需要用到的ICMP的类型是回送请求(8)。
因为ICMP报文的具体格式会因为ICMP报文的类型而各不相同,我们ping包的格式是这样的:
(2) ICMP包的组装
对照上面的ping包格式,我们封装ping包的代码可以这么写:
void icmp_pack(struct icmp* icmphdr, int seq, int length)
{
int i = 0;
icmphdr->icmp_type = ICMP_ECHO; //类型填回送请求
icmphdr->icmp_code = 0;
icmphdr->icmp_cksum = 0; //注意,这里先填写0,很重要!
icmphdr->icmp_seq = seq; //这里的序列号我们填1,2,3,4....
icmphdr->icmp_id = pid & 0xffff; //我们使用pid作为icmp_id,icmp_id只是2字节,而pid有4字节
for(i=0;i<length;i++)
{
icmphdr->icmp_data[i] = i; //填充数据段,使ICMP报文大于64B
}
icmphdr->icmp_cksum = cal_chksum((unsigned short*)icmphdr, length); //校验和计算
}
这里再三提醒一下,icmp_cksum 必须先填写为0再执行校验和算法计算,否则ping时对方主机会因为校验和计算错误而丢弃请求包,导致ping的失败。我一个同事曾经就因为这么一个错误而排查许久,血的教训请铭记。
这里简单介绍一下checksum(校验和)。
计算机网络通信时,为了检验在数据传输过程中数据是否发生了错误,通常在传输数据的时候连同校验和一块传输,当接收端接受数据时候会从新计算校验和,如果与原校验和不同就视为出错,丢弃该数据包,并返回icmp报文。
算法基本思路:
IP/ICMP/IGMP/TCP/UDP等协议的校验和算法都是相同的,采用的都是将数据流视为16位整数流进行重复叠加计算。为了计算检验和,首先把检验和字段置为0。然后,对有效数据范围内中每个16位进行二进制反码求和,结果存在检验和字段中,如果数据长度为奇数则补一字节0。当收到数据后,同样对有效数据范围中每个16位数进行二进制反码的求和。由于接收方在计算过程中包含了发送方存在首部中的检验和,因此,如果首部在传输过程中没有发生任何差错,那么接收方计算的结果应该为全0或全1(具体看实现了,本质一样) 。如果结果不是全0或全1,那么表示数据错误。
/*校验和算法*/
unsigned short cal_chksum(unsigned short *addr,int len)
{ int nleft=len;
int sum=0;
unsigned short *w=addr;
unsigned short answer=0;
/*把ICMP报头二进制数据以2字节为单位累加起来*/
while(nleft>1)
{
sum+=*w++;
nleft-=2;
}
/*若ICMP报头为奇数个字节,会剩下最后一字节。把最后一个字节视为一个2字节数据的高字节,这个2字节数据的低字节为0,继续累加*/
if( nleft==1)
{
*(unsigned char *)(&answer)=*(unsigned char *)w;
sum+=answer;
}
sum=(sum>>16)+(sum&0xffff);
sum+=(sum>>16);
answer=~sum;
return answer;
}
(3) ICMP包的解包
知道怎么封装包,那解包就也不难了,注意的是,收到一个ICMP包,我们不要就认为这个包就是我们发出去的ICMP回送回答包,我们需要加一层代码来判断该ICMP报文的id和seq字段是否符合我们发送的ICMP报文的设置,来验证ICMP回复包的正确性。
int icmp_unpack(char* buf, int len)
{
int iphdr_len;
struct timeval begin_time, recv_time, offset_time;
int rtt; //round trip time
struct ip* ip_hdr = (struct ip *)buf;
iphdr_len = ip_hdr->ip_hl*4;
struct icmp* icmp = (struct icmp*)(buf+iphdr_len); //使指针跳过IP头指向ICMP头
len-=iphdr_len; //icmp包长度
if(len < 8) //判断长度是否为ICMP包长度
{
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid icmp packet.Its length is less than 8\n");
return -1;
}
//判断该包是ICMP回送回答包且该包是我们发出去的
if((icmp->icmp_type == ICMP_ECHOREPLY) && (icmp->icmp_id == pid))
{
if((icmp->icmp_seq < 0) || (icmp->icmp_seq > PACKET_SEND_MAX_NUM))
{
fprintf(stderr, "icmp packet seq is out of range!\n");
return -1;
}
ping_packet[icmp->icmp_seq].flag = 0;
begin_time = ping_packet[icmp->icmp_seq].begin_time; //去除该包的发出时间
gettimeofday(&recv_time, NULL);
offset_time = cal_time_offset(begin_time, recv_time);
rtt = offset_time.tv_sec*1000 + offset_time.tv_usec/1000; //毫秒为单位
printf("%d byte from %s: icmp_seq=%u ttl=%d rtt=%d ms\n",
len, inet_ntoa(ip_hdr->ip_src), icmp->icmp_seq, ip_hdr->ip_ttl, rtt);
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid ICMP packet! Its id is not matched!\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
二、发包线程的搭建
根据PING程序的框架,我们需要建立一个线程用于ping包的发送,我的想法是这样的:使用sendto进行发包,发包速率我们维持在1秒1发,我们需要用一个全局变量记录第一个ping包发出的时间,除此之外,我们还需要一个全局变量来记录我们发出的ping包到底有几个,这两个变量用于后来收到ping包回复后的数据计算。
void ping_send()
{
char send_buf[128];
memset(send_buf, 0, sizeof(send_buf));
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL); //记录第一个ping包发出的时间
while(alive)
{
int size = 0;
gettimeofday(&(ping_packet[send_count].begin_time), NULL);
ping_packet[send_count].flag = 1; //将该标记为设置为该包已发送
icmp_pack((struct icmp*)send_buf, send_count, 64); //封装icmp包
size = sendto(rawsock, send_buf, 64, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&dest, sizeof(dest));
send_count++; //记录发出ping包的数量
if(size < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "send icmp packet fail!\n");
continue;
}
sleep(1);
}
}
三、收包线程的搭建
我们同样建立一个接收包的线程,这里我们采用select函数进行收包,并为select函数设置超时时间为200us,若发生超时,则进行下一个循环。同样地,我们也需要一个全局变量来记录成功接收到的ping回复包的数量。
void ping_recv()
{
struct timeval tv;
tv.tv_usec = 200; //设置select函数的超时时间为200us
tv.tv_sec = 0;
fd_set read_fd;
char recv_buf[512];
memset(recv_buf, 0 ,sizeof(recv_buf));
while(alive)
{
int ret = 0;
FD_ZERO(&read_fd);
FD_SET(rawsock, &read_fd);
ret = select(rawsock+1, &read_fd, NULL, NULL, &tv);
switch(ret)
{
case -1:
fprintf(stderr,"fail to select!\n");
break;
case 0:
break;
default:
{
int size = recv(rawsock, recv_buf, sizeof(recv_buf), 0);
if(size < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"recv data fail!\n");
continue;
}
ret = icmp_unpack(recv_buf, size); //对接收的包进行解封
if(ret == -1) //不是属于自己的icmp包,丢弃不处理
{
continue;
}
recv_count++; //接收包计数
}
break;
}
}
}
四、中断处理
我们规定了一次ping发送的包的最大值为64个,若超出该数值就停止发送。作为PING的使用者,我们一般只会发送若干个包,若有这几个包顺利返回,我们就crtl+c中断ping。这里的代码主要是为中断信号写一个中断处理函数,将alive这个全局变量设置为0,进而使发送ping包的循环停止而结束程序。
void icmp_sigint(int signo)
{
alive = 0;
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
time_interval = cal_time_offset(start_time, end_time);
}
signal(SIGINT, icmp_sigint);
五、总体实现
各模块介绍完了,现在贴出完整代码。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <netinet/ip.h>
#include <netinet/ip_icmp.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <sys/time.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <netdb.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#define PACKET_SEND_MAX_NUM 64
typedef struct ping_packet_status
{
struct timeval begin_time;
struct timeval end_time;
int flag; //发送标志,1为已发送
int seq; //包的序列号
}ping_packet_status;
ping_packet_status ping_packet[PACKET_SEND_MAX_NUM];
int alive;
int rawsock;
int send_count;
int recv_count;
pid_t pid;
struct sockaddr_in dest;
struct timeval start_time;
struct timeval end_time;
struct timeval time_interval;
/*校验和算法*/
unsigned short cal_chksum(unsigned short *addr,int len)
{ int nleft=len;
int sum=0;
unsigned short *w=addr;
unsigned short answer=0;
/*把ICMP报头二进制数据以2字节为单位累加起来*/
while(nleft>1)
{
sum+=*w++;
nleft-=2;
}
/*若ICMP报头为奇数个字节,会剩下最后一字节。把最后一个字节视为一个2字节数据的高字节,这个2字节数据的低字节为0,继续累加*/
if( nleft==1)
{
*(unsigned char *)(&answer)=*(unsigned char *)w;
sum+=answer;
}
sum=(sum>>16)+(sum&0xffff);
sum+=(sum>>16);
answer=~sum;
return answer;
}
struct timeval cal_time_offset(struct timeval begin, struct timeval end)
{
struct timeval ans;
ans.tv_sec = end.tv_sec - begin.tv_sec;
ans.tv_usec = end.tv_usec - begin.tv_usec;
if(ans.tv_usec < 0) //如果接收时间的usec小于发送时间的usec,则向sec域借位
{
ans.tv_sec--;
ans.tv_usec+=1000000;
}
return ans;
}
void icmp_pack(struct icmp* icmphdr, int seq, int length)
{
int i = 0;
icmphdr->icmp_type = ICMP_ECHO;
icmphdr->icmp_code = 0;
icmphdr->icmp_cksum = 0;
icmphdr->icmp_seq = seq;
icmphdr->icmp_id = pid & 0xffff;
for(i=0;i<length;i++)
{
icmphdr->icmp_data[i] = i;
}
icmphdr->icmp_cksum = cal_chksum((unsigned short*)icmphdr, length);
}
int icmp_unpack(char* buf, int len)
{
int iphdr_len;
struct timeval begin_time, recv_time, offset_time;
int rtt; //round trip time
struct ip* ip_hdr = (struct ip *)buf;
iphdr_len = ip_hdr->ip_hl*4;
struct icmp* icmp = (struct icmp*)(buf+iphdr_len);
len-=iphdr_len; //icmp包长度
if(len < 8) //判断长度是否为ICMP包长度
{
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid icmp packet.Its length is less than 8\n");
return -1;
}
//判断该包是ICMP回送回答包且该包是我们发出去的
if((icmp->icmp_type == ICMP_ECHOREPLY) && (icmp->icmp_id == pid))
{
if((icmp->icmp_seq < 0) || (icmp->icmp_seq > PACKET_SEND_MAX_NUM))
{
fprintf(stderr, "icmp packet seq is out of range!\n");
return -1;
}
ping_packet[icmp->icmp_seq].flag = 0;
begin_time = ping_packet[icmp->icmp_seq].begin_time;
gettimeofday(&recv_time, NULL);
offset_time = cal_time_offset(begin_time, recv_time);
rtt = offset_time.tv_sec*1000 + offset_time.tv_usec/1000; //毫秒为单位
printf("%d byte from %s: icmp_seq=%u ttl=%d rtt=%d ms\n",
len, inet_ntoa(ip_hdr->ip_src), icmp->icmp_seq, ip_hdr->ip_ttl, rtt);
}
else
{
fprintf(stderr, "Invalid ICMP packet! Its id is not matched!\n");
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
void ping_send()
{
char send_buf[128];
memset(send_buf, 0, sizeof(send_buf));
gettimeofday(&start_time, NULL); //记录第一个ping包发出的时间
while(alive)
{
int size = 0;
gettimeofday(&(ping_packet[send_count].begin_time), NULL);
ping_packet[send_count].flag = 1; //将该标记为设置为该包已发送
icmp_pack((struct icmp*)send_buf, send_count, 64); //封装icmp包
size = sendto(rawsock, send_buf, 64, 0, (struct sockaddr*)&dest, sizeof(dest));
send_count++; //记录发出ping包的数量
if(size < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr, "send icmp packet fail!\n");
continue;
}
sleep(1);
}
}
void ping_recv()
{
struct timeval tv;
tv.tv_usec = 200; //设置select函数的超时时间为200us
tv.tv_sec = 0;
fd_set read_fd;
char recv_buf[512];
memset(recv_buf, 0 ,sizeof(recv_buf));
while(alive)
{
int ret = 0;
FD_ZERO(&read_fd);
FD_SET(rawsock, &read_fd);
ret = select(rawsock+1, &read_fd, NULL, NULL, &tv);
switch(ret)
{
case -1:
fprintf(stderr,"fail to select!\n");
break;
case 0:
break;
default:
{
int size = recv(rawsock, recv_buf, sizeof(recv_buf), 0);
if(size < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"recv data fail!\n");
continue;
}
ret = icmp_unpack(recv_buf, size); //对接收的包进行解封
if(ret == -1) //不是属于自己的icmp包,丢弃不处理
{
continue;
}
recv_count++; //接收包计数
}
break;
}
}
}
void icmp_sigint(int signo)
{
alive = 0;
gettimeofday(&end_time, NULL);
time_interval = cal_time_offset(start_time, end_time);
}
void ping_stats_show()
{
long time = time_interval.tv_sec*1000+time_interval.tv_usec/1000;
/*注意除数不能为零,这里send_count有可能为零,所以运行时提示错误*/
printf("%d packets transmitted, %d recieved, %d%c packet loss, time %ldms\n",
send_count, recv_count, (send_count-recv_count)*100/send_count, '%', time);
}
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int size = 128*1024;//128k
struct protoent* protocol = NULL;
char dest_addr_str[80];
memset(dest_addr_str, 0, 80);
unsigned int inaddr = 1;
struct hostent* host = NULL;
pthread_t send_id,recv_id;
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("Invalid IP ADDRESS!\n");
return -1;
}
protocol = getprotobyname("icmp"); //获取协议类型ICMP
if(protocol == NULL)
{
printf("Fail to getprotobyname!\n");
return -1;
}
memcpy(dest_addr_str, argv[1], strlen(argv[1])+1);
rawsock = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_RAW,protocol->p_proto);
if(rawsock < 0)
{
printf("Fail to create socket!\n");
return -1;
}
pid = getpid();
setsockopt(rawsock, SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &size, sizeof(size)); //增大接收缓冲区至128K
bzero(&dest,sizeof(dest));
dest.sin_family = AF_INET;
inaddr = inet_addr(argv[1]);
if(inaddr == INADDR_NONE) //判断用户输入的是否为IP地址还是域名
{
//输入的是域名地址
host = gethostbyname(argv[1]);
if(host == NULL)
{
printf("Fail to gethostbyname!\n");
return -1;
}
memcpy((char*)&dest.sin_addr, host->h_addr, host->h_length);
}
else
{
memcpy((char*)&dest.sin_addr, &inaddr, sizeof(inaddr));//输入的是IP地址
}
inaddr = dest.sin_addr.s_addr;
printf("PING %s, (%d.%d.%d.%d) 56(84) bytes of data.\n",dest_addr_str,
(inaddr&0x000000ff), (inaddr&0x0000ff00)>>8,
(inaddr&0x00ff0000)>>16, (inaddr&0xff000000)>>24);
alive = 1; //控制ping的发送和接收
signal(SIGINT, icmp_sigint);
if(pthread_create(&send_id, NULL, (void*)ping_send, NULL))
{
printf("Fail to create ping send thread!\n");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&recv_id, NULL, (void*)ping_recv, NULL))
{
printf("Fail to create ping recv thread!\n");
return -1;
}
pthread_join(send_id, NULL);//等待send ping线程结束后进程再结束
pthread_join(recv_id, NULL);//等待recv ping线程结束后进程再结束
ping_stats_show();
close(rawsock);
return 0;
}
编译以及实验现象如下:
我的实验环境是两台服务器,发起ping的主机是172.0.5.183,被ping的主机是172.0.5.182,以下是我的两次实验现象(ping IP和ping 域名)。
特别注意:
只有root用户才能利用socket()函数生成原始套接字,要让Linux的一般用户能执行以上程序,需进行如下的特别操作:用root登陆,编译以上程序gcc -lpthread -o ping ping.c
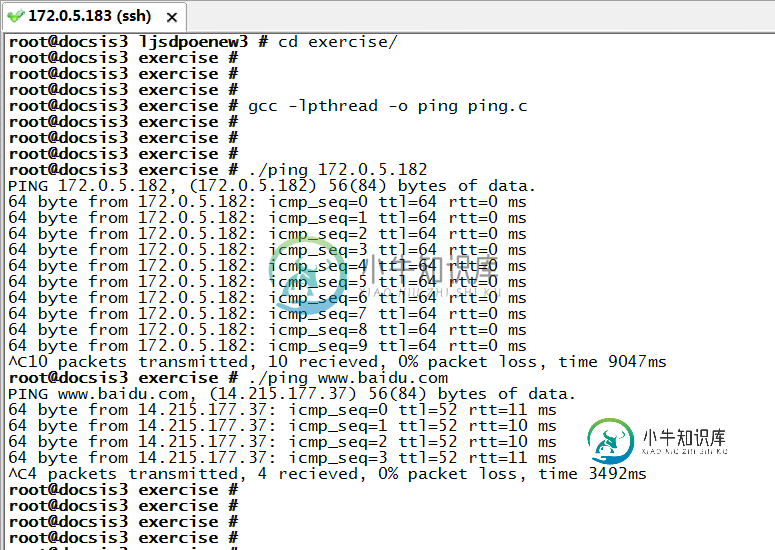
实验现象可以看出,PING是成功的,表明两主机间的网络是通的,发出的所有ping包都收到了回复。
下面是Linux系统自带的PING程序,我们可以对比一下我们设计的PING程序跟系统自带的PING程序有何不同。
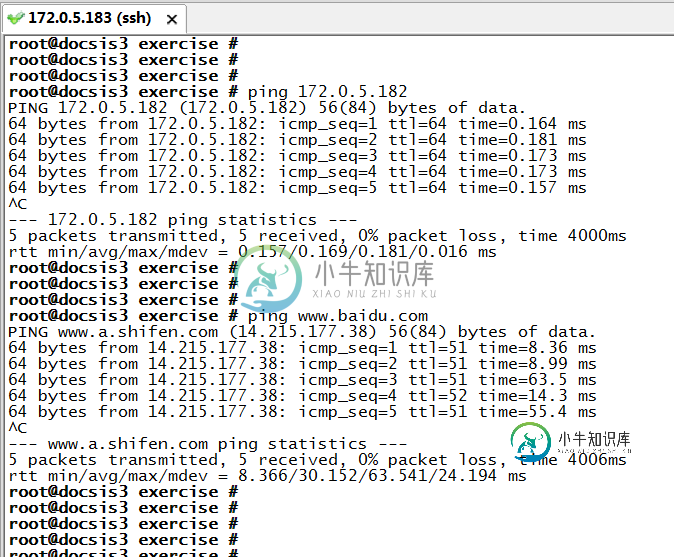
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
本文向大家介绍linux编程之pipe()函数详解,包括了linux编程之pipe()函数详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 管道是一种把两个进程之间的标准输入和标准输出连接起来的机制,从而提供一种让多个进程间通信的方法,当进程创建管道时,每次都需要提供两个文件描述符来操作管道。其中一个对管道进行写操作,另一个对管道进行读操作。对管道的读写与一般的IO系统函数一致,使用write()函数
-
本文向大家介绍Linux Socket 编程简介和实现,包括了Linux Socket 编程简介和实现的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在 TCP/IP 协议中,"IP地址 + TCP或UDP端口号" 可以唯一标识网络通讯中的一个进程,"IP地址+端口号" 就称为 socket。本文以一个简单的 TCP 协议为例,介绍如何创建基于 TCP 协议的网络程序。 TCP 协议通讯流程 下图描述了
-
本文向大家介绍Linux 进程通信之FIFO的实现,包括了Linux 进程通信之FIFO的实现的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 FIFO通信(first in first out) FIFO 有名管道,实现无血缘关系进程通信。 创建一个管道的伪文件 a.mkfifo testfifo 命令创建 b.也可以使用函数int mkfifo(const char *pathname, mode_t
-
本文向大家介绍Linux网络编程之UDP Socket程序示例,包括了Linux网络编程之UDP Socket程序示例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在网络传输协议中,TCP协议提供的是一种可靠的,复杂的,面向连接的数据流(SOCK_STREAM)传输服务,它通过三段式握手过程建立连接。TCP有一种“重传确认”机制,即接收端收到数据后要发出一个肯定确认的信号,发送端如果收到接收端肯定确认
-
本文向大家介绍对Linux下shell编程之for循环的实例讲解,包括了对Linux下shell编程之for循环的实例讲解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 linux 下 for 循环中可以使用 break 和 continue 关键字来跳出循环, 和java 用法一致 一、常用for循环结构 二、常用测试结构 1. 输出3次uptime 2. 批量解压缩当前文件夹下所有的.tar.gz
-
本文向大家介绍JavaScript之AOP编程实例,包括了JavaScript之AOP编程实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了JavaScript之AOP编程。分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下: 希望本文所述对大家的javascript程序设计有所帮助。

