Android App中各种数据保存方式的使用实例总结
少量数据保存之SharedPreferences接口实例
SharedPreferences数据保存主要是通过键值的方式存储在xml文件中
xml文件在data/此程序的包名/XX.xml。
格式:
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='utf-8' standalone='yes' ?> <map> <int name="count" value="3" /> <string name="time">写入日期:2013年10月07日,时间:11:28:09</string> </map>
SharedPreferences读写的基本步骤:
读:
1.通过Context的getSharedPreferences获取SharedPreferences接口的对象share:SharedPreferences share = this.getSharedPreferences("share",Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
"shre"保存的xml文件名 ,Context.MODE_PRIVATE 保存的类型为只被本程序访问 (还有MODE_WORLD_READABLE表示其余的程序能够读不能写,MODE
_WORLD_WRITEBLE能读写 这两个都在api17的时候被废了)
2.通过share的getXXX的方法获取指定key的值 : share.getInt("count", 0);
写:
1.通过SharedPreferences对象的edit()方法获取Edit对象:Edit editor = share.edit();
2.通过editor对象的putXXX方法来写入值 :editor.putInt("count", 1);
3.调用Editor的commit()方法提交修改值 :editor.commit();
访问其他程序的SharedPreferences
访问其他程序的SharedPreferences 的读写唯一不同的是先的获取该程序的Context接口对象:this.createPackageContext(packageName, flags)
packageName为要该目标程序的包名,flags访问类型
其余的就和上面的步骤差不多 就不再概叙
实例
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <Button android:id="@+id/write" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:text="写入数据" /> <Button android:id="@+id/read" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:text="读入数据" /> <TextView android:id="@+id/txtCount" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/txt1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
package com.android.xiong.sharepreferencestest;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.content.Context;
import android.content.SharedPreferences;
import android.content.SharedPreferences.Editor;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button write;
private Button read;
private TextView txt1;
private TextView countTxt;
SharedPreferences share ;
Editor editor;
int countO=0;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
//获取SharedPreferences对象
share = this.getSharedPreferences("share",
Context.MODE_PRIVATE);
//获取Editor对象
editor = share.edit();
write = (Button) findViewById(R.id.write);
read = (Button) findViewById(R.id.read);
txt1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txt1);
countTxt=(TextView)findViewById(R.id.txtCount);
//获取share中key为count的值
countO=share.getInt("count", 0);
countO++;
//修改share中key为count的值
editor.putInt("count", countO);
//提交修改
editor.commit();
System.out.println("该应用程序使用了:"+countO+"次");
countTxt.setText("该应用程序使用了:"+countO+"次");
OnClickListener writeListener = new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
SimpleDateFormat data = new SimpleDateFormat(
"写入日期:yyyy年MM月dd日,时间:hh:mm:ss");
editor.putString("time",
data.format(new Date()));
editor.commit();
}
};
OnClickListener readListener=new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
if(!share.contains("share")){
txt1.setText(share.getString("time", null));
}
}
};
write.setOnClickListener(writeListener);
read.setOnClickListener(readListener);
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
机身内存数据读写(Internal Storage)
1.机身内存读取主要用个两个类文件输入流(FileInputStream)和文件输出流(FileOutputStream): FileInputStream fileInput = this.openFileInput("test.txt") 第一个参数为 data/此程序包名/data/test.txt 文件下 的文件名 ;
FileOutputStream fileOut = this.openFileOutput("test.txt",this.MODE_APPEND)第一个参数表示文件名 第二个参数表示打开的方式
2.获取了文件输入输出流之后 其后的文件的读写和基本的IO操作一样
机身内存数据读写实例
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <EditText android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@+id/ed1" android:inputType="textMultiLine"/> <Button android:id="@+id/write" android:text="写入" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> <Button android:id="@+id/read" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="读入"/> <EditText android:id="@+id/ed2" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType="textMultiLine"/> <Button android:id="@+id/delete" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="删除指定的文件" /> <EditText android:id="@+id/ed3" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> </LinearLayout>
package com.android.xiong.fileiotest;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.List;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button read;
private Button write;
private EditText ed1;
private EditText ed2;
private EditText ed3;
private Button delete;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
read = (Button) findViewById(R.id.read);
write = (Button) findViewById(R.id.write);
delete = (Button) findViewById(R.id.delete);
ed3 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.ed3);
ed2 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.ed2);
ed1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.ed1);
write.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String str = ed1.getText().toString();
if (!str.equals("")) {
write(str);
}
}
});
read.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
read();
}
});
delete.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
String str = ed3.getText().toString();
if (!str.equals("")) {
deleteFiles(str);
} else {
ed3.setText(str + ":该文件输入错误或不存在!");
}
}
});
}
private void write(String content) {
try {
// 以追加的方式打开文件输出流
FileOutputStream fileOut = this.openFileOutput("test.txt",
this.MODE_APPEND);
// 写入数据
fileOut.write(content.getBytes());
// 关闭文件输出流
fileOut.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
private void read() {
try {
ed2.setText("");
// 打开文件输入流
FileInputStream fileInput = this.openFileInput("test.txt");
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(
fileInput));
String str = null;
StringBuilder stb = new StringBuilder();
while ((str = br.readLine()) !=null ) {
stb.append(str);
}
ed2.setText(stb);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//删除指定的文件
private void deleteFiles(String fileName) {
try {
// 获取data文件中的所有文件列表
List<String> name = Arrays.asList(this.fileList());
if (name.contains(fileName)) {
this.deleteFile(fileName);
ed3.setText(fileName + ":该文件成功删除!");
} else
ed3.setText(fileName + ":该文件输入错误或不存在!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
SDcard(External Storage)读写数据实例
1.SDcard数据读写需要注定的先要在Androidmainfest.xml文件中注册新建删除和读写的权限 :
<!-- 在SD卡上创建与删除权限 --> <uses-permission Android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_FORMAT_FILESYSTEMS" /> <!-- 向SD卡上写入权限 --> <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
2.读写的基本流程就是:
2.1 通过Environment类的getExternalStorageState()方法来判断手机是否有SDcard:
Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)
2.2 最通过getExternalStorageDirectory()方法来获取文件目录:
读写的文件都在sdcrad文件夹中 通过File Explorer可以导出来File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory().getCanonicalPath() + "/test.txt");
2.3 其后就和基本IO操作相同了
2.4还有要注意一点的是 在运行的模拟器的时候要附带虚拟的SDcard时 要在Run as->Run Configurations 中要关联一下 如下图
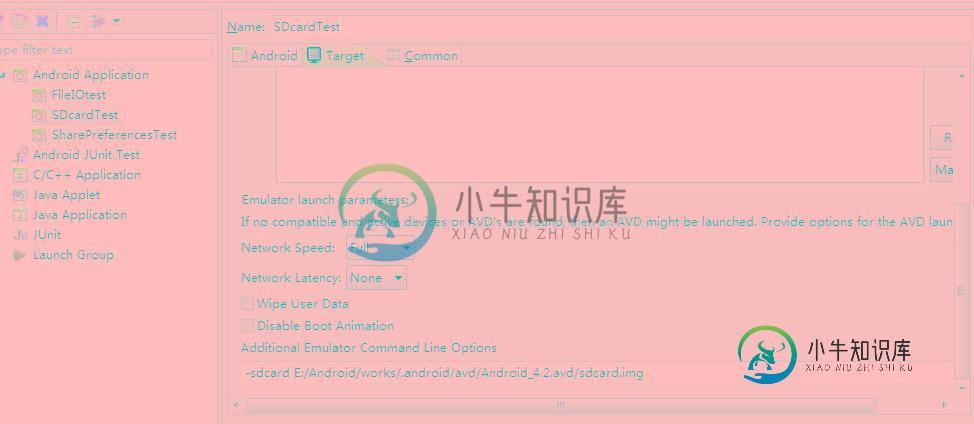 SDcard数据读写实例
SDcard数据读写实例
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:gravity="center_horizontal" android:orientation="vertical" tools:context=".MainActivity" > <EditText android:id="@+id/ed1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:inputType="textMultiLine"/> <Button android:id="@+id/write" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="写入SD卡中"/> <Button android:id="@+id/read" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="读取SD文件"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/txt1" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"/> </LinearLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.android.xiong.sdcardtest"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="14"
android:targetSdkVersion="17" />
<!-- 在SD卡上创建与删除权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.MOUNT_FORMAT_FILESYSTEMS" />
<!-- 向SD卡上写入权限 -->
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.WRITE_EXTERNAL_STORAGE" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.android.xiong.sdcardtest.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
package com.android.xiong.sdcardtest;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.os.Environment;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
private Button write;
private Button read;
private EditText ed1;
private TextView txt1;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
write = (Button) findViewById(R.id.write);
read = (Button) findViewById(R.id.read);
ed1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.ed1);
txt1 = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.txt1);
write.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
writeSDcard(ed1.getText().toString());
}
});
read.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
txt1.setText(readSDcard());
}
});
}
// 把数据写入SD卡
private void writeSDcard(String str) {
try {
// 判断是否存在SD卡
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(
Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
// 获取SD卡的目录
File file = Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory();
FileOutputStream fileW = new FileOutputStream(file.getCanonicalPath() + "/test.txt");
fileW.write(str.getBytes());
fileW.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 从SD卡中读取数据
private String readSDcard() {
StringBuffer str = new StringBuffer();
try {
// 判断是否存在SD
if (Environment.getExternalStorageState().equals(
Environment.MEDIA_MOUNTED)) {
File file = new File(Environment.getExternalStorageDirectory()
.getCanonicalPath() + "/test.txt");
// 判断是否存在该文件
if (file.exists()) {
// 打开文件输入流
FileInputStream fileR = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader reads = new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(fileR));
String st = null;
while ((st =reads.readLine())!=null ) {
str.append(st);
}
fileR.close();
} else {
txt1.setText("该目录下文件不存在");
}
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str.toString();
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
SQLite简介和简单的登录与注册源代码
1.获取SQLiteDatabase对象db创建数据库或连接数据库:SQLiteDatabasedb = SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(MainActivity.this.getFilesDir().toString()+ "/test.dbs", null);如果目录下有test.dbs数据库则是连接没有就是创建
2.用对象db的方法来执行sql语句:db.execSQL(String sql) 此方法木有返回值 所以查询不好弄。查询一般用db.rawQuery返回一个Cursor对象(相当与jdbc中的ResultSet),Cursor有如下几个方法来查询数据:
2.1 move ToFirst 将记录指针跳到第一行
2.2 moveToLast将记录指针跳到最后一行
2.3 moveNext将记录指针移到下一行
2.4moveToPosition( int ss)将记录指针跳到指定的ss行
2.5moveToPrevious将记录指针跳到上一行
将记录指针跳到指定的行之后就可以通过对象的getXXX方法来获取数据 :如 Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery("select na,pw from user where na=? and pw=?", new String []{name,pwd});
3.回收资源close
当然以SQLiteDatabase对象还可以调用许多方法来操作数据库,不过俺是觉得这几个方法基本够了
简单的登录与注册源代码:
(仅此来练习SQLite的操作 一般注册的信息都样上传到服务器而不会是存储在手机数据库)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.android.xiong.sqlitelogin"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0" >
<uses-sdk
android:minSdkVersion="8"
android:targetSdkVersion="14" />
<application
android:allowBackup="true"
android:icon="@drawable/ic_launcher"
android:label="@string/app_name"
android:theme="@style/AppTheme" >
<activity
android:name="com.android.xiong.sqlitelogin.MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
<activity
android:name="com.android.xiong.sqlitelogin.RegistersActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name" >
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
tools:context=".MainActivity" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/login"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="30dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:textColor="#8a2be2"
android:textSize="35dp"
android:text="登录界面" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtname"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/login"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:textSize="28dp"
android:text="用户帐号:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edname"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:layout_below="@id/login"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/txtname"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:hint="请输入用户帐号"/>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtpassword"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/txtname"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:textSize="28dp"
android:text="用户密码:"/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edpassword"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/edname"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/txtpassword"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:inputType="textPassword"
android:hint="请输入用户密码"/>
<LinearLayout
android:layout_below="@id/edpassword"
android:orientation="horizontal"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btregister"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:text="用户注册"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/btlogin"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:text="用户登录"/>
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" >
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txt1"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_margin="30dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:text="注册界面"
android:textColor="#8a2be2"
android:textSize="35dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtname1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/txt1"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:text="帐号:"
android:textSize="28dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edname1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_below="@id/txt1"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/txtname1"
android:layout_marginBottom="30dp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/txtpassword1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/txtname1"
android:layout_marginRight="5dp"
android:text="密码:"
android:textSize="28dp" />
<EditText
android:id="@+id/edpassword1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_alignParentRight="true"
android:layout_below="@id/edname1"
android:layout_toRightOf="@id/txtpassword1" />
<LinearLayout
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@id/edpassword1"
android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<Button
android:id="@+id/btregister1"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_marginRight="20dp"
android:text="提交数据" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
package com.android.xiong.sqlitelogin;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.Cursor;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteException;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.Menu;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
// 帐号和密码
private EditText edname;
private EditText edpassword;
private Button btregister;
private Button btlogin;
// 创建SQLite数据库
public static SQLiteDatabase db;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
edname = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edname);
edpassword = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edpassword);
btregister = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btregister);
btlogin = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btlogin);
db = SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(MainActivity.this.getFilesDir().toString()
+ "/test.dbs", null);
// 跳转到注册界面
btregister.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Intent intent = new Intent();
intent.setClass(MainActivity.this, RegistersActivity.class);
startActivity(intent);
}
});
btlogin.setOnClickListener(new LoginListener());
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
db.close();
}
class LoginListener implements OnClickListener {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String name = edname.getText().toString();
String password = edpassword.getText().toString();
if (name.equals("") || password.equals("")) {
// 弹出消息框
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this).setTitle("错误")
.setMessage("帐号或密码不能空").setPositiveButton("确定", null)
.show();
} else {
isUserinfo(name, password);
}
}
// 判断输入的用户是否正确
public Boolean isUserinfo(String name, String pwd) {
try{
String str="select * from tb_user where name=? and password=?";
Cursor cursor = db.rawQuery(str, new String []{name,pwd});
if(cursor.getCount()<=0){
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this).setTitle("错误")
.setMessage("帐号或密码错误!").setPositiveButton("确定", null)
.show();
return false;
}else{
new AlertDialog.Builder(MainActivity.this).setTitle("正确")
.setMessage("成功登录").setPositiveButton("确定", null)
.show();
return true;
}
}catch(SQLiteException e){
createDb();
}
return false;
}
}
// 创建数据库和用户表
public void createDb() {
db.execSQL("create table tb_user( name varchar(30) primary key,password varchar(30))");
}
@Override
public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) {
// Inflate the menu; this adds items to the action bar if it is present.
getMenuInflater().inflate(R.menu.main, menu);
return true;
}
}
package com.android.xiong.sqlitelogin;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.app.AlertDialog;
import android.content.DialogInterface;
import android.content.Intent;
import android.database.sqlite.SQLiteDatabase;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.EditText;
public class RegistersActivity extends Activity {
private EditText edname1;
private EditText edpassword1;
private Button btregister1;
SQLiteDatabase db;
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onDestroy();
db.close();
}
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.register);
edname1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edname1);
edpassword1 = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.edpassword1);
btregister1 = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btregister1);
btregister1.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(View v) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
String name = edname1.getText().toString();
String password = edpassword1.getText().toString();
if (!(name.equals("") && password.equals(""))) {
if (addUser(name, password)) {
DialogInterface.OnClickListener ss = new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() {
@Override
public void onClick(DialogInterface dialog,
int which) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// 跳转到登录界面
Intent in = new Intent();
in.setClass(RegistersActivity.this,
MainActivity.class);
startActivity(in);
// 销毁当前activity
RegistersActivity.this.onDestroy();
}
};
new AlertDialog.Builder(RegistersActivity.this)
.setTitle("注册成功").setMessage("注册成功")
.setPositiveButton("确定", ss).show();
} else {
new AlertDialog.Builder(RegistersActivity.this)
.setTitle("注册失败").setMessage("注册失败")
.setPositiveButton("确定", null);
}
} else {
new AlertDialog.Builder(RegistersActivity.this)
.setTitle("帐号密码不能为空").setMessage("帐号密码不能为空")
.setPositiveButton("确定", null);
}
}
});
}
// 添加用户
public Boolean addUser(String name, String password) {
String str = "insert into tb_user values(?,?) ";
MainActivity main = new MainActivity();
db = SQLiteDatabase.openOrCreateDatabase(this.getFilesDir().toString()
+ "/test.dbs", null);
main.db = db;
try {
db.execSQL(str, new String[] { name, password });
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
main.createDb();
}
return false;
}
}
-
本文向大家介绍Android应用开发中数据的保存方式总结,包括了Android应用开发中数据的保存方式总结的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一、保存文件到手机内存 二、保存文件到SD卡 获取手机sd空间的大小: 加入写外部存储的权限: 三、Sharedpreferences的使用 SharedPreference是开发中常用的一种存储方式,主要存储一些系统不变的参数如是否是第一次进入应用程
-
本文向大家介绍Hibernate的各种保存方式的区别详解,包括了Hibernate的各种保存方式的区别详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 hibernate的保存 hibernate对于对象的保存提供了太多的方法,他们之间有很多不同,这里细说一下,以便区别: 一、预备知识: 在所有之前,说明一下,对于hibernate,它的对象有三种状态,transient、persistent、
-
本文向大家介绍详解IOS四种保存数据的方式,包括了详解IOS四种保存数据的方式的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在iOS开发过程中,不管是做什么应用,都会碰到数据保存的问题。将数据保存到本地,能够让程序的运行更加流畅,不会出现让人厌恶的菊花形状,使得用户体验更好。下面介绍一下数据保存的方式: 1.NSKeyedArchiver:采用归档的形式来保存数据,该数据对象需要遵守NSCoding协
-
本文向大家介绍vue中各种通信传值方式总结,包括了vue中各种通信传值方式总结的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 1、路由通信传值 路由通信是通过路由跳转用query把参数带过去,也是vue常用的通信手段。 例子:创建并在路由注册一个组件Head 创建另一个组件About并在路由注册 路由注册的简单代码 2、sessionStorage本地缓存通信 还是列举上面的例子,将它们稍微改一改就可以
-
我的团队目前有几个试用版客户在使用我们的产品。当前将客户的数据库升级到最新版本的方法包括重新初始化数据库和手工重新创建客户配置,这并不多,但肯定很繁琐,并且会随着我们实施某种迁移策略而改变。 我的问题是,是否可以使用flyway(或其他一些工具)来管理我们产品的所有实例的数据库模式迁移,同时保留独立的实例数据?解决这类问题的最佳方法是什么。
-
本文向大家介绍JavaScript中的各种操作符使用总结,包括了JavaScript中的各种操作符使用总结的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一元操作符 只能操作一个值的操作符叫一元操作符。 一元操作符是ECMAScript中最简单的操作符。 1.递增和递减操作符 递增递减操作符直接借鉴C,而且各有两个版本:前置型和后置型。顾明思义,前置型应该让位于要操作的变量之前,而后置型应该位于要操作的

