Python读取图片属性信息的实现方法
本文是利用Python脚本读取图片信息,有几个说明如下:
1、没有实现错误处理
2、没有读取所有信息,大概只有 GPS 信息、图片分辨率、图片像素、设备商、拍摄设备等
3、简单修改后应该能实现暴力修改图片的 GPS 信息
4、但对于本身没有 GPS 信息的图片,实现则非常复杂,需要仔细计算每个描述符的偏移量
脚本运行后,读取结果如下
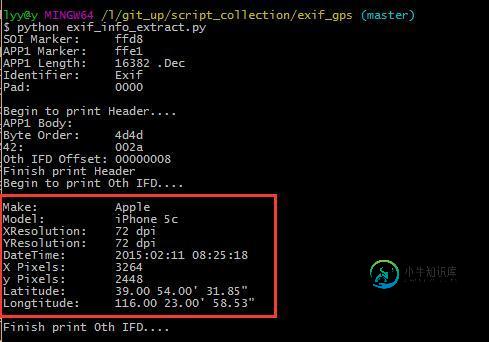
脚本读取的信息
这里和 Windows 属性查看器读到的内容完全一致
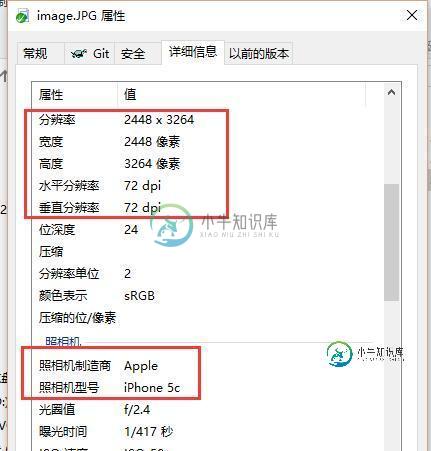
图片信息1
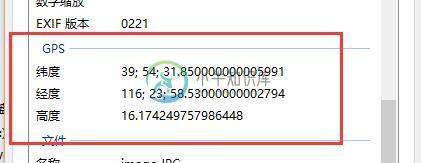
图片信息2
源码如下
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
import binascii
class ParseMethod(object):
@staticmethod
def parse_default(f, count, offset):
pass
@staticmethod
def parse_latitude(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
latitude = [0,0,0]
for i in xrange(count):
byte = f.read(4)
numerator = byte.encode('hex')
byte = f.read(4)
denominator = byte.encode('hex')
latitude[i] = float(int(numerator, 16)) / int(denominator, 16)
print 'Latitude:\t%.2f %.2f\' %.2f\"' % (latitude[0], latitude[1], latitude[2])
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_longtitude(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
longtitude = [0,0,0]
for i in xrange(count):
byte = f.read(4)
numerator = byte.encode('hex')
byte = f.read(4)
denominator = byte.encode('hex')
longtitude[i] = float(int(numerator, 16)) / int(denominator, 16)
print 'Longtitude:\t%.2f %.2f\' %.2f\"' % (longtitude[0], longtitude[1], longtitude[2])
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_make(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(count)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'Make:\t\t' + binascii.a2b_hex(a)
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_model(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(count)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'Model:\t\t' + binascii.a2b_hex(a)
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_datetime(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(count)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'DateTime:\t' + binascii.a2b_hex(a)
f.seek(old_pos)
# rational data type, 05
@staticmethod
def parse_xresolution(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(4)
numerator = byte.encode('hex')
byte = f.read(4)
denominator = byte.encode('hex')
xre = int(numerator, 16) / int(denominator, 16)
print 'XResolution:\t' + str(xre) + ' dpi'
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_yresolution(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(4)
numerator = byte.encode('hex')
byte = f.read(4)
denominator = byte.encode('hex')
xre = int(numerator, 16) / int(denominator, 16)
print 'YResolution:\t' + str(xre) + ' dpi'
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_exif_ifd(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
exif_ifd_number = int(a, 16)
for i in xrange(exif_ifd_number):
byte = f.read(2)
tag_id = byte.encode('hex')
#print tag_id,
byte = f.read(2)
type_n = byte.encode('hex')
#print type_n,
byte = f.read(4)
count = byte.encode('hex')
#print count,
byte = f.read(4)
value_offset = byte.encode('hex')
#print value_offset
value_offset = int(value_offset, 16)
EXIF_IFD_DICT.get(tag_id, ParseMethod.parse_default)(f, count, value_offset)
f.seek(old_pos)
@staticmethod
def parse_x_pixel(f, count, value):
print 'X Pixels:\t' + str(value)
@staticmethod
def parse_y_pixel(f, count, value):
print 'y Pixels:\t' + str(value)
@staticmethod
def parse_gps_ifd(f, count, offset):
old_pos = f.tell()
f.seek(12 + offset)
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
gps_ifd_number = int(a, 16)
for i in xrange(gps_ifd_number):
byte = f.read(2)
tag_id = byte.encode('hex')
#print tag_id,
byte = f.read(2)
type_n = byte.encode('hex')
#print type_n,
byte = f.read(4)
count = byte.encode('hex')
#print count,
byte = f.read(4)
value_offset = byte.encode('hex')
#print value_offset
count = int(count, 16)
value_offset = int(value_offset, 16)
GPS_IFD_DICT.get(tag_id, ParseMethod.parse_default)(f, count, value_offset)
f.seek(old_pos)
IFD_dict = {
'010f' : ParseMethod.parse_make ,
'0110' : ParseMethod.parse_model ,
'0132' : ParseMethod.parse_datetime ,
'011a' : ParseMethod.parse_xresolution ,
'011b' : ParseMethod.parse_yresolution ,
'8769' : ParseMethod.parse_exif_ifd ,
'8825' : ParseMethod.parse_gps_ifd
}
EXIF_IFD_DICT = {
'a002' : ParseMethod.parse_x_pixel ,
'a003' : ParseMethod.parse_y_pixel
}
GPS_IFD_DICT = {
'0002' : ParseMethod.parse_latitude ,
'0004' : ParseMethod.parse_longtitude
}
with open('image.jpg', 'rb') as f:
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'SOI Marker:\t' + a
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'APP1 Marker:\t' + a
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'APP1 Length:\t' + str(int(a, 16)) + ' .Dec'
byte = f.read(4)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'Identifier:\t' + binascii.a2b_hex(a)
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'Pad:\t\t' + a
print
print 'Begin to print Header.... '
print 'APP1 Body: '
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print 'Byte Order:\t' + a
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print '42:\t\t' + a
byte = f.read(4)
a = byte.encode('hex')
print '0th IFD Offset:\t' + a
print 'Finish print Header'
print 'Begin to print 0th IFD....'
print
#print 'Total: ',
byte = f.read(2)
a = byte.encode('hex')
interoperability_number = int(a, 16)
#print interoperability_number
for i in xrange(interoperability_number):
byte = f.read(2)
tag_id = byte.encode('hex')
#print tag_id,
byte = f.read(2)
type_n = byte.encode('hex')
#print type_n,
byte = f.read(4)
count = byte.encode('hex')
#print count,
byte = f.read(4)
value_offset = byte.encode('hex')
#print value_offset
count = int(count, 16)
value_offset = int(value_offset, 16)
# simulate switch
IFD_dict.get(tag_id, ParseMethod.parse_default)(f, count, value_offset)
print
print 'Finish print 0th IFD....'
总结
利用Python读取图片属性信息的实现方法到这就基本结束了,大家都学会了吗?希望这篇文章对大家的学习或者工作带来一定的帮助,
-
本文向大家介绍Java读取图片EXIF信息的方法,包括了Java读取图片EXIF信息的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了Java读取图片EXIF信息的方法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体分析如下: 首先介绍一下什么是EXIF,EXIF是Exchangeable Image File的缩写,这是一种专门为数码相机照片设定的格式。这种格式可以用来记录数字照片的属性信息,例如相机的
-
本文向大家介绍python获取图片颜色信息的方法,包括了python获取图片颜色信息的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了python获取图片颜色信息的方法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体分析如下: python的pil模块可以从图片获得图片每个像素点的颜色信息,下面的代码演示了如何获取图片所有点的颜色信息和每种颜色的数量。 返回结果如下 返回结果是一个元祖,每个元素的格式
-
本文向大家介绍Python读取图片EXIF信息类库介绍和使用实例,包括了Python读取图片EXIF信息类库介绍和使用实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 首先要介绍的是 Python Imaging Library,使用方法如下: 返回的清单如下: 其中59932,是一大串十六进制的字符,不知为啥。除了PIL之外,还有许多类库可供使用: Media Metadata for Python
-
案例分析 任务:爬取京东指定商品图片信息,并存储在当期目录下。 url地址:https://list.jd.com/list.html?cat=9987,653,655 分析Web的响应内容,并作出对应处理准备: 具体实现代码: import requests from bs4 import BeautifulSoup from urllib.request import urlretrieve
-
本文向大家介绍JS获取图片lowsrc属性的方法,包括了JS获取图片lowsrc属性的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了JS获取图片lowsrc属性的方法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体如下: lowsrc属性一般设置为图片的低分辨率图片地址,下面的代码可以通过点击链接显示图片的低分辨率版本 希望本文所述对大家的javascript程序设计有所帮助。
-
本文向大家介绍php获取图片信息的方法详解,包括了php获取图片信息的方法详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了php获取图片信息的方法。分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: getimagesize() 函数将测定任何 GIF,JPG,PNG,SWF,SWC,PSD,TIFF,BMP,IFF,JP2,JPX,JB2,JPC,XBM 或 WBMP 图像文件的大小并返回图像的尺寸以

