Python 项目转化为so文件实例
思路是先将py转换为c代码,然后编译c为so文件,所以要安装以下内容:
python 安装:cython
pip install cython
linux 安装:python-devel,gcc
yum install python-devel yum install gcc
初步编译
新建Test.py文件,内容如下
class test:
def __init__(self):
print('init')
def say(self):
print ('hello')
新建setup.py,内容如下
from distutils.core import setup from Cython.Build import cythonize setup(ext_modules = cythonize(["Test.py"]))
在bash中执行
python setup.py build_ext
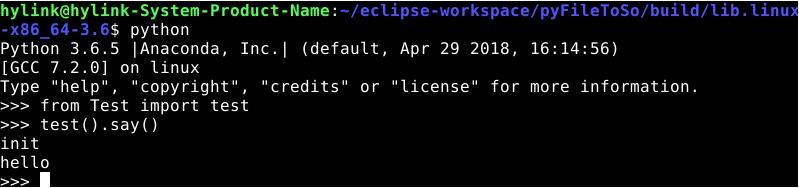
运行后会生成build文件夹,如下

现在so文件就可以像普通py文件一样导入了
集成编译
做了以下内容:
1.文件夹编译
2.删除编译出的.c文件
3.删除编译的temp文件夹
将需要编译的目录和setup.py放在同一层级,执行python setup.py,so文件在build目录下
setup.py代码如下:
'''
Created on 2019年3月27日
@author: hylink
'''
#-* -coding: UTF-8 -* -
"""
执行前提:
系统安装python-devel 和 gcc
Python安装cython
编译整个当前目录:
python py-setup.py
编译某个文件夹:
python py-setup.py BigoModel
生成结果:
目录 build 下
生成完成后:
启动文件还需要py/pyc担当,须将启动的py/pyc拷贝到编译目录并删除so文件
"""
import sys, os, shutil, time
from distutils.core import setup
from Cython.Build import cythonize
starttime = time.time()
currdir = os.path.abspath('.')
parentpath = sys.argv[1] if len(sys.argv)>1 else ""
setupfile= os.path.join(os.path.abspath('.'), __file__)
build_dir = "build"
build_tmp_dir = build_dir + "/temp"
def getpy(basepath=os.path.abspath('.'), parentpath='', name='', excepts=(), copyOther=False,delC=False):
"""
获取py文件的路径
:param basepath: 根路径
:param parentpath: 父路径
:param name: 文件/夹
:param excepts: 排除文件
:param copy: 是否copy其他文件
:return: py文件的迭代器
"""
fullpath = os.path.join(basepath, parentpath, name)
for fname in os.listdir(fullpath):
ffile = os.path.join(fullpath, fname)
#print basepath, parentpath, name,file
if os.path.isdir(ffile) and fname != build_dir and not fname.startswith('.'):
for f in getpy(basepath, os.path.join(parentpath, name), fname, excepts, copyOther, delC):
yield f
elif os.path.isfile(ffile):
ext = os.path.splitext(fname)[1]
if ext == ".c":
if delC and os.stat(ffile).st_mtime > starttime:
os.remove(ffile)
elif ffile not in excepts and os.path.splitext(fname)[1] not in('.pyc', '.pyx'):
if os.path.splitext(fname)[1] in('.py', '.pyx') and not fname.startswith('__'):
yield os.path.join(parentpath, name, fname)
elif copyOther:
dstdir = os.path.join(basepath, build_dir, parentpath, name)
if not os.path.isdir(dstdir): os.makedirs(dstdir)
shutil.copyfile(ffile, os.path.join(dstdir, fname))
else:
pass
#获取py列表
module_list = list(getpy(basepath=currdir,parentpath=parentpath, excepts=(setupfile)))
try:
setup(ext_modules = cythonize(module_list),script_args=["build_ext", "-b", build_dir, "-t", build_tmp_dir])
except Exception as e:
print (e)
else:
module_list = list(getpy(basepath=currdir, parentpath=parentpath, excepts=(setupfile), copyOther=True))
module_list = list(getpy(basepath=currdir, parentpath=parentpath, excepts=(setupfile), delC=True))
if os.path.exists(build_tmp_dir): shutil.rmtree(build_tmp_dir)
print ("complate! time:", time.time()-starttime, 's')
注意问题
1.编译后执行需要相同的python版本和编码
2.py中使用__file__内置变量的文件编译后调用时会出问题,暂时没有解决,还需要使用pyc代替
3.使用时注意权限控制
以上这篇Python 项目转化为so文件实例就是小编分享给大家的全部内容了,希望能给大家一个参考,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
本文向大家介绍Python编译为二进制so可执行文件实例,包括了Python编译为二进制so可执行文件实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 通过cpython把python的文件转换为二进制文件,达到代码保护的目的 1、下载Cython-0.28.2.tar.gz python setup.py install安装 2、创建你需要打包成二进制的python文件 3、创建一个setup.py
-
本文向大家介绍python 读文件,然后转化为矩阵的实例,包括了python 读文件,然后转化为矩阵的实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 代码流程: 1. 从文件中读入数据。 2. 将数据转化成矩阵的形式。 3. 对于矩阵进行处理。 具体的python代码如下: - 文件路径需要设置正确。 - 字符串处理。 - 字符串数组到 整型数组的转化。( nums = [int(x) for x
-
我在一个java桌面应用程序项目下工作。我用eclipse完成了我的java项目,它有许多包和单独的类文件。我的主要课程是大型机。我的问题是我必须将此项目安装到另一台计算机,我如何将我的项目转换为安装文件?
-
我用Expo工具构建了一个应用程序。。但现在我该如何应对没有世博会的情况。。我试图在react native中创建一个新项目,然后传输我编写的代码并安装我在应用程序中使用的组件。 该应用程序与世博会工作作为预期把与移动反应本地没有世博会工作作为意外和崩溃。
-
我想把我所有的java项目(223个项目)迁移到gradle项目。我使用Gradle Eclipse插件,由SpringSource STS团队开发。 目前,我所有的java项目都是这样结构的: src/log、src/tools/core、src/tools/graph、src/tests和src/someModule是java源文件夹。 将项目转换为gradle后(通过配置- 此外,问题是ja
-
我正在考虑使用博览会在React Native中构建移动应用程序,我在常见问题下注意到现有的React Native项目可以转换为博览会。 我们到底在转换什么?我真的喜欢尽可能地保持纯净和干净,而中间没有太多抽象层,这会掩盖我理解应用程序中发生的事情的能力。 我希望能对改造过程中的实际情况以及世博会为现有项目增加的内容进行更多的澄清。

