详解Sea.js中Module.exports和exports的区别

一、官方解释
因为SeaJs和Nodejs都是基于CommonJS,所以直接看的Node的官方文档解释 Module.exports The module.exports object is created by the Module system. Sometimes this is not acceptable; many want their module to be an instance of some class. To do this, assign the desired export object to module.exports. Note that assigning the desired object to exports will simply rebind the local exports variable, which is probably not what you want to do. module.exports对象是由模块系统创建的。 有时这是难以接受的;许多人希望他们的模块成为某个类的实例。 为了实现这个,需要将期望导出的对象赋值给module.exports。 注意,将期望的对象赋值给exports会简单地重新绑定到本地exports变量上,这可能不是你想要的。
exports
The exports variable is available within a module's file-level scope, and is assigned the value of module.exports before the module is evaluated. It allows a shortcut, so that module.exports.f = ... can be written more succinctly as exports.f = .... However, be aware that like any variable, if a new value is assigned to exports, it is no longer bound to module.exports: 译文:exports变量是在模块的文件级别作用域内有效的,它在模块被执行前被赋于 module.exports 的值。它有一个快捷方式,以便 module.exports.f = ... 可以被更简洁地写成exports.f = ...。 注意,就像任何变量,如果一个新的值被赋值给exports,它就不再绑定到module.exports(其实是exports.属性会自动挂载到没有命名冲突的module.exports.属性)
require
从require导入方式去理解,关键有两个变量(全局变量module.exports,局部变量exports)、一个返回值(module.exports)
function require(...) {
var module = { exports: {} };
((module, exports) => {
// 你的被引入代码 Start
// var exports = module.exports = {}; (默认都有的)
function some_func() {};
exports = some_func;
// 此时,exports不再挂载到module.exports,
// export将导出{}默认对象
module.exports = some_func;
// 此时,这个模块将导出some_func对象,覆盖exports上的some_func
// 你的被引入代码 End
})(module, module.exports);
// 不管是exports还是module.exports,最后返回的还是module.exports
return module.exports;
}
二、Demo事例
事例一:1.js
console.log(exports); // {}
console.log(module.exports); // {}
console.log(exports === module.exports); // true
console.log(exports == module.exports); // true
/**
Module {
id: '.',
exports: {},
parent: null,
filename: '/1.js',
loaded: false,
children: [],
paths:
[
'/node_modules' ]
}
*/
console.log(module);
从事例一中,可以看出来
1.每个js文件一创建,都有一个var exports = module.exports = {}; ,使exports和module.exports都指向一个空对象。
2.module是全局内置对象,exports是被var创建的局部对象。
3.module.exports和exports所指向的内存地址相同
事例二:2.js、3.js
// 2.js
exports.id = 'exports的id';
exports.id2 = 'exports的id2';
exports.func = function(){
console.log('exports的函数');
};
exports.func2 = function() {
console.log('exports的函数2');
};
module.exports = {
id: 'module.exports的id',
func:function(){
console.log('module.exports的函数');
}
};
// 3.js
var a = require('./2.js');
// 当属性和函数在module.exports都有定义时:
console.log(a.id); // module.exports的id
console.log(a.func()); // module.exports的函数
// 当属性在module.exports没有定义,函数在module.exports有定义
console.log(a.id2); // undefined
console.log(a.func()); // module.exports的函数
// 当函数在module.exports没有定义,属性在module.exports有定义
console.log(a.id); // module.exports的id
console.log(a.func2()); // 报错了 TypeError: a.func2 is not a function
由例二可以知道:
1.module.exports像是exports的大哥,当module.exports以{}整体导出时会覆盖exports的属性和方法,
2.注意,若只是将属性/方法挂载在module.exports./exports.上时,exports.id=1和module.exports.id=100,module.exports.id=function(){}和exports.id=function(){} ,最后id的值取决于exports.id和module.exports.id的顺序,谁在后,就是最后的值
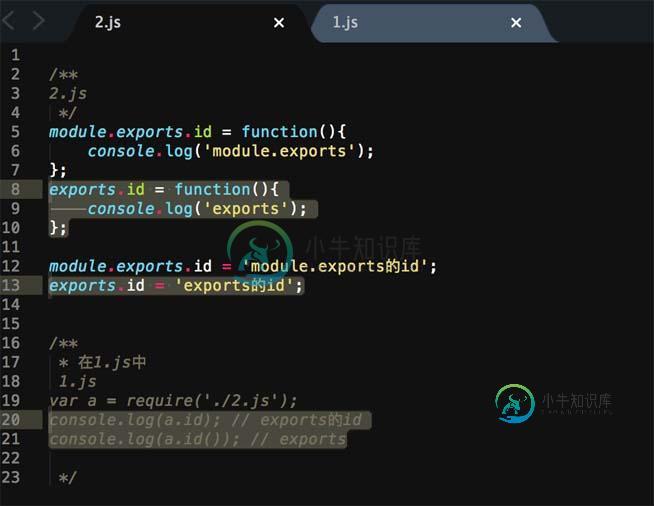
3.若exports和module.exports同时赋值时,exports所使用的属性和方法必须出现在module.exports,若属性没有在module.exports中定义的话,出现undefined,若方法没有在module.exports中定义,会抛出TypeError错误。
例三 4.js、5.js
module.exports的对象、prototype、构造函数使用
// 4.js
var a = require('./5.js');
// 若传的是类,new一个对象
var person = new a('Kylin',20);
console.log(person.speak()); // my name is Kylin ,my age is 20
// 若不需要在构造函数时初始化参数,直接调用方法/属性
// a.speak(); // my name is kylin ,my age is 20
// 5.js
// Person类
function Person(name,age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
// 为类添加方法
Person.prototype.speak = function(){
console.log('my name is '+this.name+' ,my age is '+this.age);
};
// 返回类
module.exports = Person;
// 若构造函数没有传入参数(name,age),直接传入对象
// module.exports = new Person('kylin',20);
说了这么多,其实建议就是,如果只是单一属性或方法的话,就使用exports.属性/方法。要是导出多个属性或方法或使用对象构造方法,结合prototype等,就建议使用module.exports = {} 。文章有很多地方描述的可能不是很准确,提到的点也不够全面,如果有不对的地方,还望斧正!
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作能带来一定的帮助,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流。
-
本文向大家介绍详解Node.js中exports和module.exports的区别,包括了详解Node.js中exports和module.exports的区别的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 今天看了下node.js的require方法的源码,终于搞清楚exports和module.exports的区别了。 我们知道,node.js的模块暴露有两种方法。 1. 方式一:用exports
-
require 用来加载代码,而 exports 和 module.exports 则用来导出代码。 很多新手可能会迷惑于 exports 和 module.exports 的区别,为了更好的理解 exports 和 module.exports 的关系,我们先来巩固下 js 的基础。示例: test.js var a = {name: 1} var b = a console.log(a) c
-
require 用来加载代码,而 exports 和 module.exports 则用来导出代码。 很多新手可能会迷惑于 exports 和 module.exports 的区别,为了更好的理解 exports 和 module.exports 的关系,我们先来巩固下 js 的基础。示例: test.js var a = {name: 1}; var b = a; console.log(a)
-
在这个页面(http://docs.nodejitsu.com/articles/getting-started/what-is-require)中,它指出“如果您想将exports对象设置为函数或新对象,您必须使用Module.exports对象。” 我的问题是为什么。 I console.log结果(codeResult=require(example.js)/code>),第一个是 ,第二个
-
本文向大家介绍module.exports与exports的区别是什么?相关面试题,主要包含被问及module.exports与exports的区别是什么?时的应答技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 exports 返回的是模块函数 module.exports 返回的是模块对象本身,返回的是一个类 使用上的区别是 exports的方法可以直接调用 module.exports需要new对象之后才
-
本文向大家介绍node.js中module.exports与exports用法上的区别,包括了node.js中module.exports与exports用法上的区别的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Node.js 引入了模块(Module)概念,一个模块可以通过module.exports 或 exports 将函数、变量等导出,以使其它 JavaScript 脚本通过require(

