Spring数据配置和Postgres数据库集成(没有xml配置)
我有一个基于Spring框架的项目,它只基于Java配置进行初始化。这意味着不需要使用web.xml文件。
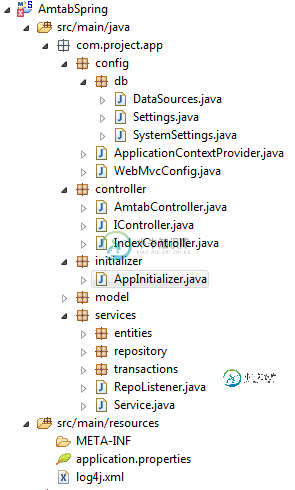
您可以在下面的图像中看到项目的结构:
- Java 7
- Spring framework 4.2.1.发布
- HibernateORM 5.0.4.final
- Spring Tool Suite IDE 3.6.2
- Maven3
- Tomcat 7
public class AppInitializer implements WebApplicationInitializer {
private static final String CONFIG_LOCATION = "com.project.app.config";
private static final String MAPPING_URL = "/";
@Override
public void onStartup(ServletContext servletContext) throws ServletException {
// Create the 'root' Spring application context
WebApplicationContext context = getContext();
// Manage the lifecycle of the root application context
servletContext.addListener(new ContextLoaderListener(context));
// Register and map the dispatcher servlet
ServletRegistration.Dynamic dispatcher = servletContext.addServlet("DispatcherServlet",
new DispatcherServlet(context));
dispatcher.setLoadOnStartup(1);
dispatcher.addMapping(MAPPING_URL);
}
private AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext getContext() {
AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigWebApplicationContext();
context.setConfigLocation(CONFIG_LOCATION);
return context;
}
}
@EnableWebMvc
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages = { "com.project.app" })
public class WebMvcConfig extends WebMvcConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Override
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addResourceHandler("/resources/**").addResourceLocations("/resources/");
}
@Override
public void addViewControllers(ViewControllerRegistry registry) {
registry.addViewController("/").setViewName("hello");
}
@Bean
public ApplicationContextProvider applicationContextProvider() {
return new ApplicationContextProvider();
}
}
数据源
@Component
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class DataSources {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSource dataSource() {
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource ds = new org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource();
String url = env.getProperty(SystemSettings.DS_URL);
String user = env.getProperty(SystemSettings.DS_USERNAME);
String pass = env.getProperty(SystemSettings.DS_PASSWORD);
ds.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(user);
ds.setPassword(pass);
return ds;
}
}
而SystemSettings保存数据库的用户名、密码和url
@Service
@Configuration
public class SystemSettings implements Settings {
public static final String DS_URL = "datasource.app.url";
public static final String DS_USERNAME = "datasource.app.username";
public static final String DS_PASSWORD = "datasource.app.password";
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Override
public String get(String key) {
return env.getProperty(key);
}
}
这些值是从Application.Properties文件中提取的,因为它在DataSources类中表示。
@Entity
@Table(name = "stop")
public class StopJPA {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
@Column(name = "id")
private Long id;
@Column(name = "description")
private String stopDescription;
@Column(name = "idStop")
private String idStop;
public StopJPA() {
}
public StopJPA(String stopDescription, String idStop) {
this.stopDescription = stopDescription;
this.idStop = idStop;
}
public Long getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getStopDescription() {
return stopDescription;
}
public void setStopDescription(String stopDescription) {
this.stopDescription = stopDescription;
}
public String getIdStop() {
return idStop;
}
public void setIdStop(String idStop) {
this.idStop = idStop;
}
}
/**
* Repository interface for StopJPA entities.
*/
@Repository
@RepositoryRestResource(collectionResourceRel = "stop", path = "stop")
public interface StopRepository extends CrudRepository<StopJPA, Long> {
StopJPA findById(@Param("id") Long id);
}
在所有这些设置和配置之后,我设法使项目运行,但没有在数据库中创建表。
- 配置步骤中缺少什么?
- 如何让Spring扫描JPA实体并创建数据库?
我的主要目的是配置Spring(通过使用Spring Data JPA)和Hibernate,使它们在不使用xml配置文件和Spring Boot依赖项的情况下协同工作。后者意味着必须“手动”配置环境。
PersistenceContext
@Component
@EnableTransactionManagement
@PropertySource("classpath:application.properties")
public class PersistenceContext {
@Autowired
private Environment env;
@Bean
@Primary
public DataSource dataSource() throws ClassNotFoundException {
org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource ds = new org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource();
String url = env.getProperty(SystemSettings.DS_URL);
String user = env.getProperty(SystemSettings.USERNAME);
String pass = env.getProperty(SystemSettings.DS_PASSWORD);
ds.setDriverClassName("org.postgresql.Driver");
ds.setUrl(url);
ds.setUsername(user);
ds.setPassword(pass);
return ds;
}
@Bean
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactory(DataSource dataSource) {
LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean entityManagerFactoryBean = new LocalContainerEntityManagerFactoryBean();
entityManagerFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource);
entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaVendorAdapter(new HibernateJpaVendorAdapter());
entityManagerFactoryBean.setPackagesToScan("com.project.app.services.entities");
Properties jpaProperties = new Properties();
// Configures the used database dialect. This allows Hibernate to create SQL
// that is optimized for the used database.
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.dialect", env.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.dialect"));
// Specifies the action that is invoked to the database when the Hibernate
// SessionFactory is created or closed.
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto",
env.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto"));
// If the value of this property is true, Hibernate writes all SQL
// statements to the console.
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.show_sql", env.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.show_sql"));
// If the value of this property is true, Hibernate will format the SQL
// that is written to the console.
jpaProperties.put("hibernate.format_sql", env.getRequiredProperty("hibernate.format_sql"));
entityManagerFactoryBean.setJpaProperties(jpaProperties);
return entityManagerFactoryBean;
}
/**
* Because we are using JPA, we have to create a transaction manager bean that integrates the
* JPA provider with the Spring transaction mechanism. We can do this by using the
* JpaTransactionManager class as the transaction manager of our application.
*
* We can configure the transaction manager bean by following these steps:
*
* -> Create a new JpaTransactionManager object. -> Configure the entity manager factory whose
* transactions are managed by the created JpaTransactionManager object.
**/
@Bean
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager(EntityManagerFactory entityManagerFactory) {
JpaTransactionManager transactionManager = new JpaTransactionManager();
transactionManager.setEntityManagerFactory(entityManagerFactory);
return transactionManager;
}
}
Ans还更新了属性文件
hibernate.dicult=org.hibernate.dicult.PostgreSQL方言
hibernate.hbm2ddl.auto=create-drop hibernate.show_sql=false
hibernate.format_sql=true
我不知道为什么它会给我这个例外。maven依赖项在那里,驱动程序也在类路径中。.有什么帮助吗?
共有1个答案
JPA没有指定DDL生成/迁移。默认情况下,Hibernate不执行DDL生成/迁移,但是如果正确配置persistence.xml,则可以执行此操作。
-
新建数据库 在本地新建一个数据库 demo 打开common/config/main-local.php 修改数据库配置 'components' => [ ... 'db' => [ 'class' => 'yii\db\Connection', 'dsn' => 'mysql:host=localhost;dbna
-
因为 Canal 是模拟 MySQL slave 的交互协议,伪装自己为 MySQL slave ,向 MySQL master 发送dump 协议,所以需要 MySql 开启 binlog 修改 mysql.cnf 中的配置 [mysqld] log-bin=mysql-bin # 开启 binlog binlog-format=ROW # 选择 ROW 模式 server_id=1 # 配置
-
ThinkCMF5安装后的生成的数据库配置文件在data/conf/database.php; <?php return [ // 数据库类型 'type' => 'mysql', // 服务器地址 'hostname' => 'localhost', // 数据库名 'database' => 'thi
-
ThinkCMF6.0安装后的生成的数据库配置文件在data/config/database.php; <?php /** * 配置文件 */ return [ // 默认使用的数据库连接配置 'default' => env('database.driver', 'mysql'), // 自定义时间查询规则 'time_query_rule'
-
数据库配置比较简单,一看就知道怎么配置,但是这里还是有几个地方需要解释一下。。。 define('DB_ACCESS', DB_ACCESS_SINGLE); //默认使用单台数据库服务器 return array ( 'mysql' => array( array( 'db_type' => 'mysql',
-
CodeIgniter 有一个配置文件用来保存数据库配置(用户名、密码、数据库名等等),这个配置文件位于 application/config/database.php。 You can also set database connection values for specific environments by placing database.php in the respective en

