pandas dataframe: loc vs query performance
乐正远
问题内容:
问题答案:
I have 2 dataframes in python that I would like to query for data.
-
DF1: 4M records x 3 columns. The query function seams more efficient than the loc function.
-
DF2: 2K records x 6 columns. The loc function seams much more efficient than the query function.
Both queries return a single record. The simulation was done by running the
same operation in a loop 10K times.
Running python 2.7 and pandas 0.16.0
Any recommendations to improve the query speed?
问题答案:
For improve performance is possible use numexpr:
import numexpr
np.random.seed(125)
N = 40000000
df = pd.DataFrame({'A':np.random.randint(10, size=N)})
def ne(df):
x = df.A.values
return df[numexpr.evaluate('(x > 5)')]
print (ne(df))
In [138]: %timeit (ne(df))
1 loop, best of 3: 494 ms per loop
In [139]: %timeit df[df.A > 5]
1 loop, best of 3: 536 ms per loop
In [140]: %timeit df.query('A > 5')
1 loop, best of 3: 781 ms per loop
In [141]: %timeit df[df.eval('A > 5')]
1 loop, best of 3: 770 ms per loop
import numexpr
np.random.seed(125)
def ne(x):
x = x.A.values
return x[numexpr.evaluate('(x > 5)')]
def be(x):
return x[x.A > 5]
def q(x):
return x.query('A > 5')
def ev(x):
return x[x.eval('A > 5')]
def make_df(n):
df = pd.DataFrame(np.random.randint(10, size=n), columns=['A'])
return df
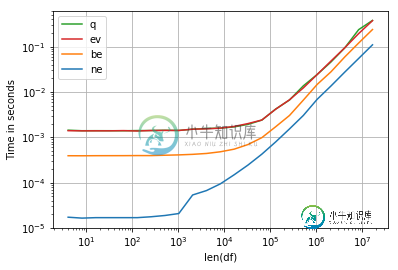
perfplot.show(
setup=make_df,
kernels=[ne, be, q, ev],
n_range=[2**k for k in range(2, 25)],
logx=True,
logy=True,
equality_check=False,
xlabel='len(df)')
类似资料:

