Java中方法重载中的Varargs
以下代码无法编译。
package varargspkg;
public class Main {
public static void test(int... i) {
for (int t = 0; t < i.length; t++) {
System.out.println(i[t]);
}
System.out.println("int");
}
public static void test(float... f) {
for (int t = 0; t < f.length; t++) {
System.out.println(f[t]);
}
System.out.println("float");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
test(1, 2); //Compilation error here quoted as follows.
}
}
发出编译时错误。
对test的引用是模棱两可的,varargspkg.Main中的方法test(int
…)和varargspkg.Main中的方法test(float …)
这似乎很明显,因为方法调用中的参数值test(1, 2);可以提升int为float
如果任何一个或两个参数都带有F或作为后缀f,则会进行编译。
但是,如果我们用相应的包装器类型表示方法签名中的接收参数,如下所示
public static void test(Integer... i) {
System.out.println("Integer" + Arrays.asList(i));
}
public static void test(Float... f) {
System.out.println("Float" + Arrays.asList(f));
}
那么对该方法的调用test(1, 2);不会发出任何编译错误。在这种情况下,要调用的方法是接受一个Integervarargs参数(上一代码段中的第一个)的方法。
为什么在这种情况下没有报告第一种情况下的错误?似乎自动装箱和自动类型升级都在这里应用。是否先应用自动装箱才能解决错误?
Oracle文档说,
一般来说,您不应该重载varargs方法,否则程序员将很难弄清楚调用哪个重载。
此链接中的最后一句话。但是,这是为了更好地理解varargs。
另外要添加下面的代码,编译也很好。
public class OverLoading {
public static void main(String[] args) {
load(1);
}
public static void load(int i) {
System.out.println("int");
}
public static void load(float i) {
System.out.println("float");
}
}
编辑:
以下是指示编译错误的快照。我创建了一个新的应用程序,因此程序包名称不同。
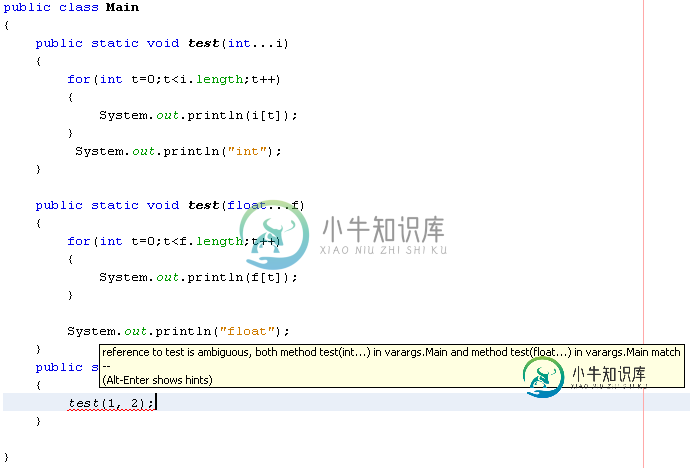
我正在使用JDK 6。
问题答案:
You can either Widen or Box but you cannot do both, unless you are boxing and widening to Object (An int to Integer(Boxing) and then Integer to
Object(Widening) is legal, since every class is a subclass of Object, so it
is possible for Integer to be passed to Object parameter)
Similarly an int to Number is also legal (int -> Integer -> Number) Since
Number is the super class of Integer it is possible.
Let’s see this in your example: -
public static void test(Integer...i)
public static void test(Float...f)
There are some rules that are followed when selecting which overloaded method
to select, when Boxing, Widening, and Var-args are combined: -
- Primitive widening uses the
smallestmethod argument possible - Wrapper type cannot be widened to another Wrapper type
- You can Box from int to Integer and widen to Object but no to Long
- Widening beats Boxing, Boxing beats Var-args.
- You can Box and then Widen (An
intcan becomeObjectviaInteger) - You cannot Widen and then Box (An
intcannot becomeLong) - You cannot combine var-args, with either widening or boxing
So, based on the above given rules: -
When you pass two integers to above functions,
- according to rule 3, it will have to be first
Widenedand thenBoxedto fit into aLong, which is illegal according to rule 5 (You cannot Widen and then Box). - So, it is Boxed to store in
Integervar-args.
But in first case, where you have methods with var-args of primitive types:
public static void test(int...i)
public static void test(float...f)
Then test(1, 2) can invoke both the methods (Since neither of them is more
suitable for rule 1 to apply) : -
- In first case it will be
var-args - In second case, it will be Widening and then Var-args (which is allowed)
Now, when you have methods with exactly one int and one flost: -
public static void test(int i)
public static void test(float f)
Then on invoking using test(1), rule 1 is followed, and smallest possible
widening (i.e. the int where no widening is needed at all) is chosen. So 1st
method will be invoked.
For more information, you can refer to JLS - Method Invocation Conversion
-
问题内容: 这是我对Java中的重载解析的了解: 编译器尝试从给定的重载方法定义中解析方法调用的过程称为重载解析。如果编译器找不到确切的匹配项,则仅通过使用向上转换来查找最接近的匹配(永远不会进行向下转换)。 这是一堂课: 如预期的那样,输出为10。 但是,如果我稍微更改类定义并更改第二个重载方法。 输出为8。 在这里我很困惑。如果从不使用向下转换,那么为什么只打印8个?为何编译器会选择以参数为参
-
本文向大家介绍Java Varargs中的方法重载和歧义,包括了Java Varargs中的方法重载和歧义的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在Java中使用变量参数时存在歧义。发生这种情况是因为两种方法绝对可以有效地被数据值调用。因此,编译器不知道该调用哪种方法。 示例 输出结果 名为Demo的类定义了一个名为“ my_fun”的函数,该函数采用可变数量的浮点值。使用“ for”循环将这些
-
可能重复:NULL参数的方法重载 以下代码编译并运行良好。 在此代码中,要调用的方法是接受字符串类型参数的方法 医生说。 如果多个成员方法既可访问又适用于方法调用,则需要选择一个来为运行时方法调度提供描述符。Java编程语言使用选择最具体方法的规则。 但我不明白,当代码中接受原语int参数的方法之一被修改为接受包装器类型Integer的参数时,例如, 发出编译时错误。 对temp的引用不明确,me
-
问题内容: 以下代码可以编译并正常运行。 在此代码中,要调用的方法是接受type参数的方法 该文档说。 如果多个成员方法既可访问又可应用于方法调用,则必须选择一个成员方法来为运行时方法分派提供描述符。Java编程语言使用选择最具体方法的规则。 但是我不明白何时将接受原始参数的代码中的方法之一修改为接受包装器类型的参数,例如, 发出编译时错误。 对temp的引用含糊不清,methodoverload
-
问题内容: 我在Javascript代码中使用以下方法重载。 我不明白的是,如果我调用javascript应该调用第一个函数,但是问题是javascript实际上调用了第三个函数。这是为什么?如何调用第一和第二函数?这是什么原因呢?有没有一种合适的方法可以在Javascript中实现方法重载?行业标准是什么? 问题答案: JavaScript不支持方法重载(如Java或类似方法),您的第三个函数将
-
本文向大家介绍在Java中使用方法重载,包括了在Java中使用方法重载的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一个类可以有多个具有相同名称的方法,但方法的参数列表不应相同。这称为方法重载。方法重载有点类似于构造函数重载。 演示此的程序如下所示- 示例 输出结果 现在让我们了解上面的程序。 在方法重载的实现中,使用三种方法创建PrintValues类。其中一个采用int类型的参数,另一个采用dou

