JILL.py
The enhanced Python fork of JILL -- Julia Installer for Linux (and every other platforms) -- Light
Features
- download Julia releases from the nearest mirror server
- support all platforms and architectures
- manage multiple julia releases
- easy-to-use CLI tool
Install JILL
For the first time users of jill, you will need to install it using pip: pip install jill --user -U. Also use this to upgrade JILL version.
Python >= 3.6 is required. For base docker images, you also need to make sure wget and gnupgare installed.
Installing Julias
When you type jill install, it does the following things:
- query the latest version
- download, verify, and install julia
- make symlinks, e.g.,
julia,julia-1,julia-1.6
For common Julia users:
- Get the latest stable release:
jill install - Get the latest 1.y.z release:
jill install 1 - Get the latest 1.6.z release:
jill install 1.6 - Get the specific version:
jill install 1.6.2,jill install 1.7.0-beta3 - Get the latest release (including unstable ones):
jill install --unstable
For Julia developers and maintainers:
- Get the nightly builds:
jill install latest. This gives youjulia-latest. - Checkout CI build artifacts of specific commit in the Julia Repository:
jill install 1.8.0+cc4be25c(<major>.<minor>.<patch>+<build>with at least the first 7 characters of thehash). This gives youjulia-dev.
Some flags that can be useful:
- No confirmation before installation:
jill install --confirm - Download from Official source:
jill install --upstream Official - Keep downloaded contents after installation:
jill install --keep_downloads - Force a reinstallation:
jill install --reinstall
The symlinks
To start Julia, you can use predefined JILL symlinks such as julia. jill install uses the following rule makes surethat you're always using the latest stable release.
Stable releases:
juliapoints to the latest Julia release.julia-1points to the latest 1.y.z Julia release.julia-1.6points to the latest 1.6.z Julia release.
For unstable releases such as 1.7.0-beta3, installing it via jill install 1.7 --unstable orjill install 1.7.0-beta3 will only give you julia-1.7; it won't make symlinks for julia orjulia-1.
To dance on edge:
julia-latestpoints to the nightly build fromjill install latestjulia-devpoints to the julia CI build artifacts from, for example,jill install 1.8.0+cc4be25c.
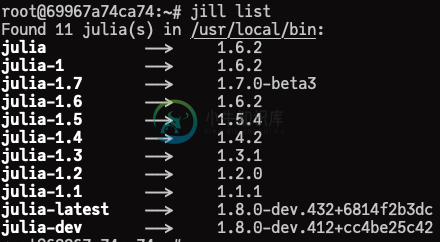
List symlinks and their target versions
jill list [version] gives you every symlinks and their target Julia versions.
Change symlink target
For non-windows system, you are free to use ln command to change the symlink targets. For Windowsit uses an entry .cmd file for this so you'll need to copy them. In the meantime, jill switchprovides a simple and unified way to do this:
jill switch 1.6: letjuliapoints to the latest julia 1.6.z release.jill switch <path/to/my/own/julia/executable>: letjuliapoints to custom executables.jill switch 1.6 --target julia-1: letjulia-1points to the latest julia 1.6.z release.
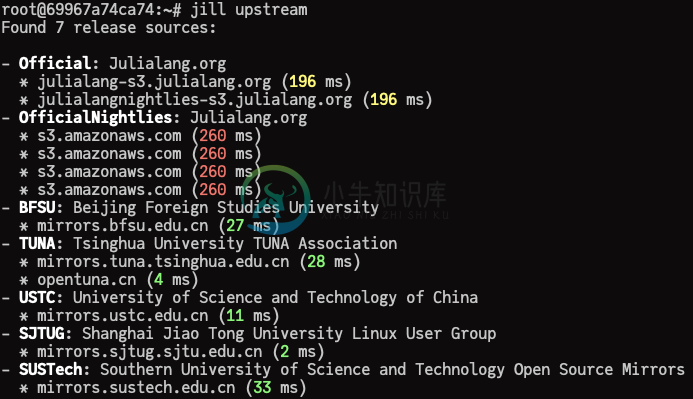
About downloading upstreams
By default, JILL tries to be smart and will download contents from the nearest upstream. You canget the information of all upstreams via jill upstream. Here's what I get in my laptop, I live inChina so the official upstreams aren't so accessible for me :(
To temporarily disable this feature, you can use flag --upstream <server_name>. For instance,jill install --upstream Official will faithfully download from the official julialang s3 bucket.
To permanently disable this feature, you can set environment variable JILL_UPSTREAM.
Note that flag is of higher priority than environment variable. For example, if JILL_UPSTREAM isset to mirror server "TUNA", you can still download from the official source via jill install --upstream Official.
About installation and symlink directories
Here's the default JILL installation and symlink directories:
| system | installation directory | symlink directory |
|---|---|---|
| macOS | /Applications |
~/.local/bin |
| Linux/FreeBSD | ~/packages/julias |
~/.local/bin |
| Windows | ~\AppData\Local\julias |
~\AppData\Local\julias\bin |
For example, on Linux jill install 1.6.2 will have a julia folder in ~/packages/julias/julia-1.6and symlinks julia/julia-1/julia-1.6 created in ~/.local/bin.
Particularly, if you're using jill as root user, you will do a system-wide installation:
- Installation directory will be
/opt/juliasfor Linux/FreeBSD. - Symlink directory will be
/usr/local/binfor Linux/FreeBSD/macOS.
To change the default JILL installation and symlink directories, you can set environment variablesJILL_INSTALL_DIR and JILL_SYMLINK_DIR.
(Deprecated) jill install also provides two flag --install_dir <dirpath> and --symlink_dir <dirpath>, they have higher priority than the environment variables JILL_INSTALL_DIR andJILL_SYMLINK_DIR.
JILL environment variables
jill is made as a convenient tool and it can sometimes be annoying passing flags to it. There aresome predefined environment variables that you can use to set the default values:
- Specify a default downloading upstream
JILL_UPSTREAM:--upstream - Override default symlink directory
JILL_SYMLINK_DIR:--symlink_dir - Override default installation directory
JILL_INSTALL_DIR:--install_dir
The flag version has higher priority than the environment variable version.
Advanced: Example with cron
If you're tired of seeing (xx days old master) in your nightly build version, then jill canmake your nightly build always the latest version using cron:
# /etc/cron.d/jill
PATH=/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/bin
# install a fresh nightly build every day
* 0 * * * root jill install latest --confirm --upstream Official
Advanced: Registering a new public releases upstream
If it's an public mirror and you want to share it worldwide to other users of JILL. You can add anentry to the public registry, make a PR, then I will tag a new releasefor that.
Please check the sources.json format for more detailed information on theformat.
Advanced: Specifying custom (private) downloading upstream
To add new private upstream, you can create a file ~/.config/jill/sources.json (fow Windows it is~/AppData/Local/julias/sources.json) and add your own upstream configuration just like the JILLsources.json does. Once this is done JILL will recognize this newupstream entry.
Please check the sources.json format for more detailed information on theformat.
Advanced: make a Julia release mirror
There are two ways to do so:
- use
aws s3 sync, this should be the easiest way to do so I highly recommend this. - (Deprecated) use
jill mirrorcommand with mirror config example. Ididn't know about theaws s3 syncstuff when I implemented this.
The Julia release mirror does not contain Julia package contents, to mirror all the Julia packagesand artifacts (which requires >1.5Tb storage), you can use StorageMirrorServer.jl.
Advanced: The Python API
jill.py also provides a set of Python API:
from jill.install import install_julia
from jill.download import download_package
# equivalent to `jill install --confirm`
install_julia(confirm=True)
# equivalent to `jill download`
download_package()
You can read its docstring (e.g., ?install_julia) for more information.
FAQs
Why you should use JILL?
Distro package managers (e.g., apt, pac) is likely to provide a broken Julia with incorrectbinary dependencies (e.g., LLVM ) versions. Hence it's recommended to download and extract theJulia binary provided in Julia Downloads. jill.py doesn't doanything magical, but just makes such operation even stupid.
Why I make the python fork of JILL?
At first I found myself needing a simple tool to download and install Julia on my macbook andservers in our lab, I made my own shell scripts and I'd like to share it with others. Then I foundthe jill.sh project, Abel knows a lot shell so I decide to contribute my macOS Juliainstaller to jill.sh.
There are three main reasons for why I decided to start my Python fork:
- I live in China. Downloading resources from GitHub and AWS s3 buckets is a painful experience.Thus I want to support downloading from mirror servers. Adding mirror server support to jill.sh isquite complicated and can easily become a maintenance nightmare.
- I want to make a cross platform installer that everyone can use, not just Linux/macOS users. Shellscripts doesn't allow this as far as I can tell. In contrast, Python allows this.
- Most importantly, back to when I start this project, I knew very little shell, I knew nothingabout C/C++/Rust/Go and whatever you think a good solution is. I happen to knew a few Python.
For some "obvious" reason, Julia People don't like Python and I understand it. (I also don't likePython after being advanced Julia user for more than 3 years) But to be honest, revisiting thisproject, I find using Python is one of the best-made decision during the entire project. Here is thereason: no matter how you enjoy Julia (or C++, Rust), Python is one of the best successfulprogramming language for sever maintenance purpose. Users can easily found tons of "how-to"solutions about Python and it's easy to write, deploy, and ship Python codes to the world via PyPI.
And again, I live in China so I want to rely on services that are easily accessible in China, PyPIis, GitHub and AWS S3 bucket aren't. A recent Julia installer project juliaup written in Rustsolves the Python dependency problem very well, but the tradeoff is that juliaup needs its owndistributing system (currently GitHub and S3 bucket) to make sure it can be reliably downloaded touser machine. And for this it just won't be as good as PyPI in the foreseeable future.
Is it safe to use jill.py?
Yes, jill.py use GPG to check every tarballs after downloading. Also, *.dmg/*.pkg for macOSand .exe for Windows are already signed.
What's the difference between jill.sh and jill.py
jill.sh is a shell script that works quite well on Linux x86/x64 machines. jill.py isan enhanced python package that focus on Julia installation and version management, and brings aunified user experience on all platforms.
Why julia fails to start
The symlink julia are stored in JILL predefined symlinksdir thus you have to make sure this folder is inPATH. Search "how to add folder to PATH on xxx system" you will get a lot of solutions.
How do I use multiple patches releases (e.g., 1.6.1 and 1.6.2)
Generally, you should not care about patch version differences so jill.py make it explicitly thatonly one of 1.6.x can exist. If you insist to have multiple patch versions, you could use jill install --install_dir <some_other_folder> to install Julia in other folder, and then manually makea symlink back. As I just said, in most cases, common users should not care about this patch versiondifference and should just use the latest patch release.
How to only download contents without installation?
Use jill download [version] [--sys <system>] [--arch <arch>]. Check jill download --help formore details.
Linux with musl libc
For Julia (>= 1.5.0) in Linux with musl libc, you can just do jill install and it gives you theright Julia binary. To download the musl libc binary using jill download, you will need to pass--sys musl flag.
MacOS with Apple silicon (M1)
Yes it's supported. But I don't have access to M1 machine so I can't test it.
-
【问题描述】Jill要进行一次旅行,沿途中要经过若干个城市。对于每两个相邻城市之间的路程,他都可以选择骑自选车或是坐公车汽车。如果沿途风景怡人,则他更喜欢骑自选车来完成这段路程。 Jill对每段路程都有评出了一个满意度,这是一个非零整数,所有他喜欢的路程标以正数,不喜欢的路程标以负数,数的绝对值大小代表他喜欢/不喜欢的程度。 如果在本次旅行中只允许在一段连续路程中骑自行车,而剩下的路程都坐公共汽车
-
一、 作为一个模板语言,它的主要优势是可以省去很多重复的前端代码,用类似于后台循环代码等方式来产生html,首先,需要读入一个带有模板语言的html 模板,类似于如下: <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> </head> <body> <p style='font-size:15px; font-
-
一:渲染模版 要渲染一个模板,通过render_template方法即可。 @app.route('/about/') def about(): return render_template('about.html',**{'user':'username'}) 渲染模版时有两种传递参数的方式:用 var='value' 传递一个参数;使用字典组织多个参数,并且加两个*号转换成关键字参数传入。 p
-
Jupyter Lab 安装 史上最全Jupyter Lab 配置 JupyterLab:程序员的笔记本神器 Jupyter Lab 用法 JupyterLab基本使用 利器|JupyterLab 数据分析必备IDE完全指南 Jupyter Notebook插入图片的4种方法 Jupyter Lab 启动 $ conda activate tf_2c $ jupyter lab
-
在android 开发中,经常会出现稀奇古怪的问题,今天发现一个奇怪的问题, Cannot load Jill from build tools. 在Android studio 2.3.3上面,以前的项目从来没有出现这个问题,在android studio 3.2的时候,在用android studio 2.3.3 就出现问题,为什么呢? 经过多次尝试得到一个结论,在添加Lambda 时,
-
DISCLAIMER: This is not an official google project, this is just something I wrote while at Google. Pyringe What this is Pyringe is a python debugger capable of attaching to running processes, inspect
-
GIL:Global Interpreter Lock, 全局解释器锁定,是指python虚拟机在执行多线程程序时,任一时刻只有一个线程在执行,这使得多线程程序无法充分利用CPU。对于一般的多线程跟IO绑定的程序,GIL影响并不明显,因为多线程跟IO绑定大多时间在等待,CPU并不是瓶颈,只有计算量大的应用才是瓶颈,GIL会限制性能的发挥。 为什么会存在GIL,因为python为了模拟多线程
-
输出整体内容,不带省略号 import pandas as pd pd.set_option('display.max_columns', None) pd.set_option('display.max_rows', None) pd.set_option('max_colwidth',200)