concurrency-logger
HTTP logging middleware especially useful to unwind concurrent operations without losing the request context
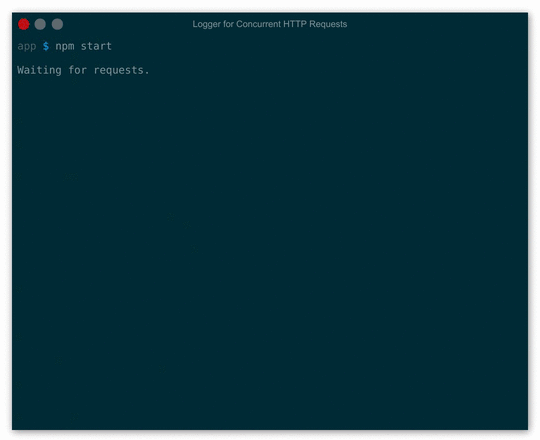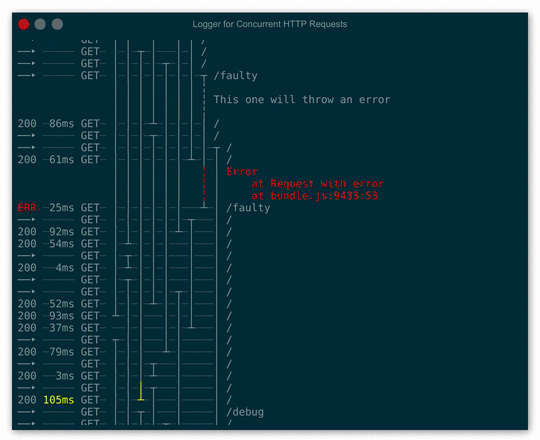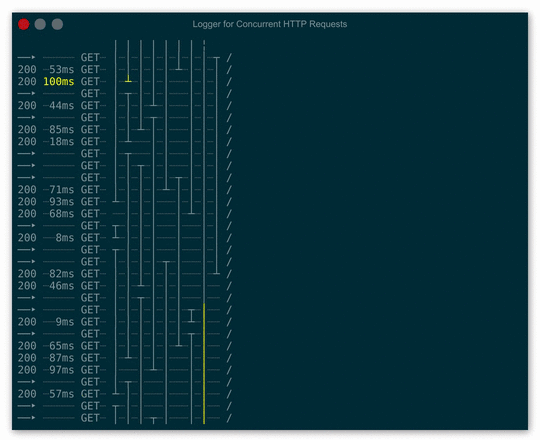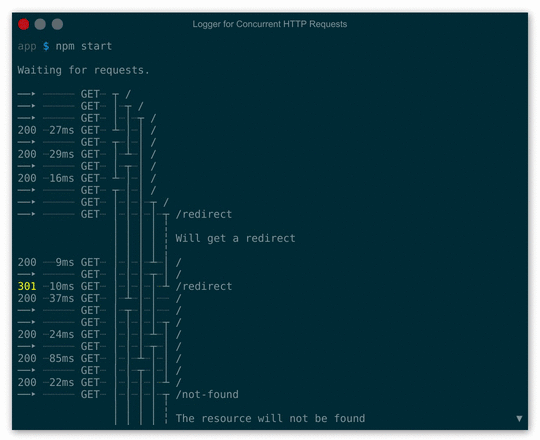
Launch demo in your browser
Install
$ npm install concurrency-logger
Usage
With koa
Basic usage
import Koa from 'koa';
import createLogger from 'concurrency-logger';
const app = new Koa;
// Logger is stateful as it contains information about concurrent requests
// Same instance needs to be reused across requests
const logger = createLogger(/* options */);
app.use(logger);
Log from middleware
// Log something in context to a specific request to trace it back easily -
// also when there are multiple concurrent requests
app.use(async (context, next) => {
context.log('Log!');
context.log.info('Info!');
context.log.error('Error!');
await next();
});
Attach more context to the log
const logger = createLogger({
req: context => (
context.originalUrl + '\n' +
context.get('User-Agent')
)
});
Include localized timestamps
const logger = createLogger({
timestamp: true
});
Write log to file
import { createWriteStream } from 'fs';
// To read log use program that interprets ANSI escape codes,
// e.g. cat or less -r
const log = createWriteStream('logs/requests.log');
const logger = createLogger({
reporter: log
});
Adjust alert levels per method and response time
const logger = createLogger({
getLevel: (responseTime, context) => {
/*
GET
0 - 99ms: 0
100 - 149ms: 1
150 - 199ms: 2
200 - 249ms: 3
250 - 299ms: 4
300 - 349ms: 5
> 350ms : 6
POST
0 - 149ms: 0
150 - 225ms: 1
... : ...
*/
let threshold = 50; // ms
if (['POST', 'PUT'].includes(context.method)) {
threshold *= 1.5;
}
return Math.floor(responseTime / threshold) - 1;
}
});
Standalone
import createLogger from 'concurrency-logger';
const logger = createLogger(/* options */);
(async () => {
const context = {
method: 'GET',
originalUrl: '/'
};
const next = async () => {
await new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, 100));
context.status = 200;
};
try {
await logger(context, next);
} catch (error) {
// Errors are passed through
}
})();
API
| Option | Type | Default | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| minSlots | integer | 1 |
Amount of space that is provisioned to display concurrent request lanes. Number of lanes will automatically scale up as the number of concurrent requests grow. | 3 |
| getLevel | integer: function(responseTime: integer) | responseTime => Math.floor(responseTime / 50) - 1 |
Map response time to alert level. Alert levels go from 0 (default color) to 6 (dark red). By default that means <100ms: 0, <150ms: 1 <200ms: 2, ..., >=350ms: 6. |
responseTime => Math.floor(responseTime / 100) |
| width | integer, boolean(false) |
undefined |
If no width is provided, it will be dynamically read from process.stdout.columns. Pass in an integer to break all lines according to the specified fixed (terminal character) width. Pass in false if you want the lines not to break at all. |
80, 132, false |
| timestamp | boolean | false |
Print localized timestamp for every requests. | true, false |
| slim | boolean | false |
"Slim mode": don't use an extra character between request lanes to shrink width, but make them harder to separate visually. | true, false |
| reporter | writable stream | process.stdout |
Specify a stream that handles the output lines. Write to terminal or stream to a log file, for example. Note that the lines contain ANSI color codes, so when streaming to a file you might need a program that can read those. E.g. less -r requests.log |
require('fs').createWriteStream('logs/requests.log') |
| req | any: function(context: object) | context => context.originalUrl |
Attach additional information to the request log line. | context => context.originalUrl + '\n' + context.get('User-Agent') |
| res | any: function(context: object) | context => context.originalUrl |
Attach additional information to the response log line. | context => context.originalUrl + '\n' + context.get('User-Agent') |
Developing
Install development dependencies
$ npm install
Create new fixtures to test against
$ npm run create-fixtures
Manually review fixtures (you need a program that renders ANSI escape codes)
$ less -r test/fixtures/*
Run tests
$ npm test
Run code linter
$ npm run lint
Compile to ES5 from /src to /lib
$ npm run compile
Initialize demo project
$ git clone git@github.com:PabloSichert/concurrency-logger demo
$ cd demo
demo $ git checkout gh-pages
demo $ npm install
Build demo
demo $ npm run compile
-
pt-config-diff 比较mysql配置文件和服务器参数 示例:pt-config-diff /etc/my.cnf h=192.168.53.11 --user=root --password=123456 --socket=/tmp/mysql.sock pt-config-dirr /etc/my.cnf /etc/my_slave.cnf 内容如下:21 config differ
-
线程创建后有几种情况会取消 1. 用户点击cancel取消 2. 超时取消,比如网页加载中有部分信息没被加载出来 3. 应用程序的逻辑设计,比如在多线程情况下,有一个线程找到了result,其他线程停止作业。 4. error。exception 5. 关闭程序,关闭服务 常用中断方式 while (!isCancelled) { doSomething(); } 每次都去检查一
-
【Python】concurrency best practice -- for HTTP (RESTful) API concurrent.furture.ThreadPoolExecutor N/A die thread detail: N/A """die_threads.py""" from functools import wraps from logging import getLo
-
Look at the concurrency model this uses... Receiving CheckTx Broadcasting new tx Interfaces with consensus engine, reap/update while checking Calling the ABCI app (ordering. callbacks. how proxy works
-
Concurrency Kit 提供了大量的并发原生方法和数据结构用于帮助设计和实现高性能的系统开发。该项目最大限度的降低对操作系统的相关性,提供统一的接口,便于程序在不同系统间的移植。
-
问题内容: 我有一个servlet,它为用户做一些工作,然后减少用户的信用。当我实时查看数据库中的用户信用时,如果有来自同一用户的许多并发请求,则由于并发控制,信用被错误地扣除。假设我有一台服务器,并且数据库管理处于hibernate状态。我正在使用事务控制来处理整个请求,请参见代码以获取详细信息。我有几个问题: 当面对来自同一用户的多个并发请求时,为什么db中的信用计数器到处跳?为什么我的交易控
-
并发性使程序一次在多个线程上运行。 并发程序的一个示例是Web服务器同时响应许多客户端。 通过消息传递并发很容易,但如果它们基于数据共享则很难编写。 在线程之间传递的数据称为消息。 消息可以由任何类型和任何数量的变量组成。 每个线程都有一个id,用于指定消息的收件人。 任何启动另一个线程的线程都称为新线程的所有者。 在D中启动线程 函数spawn()接受一个指针作为参数,并从该函数启动一个新线程。
-
Erlang中的并发编程需要具有以下基本原则或过程。 该清单包括以下原则 - piD = spawn(Fun) 创建一个评估Fun的新并发进程。 新进程与调用者并行运行。 一个例子如下 - 例子 (Example) -module(helloworld). -export([start/0]). start() -> spawn(fun() -> server("Hello") end)
-
Runnable/Callable Runnable接口只有一个没有返回值的方法。 trait Runnable { def run(): Unit } Callable与之类似,除了它有一个返回值 trait Callable[V] { def call(): V } 线程 Scala并发是建立在Java并发模型基础上的。 在Sun JVM上,对IO密集的任务,我们可以在一台机器运行成千

