Android aapt自动打包工具详细介绍
Android aapt自动打包工具
概念
在Android.mk中有LOCAL_AAPT_FLAGS配置项,在gradle中也有aaptOptions,那么aapt到底是干什么的呢? aapt即Android Asset Packaging Tool(Android 打包工具),在SDK的build-tools目录下。我们可以查 看,创建, 更新ZIP格式的文档附件(zip, jar, apk)。也可将资源文件编译成二进制文件,尽管你可能没有直接使用过aapt工具,但是build scripts和IDE插件会使用这个工具打包apk文件构成一个Android 应用程序。
aapt打包流程
aapt传统的打包主要是最res和Java代码的打包,aapt打包走的是单线程、流水式的任务从上到下进行打包构建。
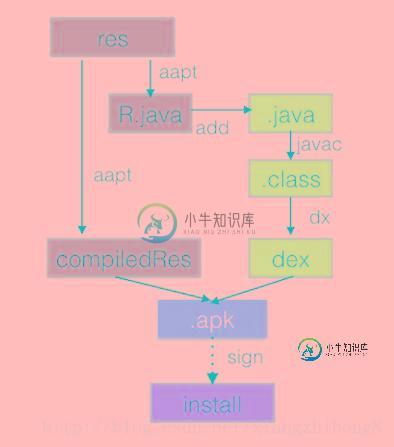
传统的aapt打包,aapt会执行2次,第一次是生成R.java,参与javac编译,第二次是对res里面的资源文件进行编译,最后APKBuilder会把DEX文件与编译好的资源文件及DEX文件进行打包成APK,签名并安装至手机。整个流程下来,没有任何缓存,没有并发,也没有增量,每次构建都是一个全新的过程,所以每次构建时间也比较恒定,代码量,资源量越多,构建时间越慢。
aapt常用的参数
我们可以通过aapt help来查看常用的参数。
Usage:
aapt l[ist] [-v] [-a] file.{zip,jar,apk}
List contents of Zip-compatible archive.
aapt d[ump] [--values] [--include-meta-data] WHAT file.{apk} [asset [asset ...]]
strings Print the contents of the resource table string pool in the APK.
badging Print the label and icon for the app declared in APK.
permissions Print the permissions from the APK.
resources Print the resource table from the APK.
configurations Print the configurations in the APK.
xmltree Print the compiled xmls in the given assets.
xmlstrings Print the strings of the given compiled xml assets.
aapt p[ackage] [-d][-f][-m][-u][-v][-x][-z][-M AndroidManifest.xml] \
[-0 extension [-0 extension ...]] [-g tolerance] [-j jarfile] \
[--debug-mode] [--min-sdk-version VAL] [--target-sdk-version VAL] \
[--app-version VAL] [--app-version-name TEXT] [--custom-package VAL] \
[--rename-manifest-package PACKAGE] \
[--rename-instrumentation-target-package PACKAGE] \
[--utf16] [--auto-add-overlay] \
[--max-res-version VAL] \
[-I base-package [-I base-package ...]] \
[-A asset-source-dir] [-G class-list-file] [-P public-definitions-file] \
[-S resource-sources [-S resource-sources ...]] \
[-F apk-file] [-J R-file-dir] \
[--product product1,product2,...] \
[-c CONFIGS] [--preferred-density DENSITY] \
[--split CONFIGS [--split CONFIGS]] \
[--feature-of package [--feature-after package]] \
[raw-files-dir [raw-files-dir] ...] \
[--output-text-symbols DIR]
Package the android resources. It will read assets and resources that are
supplied with the -M -A -S or raw-files-dir arguments. The -J -P -F and -R
options control which files are output.
aapt r[emove] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 ...]
Delete specified files from Zip-compatible archive.
aapt a[dd] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 ...]
Add specified files to Zip-compatible archive.
aapt c[runch] [-v] -S resource-sources ... -C output-folder ...
Do PNG preprocessing on one or several resource folders
and store the results in the output folder.
aapt s[ingleCrunch] [-v] -i input-file -o outputfile
Do PNG preprocessing on a single file.
aapt v[ersion]
Print program version.
Modifiers:
-a print Android-specific data (resources, manifest) when listing
-c specify which configurations to include. The default is all
configurations. The value of the parameter should be a comma
separated list of configuration values. Locales should be specified
as either a language or language-region pair. Some examples:
en
port,en
port,land,en_US
-d one or more device assets to include, separated by commas
-f force overwrite of existing files
-g specify a pixel tolerance to force images to grayscale, default 0
-j specify a jar or zip file containing classes to include
-k junk path of file(s) added
-m make package directories under location specified by -J
-u update existing packages (add new, replace older, remove deleted files)
-v verbose output
-x create extending (non-application) resource IDs
-z require localization of resource attributes marked with
localization="suggested"
-A additional directory in which to find raw asset files
-G A file to output proguard options into.
-F specify the apk file to output
-I add an existing package to base include set
-J specify where to output R.java resource constant definitions
-M specify full path to AndroidManifest.xml to include in zip
-P specify where to output public resource definitions
-S directory in which to find resources. Multiple directories will be scanned
and the first match found (left to right) will take precedence.
-0 specifies an additional extension for which such files will not
be stored compressed in the .apk. An empty string means to not
compress any files at all.
--debug-mode
inserts android:debuggable="true" in to the application node of the
manifest, making the application debuggable even on production devices.
--include-meta-data
when used with "dump badging" also includes meta-data tags.
--pseudo-localize
generate resources for pseudo-locales (en-XA and ar-XB).
--min-sdk-version
inserts android:minSdkVersion in to manifest. If the version is 7 or
higher, the default encoding for resources will be in UTF-8.
--target-sdk-version
inserts android:targetSdkVersion in to manifest.
--max-res-version
ignores versioned resource directories above the given value.
--values
when used with "dump resources" also includes resource values.
--version-code
inserts android:versionCode in to manifest.
--version-name
inserts android:versionName in to manifest.
--replace-version
If --version-code and/or --version-name are specified, these
values will replace any value already in the manifest. By
default, nothing is changed if the manifest already defines
these attributes.
--custom-package
generates R.java into a different package.
--extra-packages
generate R.java for libraries. Separate libraries with ':'.
--generate-dependencies
generate dependency files in the same directories for R.java and resource package
--auto-add-overlay
Automatically add resources that are only in overlays.
--preferred-density
Specifies a preference for a particular density. Resources that do not
match this density and have variants that are a closer match are removed.
--split
Builds a separate split APK for the configurations listed. This can
be loaded alongside the base APK at runtime.
--feature-of
Builds a split APK that is a feature of the apk specified here. Resources
in the base APK can be referenced from the the feature APK.
--feature-after
An app can have multiple Feature Split APKs which must be totally ordered.
If --feature-of is specified, this flag specifies which Feature Split APK
comes before this one. The first Feature Split APK should not define
anything here.
--rename-manifest-package
Rewrite the manifest so that its package name is the package name
given here. Relative class names (for example .Foo) will be
changed to absolute names with the old package so that the code
does not need to change.
--rename-instrumentation-target-package
Rewrite the manifest so that all of its instrumentation
components target the given package. Useful when used in
conjunction with --rename-manifest-package to fix tests against
a package that has been renamed.
--product
Specifies which variant to choose for strings that have
product variants
--utf16
changes default encoding for resources to UTF-16. Only useful when API
level is set to 7 or higher where the default encoding is UTF-8.
--non-constant-id
Make the resources ID non constant. This is required to make an R java class
that does not contain the final value but is used to make reusable compiled
libraries that need to access resources.
--shared-lib
Make a shared library resource package that can be loaded by an application
at runtime to access the libraries resources. Implies --non-constant-id.
--error-on-failed-insert
Forces aapt to return an error if it fails to insert values into the manifest
with --debug-mode, --min-sdk-version, --target-sdk-version --version-code
and --version-name.
Insertion typically fails if the manifest already defines the attribute.
--error-on-missing-config-entry
Forces aapt to return an error if it fails to find an entry for a configuration.
--output-text-symbols
Generates a text file containing the resource symbols of the R class in the
specified folder.
--ignore-assets
Assets to be ignored. Default pattern is:
!.svn:!.git:!.ds_store:!*.scc:.*:<dir>_*:!CVS:!thumbs.db:!picasa.ini:!*~
--skip-symbols-without-default-localization
Prevents symbols from being generated for strings that do not have a default
localization
--no-version-vectors
Do not automatically generate versioned copies of vector XML resources.
关于上面参数的具体含义大家可以自行去了解,但是有几个常用的参数是需要记住的。
aapt常用命令
1. 列出apk包的内容
aapt l[ist] [-v] [-a] file.{zip,jar,apk}
-v 以table形式列出来
-a 详细列出内容
例如:aapt l <你的apk文件>,这个命令就是查看apk内容
#### 2. 查看apk一些信息
aapt d[ump] [–values] WHAT file.{apk} [asset [asset …]]
badging Print the label and icon for the app declared in APK
permissions Print the permissions from the APK.
resources Print the resource table from the APK.
configurations Print the configurations in the APK.
xmltree Print the compiled xmls in the given assets.
xmlstrings Print the strings of the given compiled xml assets.
例如:aapt d permissions
3. 编译android资源
aapt p[ackage] [-d][-f][-m][-u][-v][-x][-z][-M AndroidManifest.xml] / [-0 extension [-0 extension …]] [-g tolerance] [-j jarfile] / [–debug-mode] [–min-sdk-version VAL] [–target-sdk-version VAL] / [–app-version VAL] [–app-version-name TEXT] [–custom-package VAL] / [–rename-manifest-package PACKAGE] / [–rename-instrumentation-target-package PACKAGE] / [–utf16] [–auto-add-overlay] / [–max-res-version VAL] / [-I base-package [-I base-package …]] / [-A asset-source-dir] [-G class-list-file] [-P public-definitions-file] / [-S resource-sources [-S resource-sources …]] [-F apk-file] [-J R-file-dir] / [–product product1,product2,…] / [raw-files-dir [raw-files-dir] …]
这个比较复杂,只解释几个关键参数。
-f 如果编译出来的文件已经存在,强制覆盖。
-m 使生成的包的目录放在-J参数指定的目录。
-J 指定生成的R.java的输出目录
-S res文件夹路径
-A assert文件夹的路径
-M AndroidManifest.xml的路径
-I 某个版本平台的android.jar的路径
-F 具体指定apk文件的输出
例如:
1). 将工程的资源编译R.java文件
aapt package -m -J
4. 打包好的apk中移除文件
aapt r[emove] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 …]
例如:aapt r <你的apk文件> AndroidManifest.xml, 这个就是将apk中的AndroidManifest移除掉
5. 添加文件到打包好的apk中
aapt a[dd] [-v] file.{zip,jar,apk} file1 [file2 …]
例如:aapt a <你的apk文件> <要添加的文件路径>, 这个就是将文件添加到打包好的apk文件中
感谢阅读,希望能帮助到大家,谢谢大家对本站的支持!
-
本文向大家介绍Android 调试工具用法详细介绍,包括了Android 调试工具用法详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文主要为大家讲解多种Android调试工具的用法。 1. 查看当前堆栈 1)功能:在程序中加入代码,使可以在logcat中看到打印出的当前函数调用关系。 2)方法: new Exception(“print
-
本文向大家介绍Node.js的包详细介绍,包括了Node.js的包详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在Node.js语言中,包和模块并没有本质的不同,包是在模块的基础上更深一步的抽象,包将某个独立的功能封装起来,用于发布、更新、依赖管理和进行版本控制。Node.js根据CommonJS规范实现了包机制,开发了npm来解决包的发布和获取需求。 Node.js的包是一个目录,其中包含J
-
本文向大家介绍YUM软件包管理工具与yum命令的详细介绍,包括了YUM软件包管理工具与yum命令的详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一、yum介绍 Yum (Yellow dog Updater, Modified) 是一个在 Fedora 中的字符前端软件包管理器。基于 RPM 包管理,能够从指定的服务器自动下载 RPM 包并且安装,可以处理依赖性关系,并且一次安装所有依赖的软件
-
本文向大家介绍IOS 静态库打包流程简化详细介绍,包括了IOS 静态库打包流程简化详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 IOS 静态库打包流程简化 在iOS开发中,我们经常会遇到开发SDK的需求。开发好的静态库后需要手动的合并.a文件,然后再拷贝相关的头文件,接着把静态库和头文件放在同一个文件里面打包发送给SDK的使用者。本文将介绍如何使用脚本,简化这一连串的过程。为了照顾广大初学者,
-
主要内容:Java16 打包工具的示例Java 14 引入了一个新的打包工具,基于 javapackager 的 jpackage。javapackager 是在 Java 8 中引入的,是 JavaFX 套件的一部分。由于 JavaFX 从 11 版本的 Java 中分离出来,因此该打包工具在标准产品中不再可用。 这个新工具旨在为操作系统提供本机安装程序。例如,Windows 的 msi/exe,MacOS 的 pkg/dmg,Li
-
主要内容:Java14 打包工具的示例Java 14 引入了一个新的打包工具,基于 javapackager 的 jpackage。javapackager 是在 Java 8 中引入的,是 JavaFX 套件的一部分。由于 JavaFX 从 11 版本的 Java 中分离出来,因此该打包工具在标准产品中不再可用。 这个新工具旨在为操作系统提供本机安装程序。例如,Windows 的 msi/exe,MacOS 的 pkg/dmg,Li

