C#构建树形结构数据(全部构建,查找构建)
摘要:
最近在做任务管理,任务可以无限派生子任务且没有数量限制,前端采用Easyui的Treegrid树形展示控件。
一、遇到的问题
获取全部任务拼接树形速度过慢(数据量大约在900条左右)且查询速度也并不快;
二、解决方法
1、Tree转化的JSON数据格式
a.JSON数据格式:
[
{
"children":[
{
"children":[
],
"username":"username2",
"password":"password2",
"id":"2",
"pId":"1",
"name":"节点2"
},
{
"children":[
],
"username":"username2",
"password":"password2",
"id":"A2",
"pId":"1",
"name":"节点2"
}
],
"username":"username1",
"password":"password1",
"id":"1",
"pId":"0",
"name":"节点1"
},
{
"children":[
],
"username":"username1",
"password":"password1",
"id":"A1",
"pId":"0",
"name":"节点1"
}
]
b.定义实体必要字段
为了Tree结构的通用性,我们可以定义一个抽象的公用实体TreeObject以保证后续涉及到的List<T>转化树形JSON
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.Linq; using System.Text; using System.Threading.Tasks; namespace MyTree.Abs { public abstract class TreeObejct { public string id { set; get; } public string pId { set; get; } public string name { set; get; } public IList<TreeObejct> children = new List<TreeObejct>(); public virtual void Addchildren(TreeObejct node) { this.children.Add(node); } } }
c.实际所需实体TreeModel让它继承TreeObject,这样对于id,pId,name,children我们就可以适用于其它实体了,这也相当于我们代码的特殊约定:
using MyTree.Abs;
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace MyTree.Models
{
public class TreeModel : TreeObejct
{
public string username { set; get; }
public string password { set; get; }
}
}
2、递归遍历
获取全部任务并转化为树形
获取全部任务转化为树形是比较简单的,我们首先获取到pId=0的顶级数据(即不存在父级的任务),我们通过顶级任务依次递归遍历它们的子节点。
b.我们暂时id以1开始则pId=0的都为顶级任务
我们首先写一段生成数据的方法:
public static IList<TreeObejct> GetData(int number = 11)
{
IList<TreeObejct> datas = new List<TreeObejct>();
for (int i = 1; i < number; i++)
{
datas.Add(new TreeModel
{
id = i.ToString(),
pId = (i - 1).ToString(),
name = "节点" + i,
username = "username" + i,
password = "password" + i
});
datas.Add(new TreeModel
{
id = "A" + i.ToString(),
pId = (i - 1).ToString(),
name = "节点" + i,
username = "username" + i,
password = "password" + i
});
}
return datas;
}
其次我们定义一些变量:
private static IList<TreeObejct> models;
private static IList<TreeObejct> models2;
private static Thread t1;
private static Thread t2;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int count = 21;
Console.WriteLine("生成任务数:"+count+"个");
Console.Read();
}
我们再写一个递归获取子节点的递归方法:
public static IList<TreeObejct> GetChildrens(TreeObejct node)
{
IList<TreeObejct> childrens = models.Where(c => c.pId == node.id.ToString()).ToList();
foreach (var item in childrens)
{
item.children = GetChildrens(item);
}
return childrens;
}
编写调用递归方法Recursion:
public static void Recursion()
{
#region 递归遍历
System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
var mds_0 = models.Where(c => c.pId == "0");//获取顶级任务
foreach (var item in mds_0)
{
item.children = GetChildrens(item);
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("----------递归遍历用时:" + sw.ElapsedMilliseconds + "----------线程名称:"+t1.Name+",线程ID:"+t1.ManagedThreadId);
#endregion
}
编写main函数启动测试:
private static IList<TreeObejct> models;
private static IList<TreeObejct> models2;
private static Thread t1;
private static Thread t2;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int count = 1001;
Console.WriteLine("生成任务数:"+count+"个");
models = GetData(count);
t1 = new Thread(Recursion);
t1.Name = "递归遍历";
t1.Start();
Console.Read();
}
输出结果:
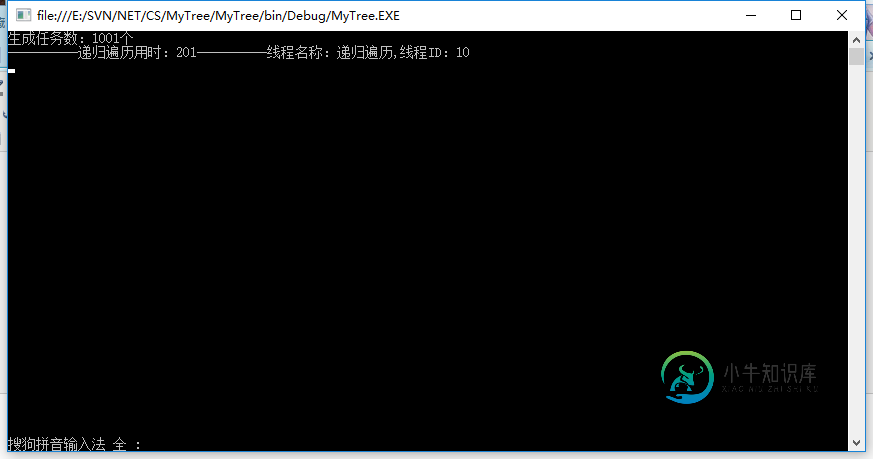
递归遍历至此结束。
3、非递归遍历
非递归遍历在操作中不需要递归方法的参与即可实现Tree的拼接
对于以上的代码,我们不需要修改,只需要定义一个非递归遍历方法NotRecursion:
public static void NotRecursion()
{
#region 非递归遍历
System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch sw2 = new System.Diagnostics.Stopwatch();
sw2.Start();
Dictionary<string, TreeObejct> dtoMap = new Dictionary<string, TreeObejct>();
foreach (var item in models)
{
dtoMap.Add(item.id, item);
}
IList<TreeObejct> result = new List<TreeObejct>();
foreach (var item in dtoMap.Values)
{
if (item.pId == "0")
{
result.Add(item);
}
else
{
if (dtoMap.ContainsKey(item.pId))
{
dtoMap[item.pId].AddChilrden(item);
}
}
}
sw2.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("----------非递归遍历用时:" + sw2.ElapsedMilliseconds + "----------线程名称:" + t2.Name + ",线程ID:" + t2.ManagedThreadId);
#endregion
}
编写main函数:
private static IList<TreeObejct> models;
private static IList<TreeObejct> models2;
private static Thread t1;
private static Thread t2;
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int count = 6;
Console.WriteLine("生成任务数:"+count+"个");
models = GetData(count);
models2 = GetData(count);
t1 = new Thread(Recursion);
t2 = new Thread(NotRecursion);
t1.Name = "递归遍历";
t2.Name = "非递归遍历";
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
Console.Read();
}
启动查看执行结果:
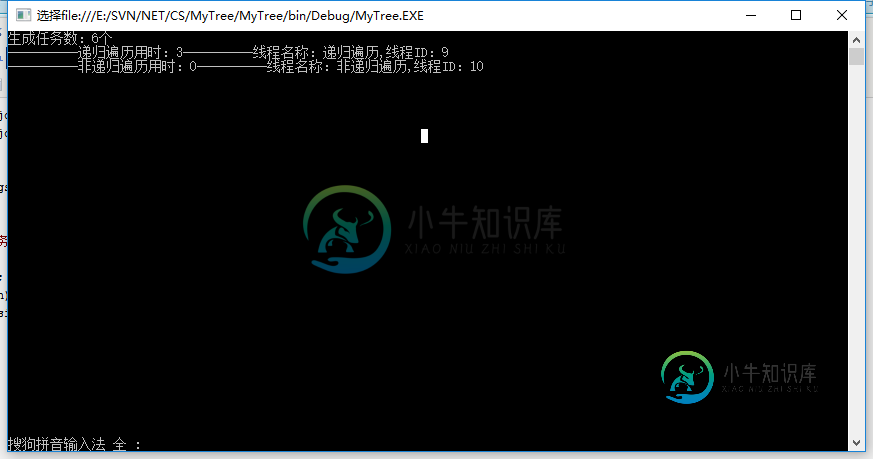
发现一个问题,递归3s,非递归0s,随后我又进行了更多的测试:
执行时间测试
| 任务个数 | 递归(ms) | 非递归(ms) |
| 6 | 3 | 0 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | 1 | 0 |
| 101 | 1 | 0 |
| 101 | 4 | 0 |
| 101 | 5 | 0 |
| 1001 | 196 | 5 |
| 1001 | 413 | 1 |
| 1001 | 233 | 7 |
| 5001 | 4667 | 5 |
| 5001 | 4645 | 28 |
| 5001 | 5055 | 7 |
| 10001 | StackOverflowException | 66 |
| 10001 | StackOverflowException | 81 |
| 10001 | StackOverflowException | 69 |
| 50001 | - | 46 |
| 50001 | - | 47 |
| 50001 | - | 42 |
| 100001 | - | 160 |
| 100001 | - | 133 |
| 100001 | - | 129 |
StackOverflowException:因包含的嵌套方法调用过多而导致执行堆栈溢出时引发的异常。 此类不能被继承。
StackOverflowException 执行堆栈溢出发生错误时引发,通常发生非常深度或无限递归。
-:没有等到结果。
当然这个测试并不专业,但是也展示出了它的效率的确满足了当前的需求。
4、查找构建树形结果
原理同上述非递归相同,不同之处是我们通过查找的数据去构建树形

我们通过查找获取到圈中的任务,再通过当前节点获取到父级节点,因为当时没考虑到任务层级的关系,因此为添加层级编号,为此可能会有重复的存在,因此我们使用HashSet<T>来剔除我们的重复数据,最终获取到有用数据再通过非递归遍历方法,我们便可以再次构建出树形(tree),来转化为JSON数据。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
我现在正在实现模拟N体问题的Barnes-Hut算法。我只想问关于建筑树的部分。 我做了两个函数来为它构建树。 我递归地构建树,并在构建时打印每个节点的数据,一切看起来都是正确的,但当程序返回到主函数时,只有树的根和根的子节点存储值。其他节点的值没有被存储,这很奇怪,因为我在递归过程中打印了它们,它们应该被存储。 这是经过修改的代码的一部分,我认为问题可能在哪里: 下面是函数set_root_an
-
主要内容:树的结点,子树和空树,结点的度和层次,有序树和无序树,森林,树的表示方法,总结之前介绍的所有的 数据结构都是 线性存储结构。本章所介绍的树结构是一种非线性存储结构,存储的是具有“一对多”关系的数据元素的集合。 (A)
-
本文向大家介绍Oracle SQL树形结构查询,包括了Oracle SQL树形结构查询的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 oracle中的select语句可以用START WITH...CONNECT BY PRIOR子句实现递归查询,connect by 是结构化查询中用到的,其基本语法是: 简单说来是将一个树状结构存储在一张表里,比如一个表中存在两个字段: id,parentid那么通过
-
问题内容: 所以,我的问题是,我想构建这两个表的树: 树应该看起来像: p p_0 p_0_0 p_0_1 p_0_1_0 p_0_1_1 q 有人可以帮我解决递归解决方案吗? 问题答案: 为此,您不需要在数据库中创建2个表,您可以仅从一个表中进行维护,如下所示 生成的数组将像 您需要使用下面的递归函数来实现它 该算法非常简单: 取所有元素的数组和当前父代的ID(最初为0 / nothing /
-
在Tableau中,可以构建层次结构以可视化数据。可以通过以下步骤在Tableau中创建它: 例如,考虑数据源,例如Sample-Superstore,以及它的维度和度量。 第1步: 首先转到工作表。然后, 选择一个维度,然后右键单击该维度以创建层次结构。 转到“层次结构(Hierarchy)”选项。 并且,单击下面屏幕截图中显示的“创建层次结构(Create Hierarchy)”选项。 第2步
-
问题内容: 是否有一个良好的可用(标准Java)数据结构来表示Java中的树? 具体来说,我需要代表以下内容: 任何节点上的树都可以有任意数量的子代 每个节点(在根之后)只是一个字符串(其子代也是字符串) 我需要能够获得代表给定节点的输入字符串的所有子代(某种形式的列表或字符串数组) 是否有可用的结构或者我需要创建自己的结构(如果这样的话,实施建议会很好)。 问题答案: 这里: 那是可用于或任
-
问题内容: 我有一个jenkins管道,其设置如下,其中Build A是管道的开始,并在完成时触发构建B,依此类推(如下所示)。到目前为止,我已经实现了Build A,B和C。我使用了Jenkins参数化的Trigger插件作为构建后的动作来触发我的构建。 无论如何,在构建B完成之后,有什么我可以根据构建B之后的构建用fork启动构建的参数的方法,如下所示。Build C和Build D是将部署到
-
C/C++ 数组允许定义可存储相同类型数据项的变量,但是结构是 C++ 中另一种用户自定义的可用的数据类型,它允许您存储不同类型的数据项。 结构用于表示一条记录,假设您想要跟踪图书馆中书本的动态,您可能需要跟踪每本书的下列属性: Title :标题 Author :作者 Subject :类目 Book ID :书的 ID 定义结构 为了定义结构,您必须使用 struct 语句。struct 语句

