Python使用os.listdir()和os.walk()获取文件路径与文件下所有目录的方法
在python3.6版本中去掉了os.path.walk()函数
os.walk()
函数声明:walk(top,topdown=True,oneerror=None)
- 1、参数top表示需要遍历的目录树的路径
- 2、参数农户topdown默认是"True",表示首先返回根目录树下的文件,然后,再遍历目录树的子目录。topdown的值为"False",则表示先遍历目录树的子目录,返回子目录下的文件,最后返回根目录下的文件
- 3、参数oneerror的默认值是"None",表示忽略文件遍历时产生的错误,如果不为空,则提供一个自定义函数提示错误信息,后边遍历抛出异常
- 4、函数返回一个元组,该元组有3个元素,这3个元素分别表示'每次遍历的路径名,目录列表和文件列表'
os.walk()实例:
import os
def walk(path):
if not os.path.exists(path):
return -1
for root,dirs,names in os.walk(path):
for filename in names:
print(os.path.join(root,filename)) #路径和文件名连接构成完整路径
if __name__=='__main__':
path = "C:\\Users\\Administrator\\Desktop\\2017-9-1"
walk(path)
输出结果:
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\2017-9-1\2017-9-1.txt
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\2017-9-1\2017-9-1storage.txt
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\2017-9-1\apk.conf
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\2017-9-1\数据采集导入质量统计_2017-09-01.docx
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\2017-9-1\test1\2017-9-1.txt
C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\2017-9-1\test2\2017-9-1.txt
1.os.listdir(path='')
其中参数path为需要列出的目录路径。该函数返回指定的文件夹包含的文件或文件夹的名字的列表。
2.walk(top, topdown=True, onerror=None, followlinks=False)
os.walk(path)返回三个值:parent, dirnames, filenames,分别表示path的路径、path路径下的文件夹的名字和path路径下文件夹以外的其他文件。
应用1:在一个目录下面只有文件时可以使用os.listdir()。
比如文件test_file文件中包含三个文件,即:
test_file:
test1.txt
test2.txt
test3.txt
可以使用如下代码获取每个文件的绝对路径:
>>> import os >>> path = r'C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file' >>> for each_file in os.listdir(path): print(os.path.join(path,each_file))
结果如下:
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\test1.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\test2.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\test3.txt
应用2:当一个目录下面既有文件又有目录(文件夹),可使用os.walk()读取里面所有文件。
比如文件test_file中既包含文件也包含文件夹:
Test_file:
file1:
test1.txt
test2.txt
test3.txt
file2:
test1.txt
test2.txt
test3.txt
test1.txt
test2.txt
test3.txt
使用os.walk()可获得:
>>> import os >>> path = r'C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file' >>> for parent,dirnames,filenames in os.walk(path): print(parent,dirnames,filenames)
结果如下:
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file ['file1', 'file2'] ['test1.txt', 'test2.txt', 'test3.txt']
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file1 [] ['test1.txt', 'test2.txt', 'test3.txt']
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file2 [] ['test1.txt', 'test2.txt', 'test3.txt']
- parent:列出了目录路径下面所有存在的目录的名称
- dirnames:文件夹名
- filenames:列出了目录路径下面所有文件的名称
通过下面代码可获得给定路径下所有的文件路径:
>>> import os >>> path = r'C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file' >>> for parent,dirnames,filenames in os.walk(path): for filename in filenames: print(os.path.join(parent,filename))
结果如下:
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\test1.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\test2.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\test3.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file1\test1.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file1\test2.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file1\test3.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file2\test1.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file2\test2.txt
C:\Users\XXN\Desktop\test_file\file2\test3.txt
应用3:编写一个程序,用户输入关键字,查找当前文件夹内(如果当前文件夹内包含文件夹,则进入文件夹继续搜索)所有含有该关键字的文本文件(.txt后缀),要求显示该文件所在的位置以及关键字在文件中的具体位置(第几行第几个字符)
思路:
1.先把当前文件夹下的.txt文件以及当前文件包含的子文件夹中的.txt文件的路径全部保存至一个txt_list列表中;
2.以读取的方式打开txt_list中每个路径的文件,并将每个文件中出现关键字的行数以及关键字索引保存至一个字典dict_keywords中。
3.按格式输出。
代码演示:
import os
def print_keywords(dict_keywords):
keys = dict_keywords.keys()
keys = sorted(keys)
for each in keys:
print('关键字出现在第 %s 行,第 %s 个位置。'% (each, str(dict_keywords[each])))
def line_keywords(line, keywords):
key_index = []
start = line.find(keywords)
while start!=-1:
key_index.append(start+1)
start = line.find(keywords, start+1)
return key_index
def file_keywords(filename, keywords):
f = open(filename,'r')
line = 0
dict_keywords = dict()
for each_line in f:
line +=1
if keywords in each_line:
key_index = line_keywords(each_line, keywords)
dict_keywords[line]= key_index
f.close()
return dict_keywords
def file_search(keywords, flag):
all_files = os.walk(os.getcwd())
txt_list = []
for each in all_files:
for filename in each[2]:
if os.path.splitext(filename)[1] == '.txt':
txt_list.append(os.path.join(each[0],filename))
for each_txt_file in txt_list:
dict_keywors = file_keywords(each_txt_file, keywords)
print('====================================================')
print('在文件【%s】中找到关键字【%s】' % (each_txt_file, keywords))
if flag in ['YES', 'Yes', 'yes']:
print_keywords(dict_keywors)
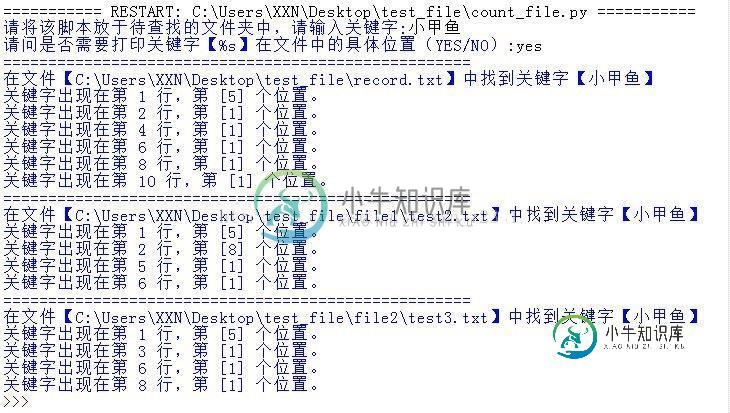
keywords = input("请将该脚本放于待查找的文件夹中,请输入关键字:")
flag = input("请问是否需要打印关键字【%s】在文件中的具体位置(YES/NO):")
file_search(keywords, flag)
运行结果如下:
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,谢谢大家对小牛知识库的支持。如果你想了解更多相关内容请查看下面相关链接
-
本文向大家介绍Python使用os.listdir和os.walk获取文件路径,包括了Python使用os.listdir和os.walk获取文件路径的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 情况1:在一个目录下面只有文件,没有文件夹,这个时候可以使用os.listdir 在我们的桌面上有一个file目录(文件夹),里面有三个文件 file(dir)| --|test1.txt --|test2.
-
本文向大家介绍python 获取文件下所有文件或目录os.walk()的实例,包括了python 获取文件下所有文件或目录os.walk()的实例的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在python3.6版本中去掉了os.path.walk()函数 os.walk() 函数声明:walk(top,topdown=True,oneerror=None) 1、参数top表示需要遍历的目录树的路径
-
本文向大家介绍Python获取文件所在目录和文件名的方法,包括了Python获取文件所在目录和文件名的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 实例如下: 输出: 以上就是小编为大家带来的Python获取文件所在目录和文件名的方法全部内容了,希望大家多多支持呐喊教程~
-
本文向大家介绍Python如何获取文件路径/目录,包括了Python如何获取文件路径/目录的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 一、获取文件路径实现 1.1 获取当前文件路径 __file__变量其实有个问题,当文件被是被调用文件时__file__总是文件的绝对路径;但当文件是直接被执行的文件时,__file__并不总是文件的绝对路径,而是你执行该文件时给python传的路径。比如你是pyth
-
本文向大家介绍PHP文件操作之获取目录下文件与计算相对路径的方法,包括了PHP文件操作之获取目录下文件与计算相对路径的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 获取目录下文件 1、获取目录下文件,不包括子目录 2、获取目录下所有文件,包括子目录 计算两个文件之间的相对路径方法 php 计算两个文件之间的相对路径方法 例如: 文件A 的路径是 /home/web/lib/img/cache.ph
-
本文向大家介绍python获取指定目录下所有文件名列表的方法,包括了python获取指定目录下所有文件名列表的方法的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本文实例讲述了python获取指定目录下所有文件名列表的方法。分享给大家供大家参考。具体实现方法如下: 这里python代码实现获取文件名列表的功能,可以指定文件中包含的字符,方便提取特定类型的文件名列表: 可以使用pip在线安装wlab 还是

