Android布局技巧之include、merge与ViewStub标签的巧用
前言
在开发中UI布局是我们都会遇到的问题,随着UI越来越多,布局的重复性、复杂度也会随之增长。
相信大家经常听到include、merge、ViewStub这样的标签,官方也提到这三种布局可用于布局的优化。今天就介绍下这三种布局的使用,记录下来,便于后续app中的使用。
include布局重用
app开发过程中,会遇到不同页面里有相同的布局,这时我们可以将这些通用的布局提取出来到一个单独的layout文件里,再使用<include>标签引入到相应的页面布局文件里,主要通过include的layout属性引用。
举个栗子
include的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:id="@+id/container" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv1" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这里是来自include布局" /> </RelativeLayout>
activity的布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv2" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="以下的内容来自include标签" /> <include android:id="@+id/container" layout="@layout/include_layout" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/tv" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" /> </RelativeLayout>
这个标签在日常工作使用还是很常见的。这里有几点需要注意下:
1、如果给include标签 和 include所加载的布局 都添加id的话,那么id要保持一致,如例子中都是container,否则是在代码中获取不到RelativeLayout容器的。 当然我们可以避免这样的问题,只需要给其中一项添加id属性就可以。
2、include布局里元素的id 要和 include所在页面布局里的其他元素id 不同,如例子中的两个textview,如果把id设置相同了,程序运行起来并不会报错,但是textview的赋值只会赋值给其中的一个。
3、如果需要给include标签设置位置属性的话,如例子中的layout_below、layout_marginTop,这时候 必须 同时设置include标签的宽高属性layout_width、layout_height,否则编译器是会报错的。一般情况不需要设置include的其他属性,直接加载布局文件 <include layout="@layout/...."/>
4、布局中可以包含两个相同的include标签,如下代码所示 两个include都加载layout="@layout/include_layout"
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="以下的内容来自include标签" /> <include android:id="@+id/container" layout="@layout/include_layout" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_below="@+id/tv" android:layout_marginTop="10dp" /> <include android:id="@+id/container2" layout="@layout/include_layout" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="80dp" /> </RelativeLayout>
可以设置不同include的id属性,引用的时候如下可以正常显示:
View view = findViewById(R.id.container2);
TextView textView = view.findViewById(R.id.tv);
textView.setText("这里是来自 第二个 include布局");
merge减少视图层级
merge标签可用于减少视图层级来优化布局,可以配合include使用,如果include标签的父布局 和 include布局的根容器是相同类型的,那么根容器的可以使用merge代替。
页面布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="以下的内容不是来自merge标签" /> <include layout="@layout/merge_layout" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" /> </LinearLayout>
先看没有使用merge的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这里是不是来自merge布局" /> </LinearLayout>
看下view层的结构:
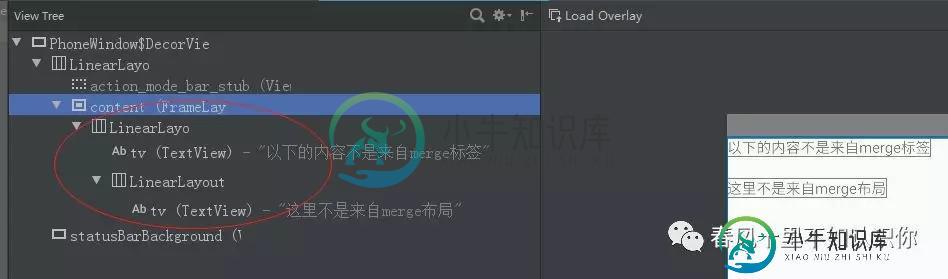
再看使用了merge的:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"> <TextView android:id="@+id/tv" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="这里是来自merge布局" /> </merge>
view层结构:
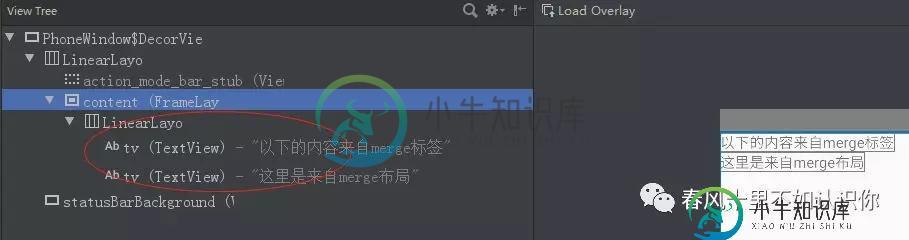
可以看到对比,减少了一层的LinearLayout的嵌套,需要注意的是使用merge的布局,在include的标签设置距离属性没有生效,可以将一些间距属性设置到include布局里元素上,具体看项目需求使用。
ViewStub按需加载
按需加载 顾名思义需要的时候再去加载,不需要的时候可以不用加载,节约内存使用。通常情况我们会使用setVisibility方法来控制视图的显示和隐藏,但是这种情况视图已经加载了。
比如app中页面里某个布局只需要在特定的情况下才显示,其余情况下可以不用加载显示,这时候可以使用ViewStub。
layout属性是需要加载布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <ViewStub android:id="@+id/viewstub" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="20dp" android:layout="@layout/viewstub_layout" /> </LinearLayout>
需要注意的是 ViewStub的inflate()方法只能被调用一次,一旦调用后,ViewStub将从视图中移除,被对应的layout布局取代,同时会保留ViewStub上设置的属性效果。
ViewStub viewstub = findViewById(R.id.viewstub); viewstub.inflate();
这篇关于include、merge、ViewStub的使用就介绍到这里了,具体使用情况还得视项目而定。
最后附上github地址https://github.com/taixiang/include (本地下载)
总结
以上就是这篇文章的全部内容了,希望本文的内容对大家的学习或者工作具有一定的参考学习价值,如果有疑问大家可以留言交流,谢谢大家对小牛知识库的支持。
-
一、<include/> 标签在布局优化中是使用最多的一个标签了,它就是为了解决重复定义布局的问题。标签就相当于C、C++中的include头文件一样,把一些常用的底层的API封装起来,需要的时候引入即可。在一些开源的J2EE中许多XML配置文件也都会使用标签,将多个配置文件组合成为一个更为复杂的配置文件,如最常见的S2SH。 在以前Android开发中,由于ActionBar设计上的不统一以及兼
-
本文向大家介绍Android抽象布局——include、merge 、ViewStub详解,包括了Android抽象布局——include、merge 、ViewStub详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 在布局优化中,Androi的官方提到了这三种布局<include />、<merge />、<ViewStub />,并介绍了这三种布局各有的优势,下面也是简单说一下他们的优势,以及怎
-
本文向大家介绍Android中使用include标签和merge标签重复使用布局,包括了Android中使用include标签和merge标签重复使用布局的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 尽管Android提供了各种组件来实现小而可复用的交互元素,你也可能因为布局需要复用一个大组件。为了高效复用完整布局,你可以使用<include/>和<merge/>标签嵌入另一个布局到当前布局。所以当你
-
本文向大家介绍Android布局技巧之创建可重用的UI组件,包括了Android布局技巧之创建可重用的UI组件的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Android平台提供了大量的UI构件,你可以将这些小的视觉块(构件)搭建在一起,呈现给用户复杂且有用的画面。然而,应用程序有时需要一些高级的视觉组件。为了满足这一需求,并且能高效的实现,你可以把多个标准的构件结合起来成为一个单独的、可重用的组件。
-
本文向大家介绍Android布局优化之ViewStub控件,包括了Android布局优化之ViewStub控件的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 ViewStub是Android布局优化中一个很不错的标签/控件,直接继承自View。虽然Android开发人员基本上都听说过,但是真正用的可能不多。 ViewStub可以理解成一个非常轻量级的View,与其他的控件一样,有着自己的属性及特定的方法
-
本文向大家介绍Android中关于CoordinatorLayout的一些实用布局技巧,包括了Android中关于CoordinatorLayout的一些实用布局技巧的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 介绍 CoordinatorLayout是一个“加强版”的 FrameLayout,它主要有两个用途: (1) 用作应用的顶层布局管理器 (2) 通过为子View指定 behavior 实现自

