理解Docker(1):Docker安装和基础用法详细介绍
Docker是一个用了一种新颖方式实现的超轻量虚拟机,在实现的原理和应用上还是和VM有巨大差别,专业的叫法是应用容器(Application Container)。(我个人还是喜欢称虚拟机)
1. 安装
1.1 在 Ubuntu 14.04 上安装 Docker
前提要求:
内核版本必须是3.10或者以上
依次执行下面的步骤:
sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get install apt-transport-https ca-certificates sudo apt-key adv --keyserver hkp://p80.pool.sks-keyservers.net:80 --recv-keys 58118E89F3A912897C070ADBF76221572C52609D 编辑 /etc/apt/sources.list.d/docker.list 文件,添加 deb https://apt.dockerproject.org/repo ubuntu-trusty main sudo apt-get update sudo apt-get purge lxc-docker apt-cache policy docker-engine apt-get upgrade sudo apt-get install linux-image-extra-$(uname -r) linux-image-extra-virtual sudo apt-get install docker-engine
至此,安装过程完成。
运行 sudo service docker start 启动 Docker 守护进程。
运行 docker version 查看 Docker 版本
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker --version Docker version 1.12.1, build 23cf638
启动第一个容器:
启动第一个Docker 容器 docker run hello-world
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker run hello-world Hello from Docker! This message shows that your installation appears to be working correctly.
它的运行成功也表明前面的安装步骤都运行正确了。
以上内容参考自 Docker 官网:https://docs.docker.com/engine/installation/linux/ubuntulinux/
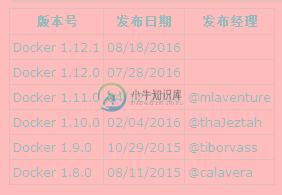
1.2 Docker 到目前(2016/09/16)为止的版本历史
2. Docker 的基本操作
2.1 Docker 容器的状态机
一个容器在某个时刻可能处于以下几种状态之一:
- created:已经被创建 (使用 docker ps -a 命令可以列出)但是还没有被启动 (使用 docker ps 命令还无法列出)
- running:运行中
- paused:容器的进程被暂停了
- restarting:容器的进程正在重启过程中
- exited:上图中的 stopped 状态,表示容器之前运行过但是现在处于停止状态(要区别于 created 状态,它是指一个新创出的尚未运行过的容器)。可以通过 start 命令使其重新进入 running 状态
- destroyed:容器被删除了,再也不存在了
你可以在 docker inspect 命令的输出中查看其详细状态:
"State": {
"Status": "running",
"Running": true,
"Paused": false,
"Restarting": false,
"OOMKilled": false,
"Dead": false,
"Pid": 4597,
"ExitCode": 0,
"Error": "",
"StartedAt": "2016-09-16T08:09:34.53403504Z",
"FinishedAt": "2016-09-16T08:06:44.365106765Z"
}
2.2 Docker 命令概述
我们可以把Docker 的命令大概地分类如下:
镜像操作: build Build an image from a Dockerfile commit Create a new image from a container's changes images List images load Load an image from a tar archive or STDIN pull Pull an image or a repository from a registry push Push an image or a repository to a registry rmi Remove one or more images search Search the Docker Hub for images tag Tag an image into a repository save Save one or more images to a tar archive (streamed to STDOUT by default) history 显示某镜像的历史 inspect 获取镜像的详细信息 容器及其中应用的生命周期操作: create Create a new container (创建一个容器) kill Kill one or more running containers inspect Return low-level information on a container, image or task pause Pause all processes within one or more containers ps List containers rm Remove one or more containers (删除一个或者多个容器) rename Rename a container restart Restart a container run Run a command in a new container (创建并启动一个容器) start Start one or more stopped containers (启动一个处于停止状态的容器) stats Display a live stream of container(s) resource usage statistics (显示容器实时的资源消耗信息) stop Stop one or more running containers (停止一个处于运行状态的容器) top Display the running processes of a container unpause Unpause all processes within one or more containers update Update configuration of one or more containers wait Block until a container stops, then print its exit code attach Attach to a running container exec Run a command in a running container port List port mappings or a specific mapping for the container logs 获取容器的日志 容器文件系统操作: cp Copy files/folders between a container and the local filesystem diff Inspect changes on a container's filesystem export Export a container's filesystem as a tar archive import Import the contents from a tarball to create a filesystem image Docker registry 操作: login Log in to a Docker registry. logout Log out from a Docker registry. Volume 操作 volume Manage Docker volumes 网络操作 network Manage Docker networks Swarm 相关操作 swarm Manage Docker Swarm service Manage Docker services node Manage Docker Swarm nodes 系统操作: version Show the Docker version information events Get real time events from the server (持续返回docker 事件) info Display system-wide information (显示Docker 主机系统范围内的信息)
比较有意思的几个命令:
(1)容器从生到死整个生命周期
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker create --name web31 training/webapp python app.py #创建名字为 web31 的容器
7465f4cb7c49555af32929bd1bc4213f5e72643c0116450e495b71c7ec128502
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' web31 #其状态为 created
created
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker start web31 #启动容器
web31
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' web31 #其状态为 running
running
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker pause web31 #暂停容器
web31
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' web31
paused
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker unpause web31 #继续容器
web31
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' web31
running
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker rename web31 newweb31 #重命名
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' newweb31
running
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker top newweb31 #在容器中运行 top 命令
UID PID PPID C STIME TTY TIME CMD
root 5009 4979 0 16:28 ? 00:00:00 python app.py
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker logs newweb31 #获取容器的日志
* Running on http://0.0.0.0:5000/ (Press CTRL+C to quit)
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker stop newweb31 #停止容器
newweb31
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' newweb31
exited
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker rm newweb31 #删除容器
newweb31
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker inspect --format='{{.State.Status}}' newweb31
Error: No such image, container or task: newweb31
(2) docker stop 和 docker kill
在docker stop 命令执行的时候,会先向容器中PID为1的进程发送系统信号 SIGTERM,然后等待容器中的应用程序终止执行,如果等待时间达到设定的超时时间(默认为 10秒,用户可以指定特定超时时长),会继续发送SIGKILL的系统信号强行kill掉进程。在容器中的应用程序,可以选择忽略和不处理SIGTERM信号,不过一旦达到超时时间,程序就会被系统强行kill掉,因为SIGKILL信号是直接发往系统内核的,应用程序没有机会去处理它。
比如运行 docker stop web5 -t 20 命令后:
2016-09-16T16:01:18.206540853+08:00 container kill b3256ef1400a7f6a6f242e377a77af5e25d3b12237c4ee7c2e9b31a5f6437868 (image=training/webapp, name=web5, signal=15)
2016-09-16T16:01:38.212352224+08:00 container kill b3256ef1400a7f6a6f242e377a77af5e25d3b12237c4ee7c2e9b31a5f6437868 (image=training/webapp, name=web5, signal=9)
2016-09-16T16:01:38.235021315+08:00 container die b3256ef1400a7f6a6f242e377a77af5e25d3b12237c4ee7c2e9b31a5f6437868 (exitCode=137, image=training/webapp, name=web5)
能看到:
- 首先 docker 向容器发出 SIGTERM 信号(signal=15)
- 等待20秒 (01:18 到 01:38)
- 再发送 SIGKILL 系统信号 (signal = 9)
- 然后容器被杀掉了 (die)
而 docker kill 命令会直接发出SIGKILL的系统信号,以强行终止容器中程序的运行。运行 docker kill web5 命令后:
2016-09-16T16:06:44.351086471+08:00 container kill b3256ef1400a7f6a6f242e377a77af5e25d3b12237c4ee7c2e9b31a5f6437868 (image=training/webapp, name=web5, signal=9)
2016-09-16T16:06:44.365116100+08:00 container die b3256ef1400a7f6a6f242e377a77af5e25d3b12237c4ee7c2e9b31a5f6437868 (exitCode=137, image=training/webapp, name=web5)
可见直接发出的是 SIGKILL 信号,容器立马就被杀掉了。
(3)使用 docker cp 在 host 和 container 之间拷贝文件或者目录
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker cp /home/sammy/mydockerbuild/Dockerfile web5:/webapp #从 host 拷贝文件到 container 里面 root@devstack:/home/sammy# root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker cp web5:/webapp/Dockerfile /home/sammy/Dockerfile #从 container 里面拷贝文件到 host 上 root@devstack:/home/sammy# ls /home/sammy chroot devstack Dockerfile mongodbdocker mydockerbuild webapp
(4)docker export 和 import
docker export:将一个容器的文件系统打包为一个压缩文件
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker export web5 -o ./web5 root@devstack:/home/sammy# ls chroot devstack Dockerfile mongodbdocker mydockerbuild web5 webapp
docker import:从一个压缩文件创建一个镜像
root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker import web5 web5img -m "imported on 0916" sha256:745bb258be0a69a517367667646148bb2f662565bb3d222b50c0c22e5274a926 root@devstack:/home/sammy# docker history web5img IMAGE CREATED CREATED BY SIZE COMMENT 745bb258be0a 6 seconds ago 324 MB imported on 0916
2.3 docker run 命令
docker run 命令会创建一个容器并启动它,它也是包含很多的参数,按照用途将它们分类如下:
cgroups 和 namespace 相关: --blkio-weight value Block IO (relative weight), between 10 and 1000 --blkio-weight-device value Block IO weight (relative device weight) (default []) --cgroup-parent string Optional parent cgroup for the container --cpu-percent int CPU percent (Windows only) --cpu-period int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) period --cpu-quota int Limit CPU CFS (Completely Fair Scheduler) quota -c, --cpu-shares int CPU shares (relative weight) --cpuset-cpus string CPUs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1) --cpuset-mems string MEMs in which to allow execution (0-3, 0,1) --device-read-bps value Limit read rate (bytes per second) from a device (default []) --device-read-iops value Limit read rate (IO per second) from a device (default []) --device-write-bps value Limit write rate (bytes per second) to a device (default []) --device-write-iops value Limit write rate (IO per second) to a device (default []) --ipc string IPC namespace to use -m, --memory string Memory limit --memory-reservation string Memory soft limit --memory-swap string Swap limit equal to memory plus swap: '-1' to enable unlimited swap --memory-swappiness int Tune container memory swappiness (0 to 100) (default -1) --kernel-memory string Kernel memory limit -u, --user string Username or UID (format: <name|uid>[:<group|gid>]) --userns string User namespace to use --uts string UTS namespace to use -h, --hostname string Container host name --pid string PID namespace to use --pids-limit int Tune container pids limit (set -1 for unlimited) --isolation string Container isolation technology --io-maxbandwidth string Maximum IO bandwidth limit for the system drive (Windows only) --io-maxiops uint Maximum IOps limit for the system drive (Windows only) linux process capabilities 相关参数: --cap-add value Add Linux capabilities (default []) --cap-drop value Drop Linux capabilities (default []) 容器运行模式和环境相关: -d, --detach Run container in background and print container ID -e, --env value Set environment variables (default []) --env-file value Read in a file of environment variables (default []) DNS 相关: --dns value Set custom DNS servers (default []) --dns-opt value Set DNS options (default []) --dns-search value Set custom DNS search domains (default []) 健康检查相关: --health-cmd string Command to run to check health --health-interval duration Time between running the check --health-retries int Consecutive failures needed to report unhealthy --health-timeout duration Maximum time to allow one check to run --no-healthcheck Disable any container-specified HEALTHCHECK IP 和端口: --ip string Container IPv4 address (e.g. 172.30.100.104) --ip6 string Container IPv6 address (e.g. 2001:db8::33) -p, --publish value Publish a container's port(s) to the host (default []) -P, --publish-all Publish all exposed ports to random ports --expose value Expose a port or a range of ports (default []) --mac-address string Container MAC address (e.g. 92:d0:c6:0a:29:33) --add-host value Add a custom host-to-IP mapping (host:ip) (default []) Volume 相关: -v, --volume value Bind mount a volume (default []) --volume-driver string Optional volume driver for the container --volumes-from value Mount volumes from the specified container(s) (default []) --storage-opt value Storage driver options for the container (default []) Network 有关: --network string Connect a container to a network (default "default") --network-alias value Add network-scoped alias for the container (default []) --link value Add link to another container (default []) --link-local-ip value Container IPv4/IPv6 link-local addresses (default []) 日志有关: --log-driver string Logging driver for the container --log-opt value Log driver options (default []) 交互性有关: -a, --attach value Attach to STDIN, STDOUT or STDERR (default []) -i, --interactive Keep STDIN open even if not attached OOM 有关: --oom-kill-disable Disable OOM Killer --oom-score-adj int Tune host's OOM preferences (-1000 to 1000) 其它(待更进一步分类): --cidfile string Write the container ID to the file --detach-keys string Override the key sequence for detaching a container --device value Add a host device to the container (default []) --disable-content-trust Skip image verification (default true) --entrypoint string Overwrite the default ENTRYPOINT of the image --group-add value Add additional groups to join (default []) --help Print usage -l, --label value Set meta data on a container (default []) --label-file value Read in a line delimited file of labels (default []) --name string Assign a name to the container --privileged Give extended privileges to this container --read-only Mount the container's root filesystem as read only --restart string Restart policy to apply when a container exits (default "no") --rm Automatically remove the container when it exits --runtime string Runtime to use for this container --security-opt value Security Options (default []) --shm-size string Size of /dev/shm, default value is 64MB --sig-proxy Proxy received signals to the process (default true) --stop-signal string Signal to stop a container, SIGTERM by default (default "SIGTERM") --sysctl value Sysctl options (default map[]) --tmpfs value Mount a tmpfs directory (default []) -t, --tty Allocate a pseudo-TTY --ulimit value Ulimit options (default []) -w, --workdir string Working directory inside the container
具体的内容以后会有专门文件分析。
3. Doker 平台的基本构成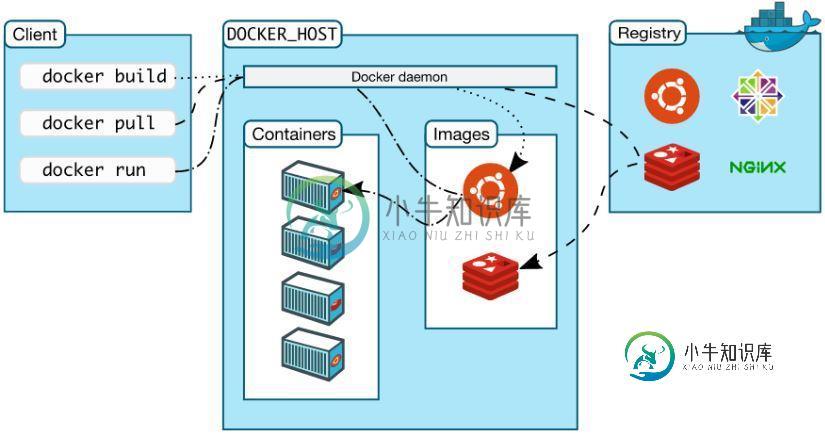
Docker 平台基本上由三部分组成:
- 客户端:用户使用 Docker 提供的工具(CLI 以及 API 等)来构建,上传镜像并发布命令来创建和启动容器
- Docker 主机:从 Docker registry 上下载镜像并启动容器
- Docker registry:Docker 镜像仓库,用于保存镜像,并提供镜像上传和下载
后面的文章会具体分析。
以上就是本文的全部内容,希望对大家的学习有所帮助,也希望大家多多支持小牛知识库。
-
本文向大家介绍Docker安装及基本使用方法详细介绍,包括了Docker安装及基本使用方法详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 Docker是一个用了一种新颖方式实现的超轻量虚拟机,在实现的原理和应用上还是和VM有巨大差别,专业的叫法是应用容器(Application Container)。(我个人还是喜欢称虚拟机) Docker应用容器相对于 VM 有以下几个优点: 启动速度快,容器
-
本文向大家介绍docker中安装quagga详细介绍,包括了docker中安装quagga详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 openstack中的虚拟路由器项目占用资源太多,需要将虚拟路由器迁移到Docker中,觉得首先要解决几个问题。 1.如何集成docker到openstack中,这个问题openstack官方给了三种方案,基于nova,heat,和单独的容器项目
-
本文向大家介绍理解Docker(2):Docker 镜像详细介绍,包括了理解Docker(2):Docker 镜像详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本系列文章将介绍Docker的有关知识: (1)Docker 安装及基本用法 (2)Docker 镜像 (3)Docker 容器的隔离性 - 使用 Linux namespace 隔离容器的运行环境 (4)Docker 容器的隔离性 -
-
本文向大家介绍docker kubernetes dashboard安装部署详细介绍,包括了docker kubernetes dashboard安装部署详细介绍的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 docker之kubernetes dashboard部署 1. 环境说明: 1). 架构: 注: 本次实验服务器环境均采用centos 7. 服务安装均采用yum install. 192.16
-
本文向大家介绍安装docker和docker-compose实例详解,包括了安装docker和docker-compose实例详解的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 1.卸载旧版本Docker 2.执行以下命令安装依赖包 3.鉴于国内网络问题,强烈建议使用国内源执行下面的命令添加 yum 软件源 4.安装Docker CE 5.设置开机启动 Docker CE 6.鉴于国内网络问题,后续拉取
-
本文向大家介绍Docker安装和基础用法 Docker入门教程第二篇,包括了Docker安装和基础用法 Docker入门教程第二篇的使用技巧和注意事项,需要的朋友参考一下 本系列文章将介绍Docker的有关知识: (1)Docker 安装及基本用法 (2)Docker 镜像 (3)Docker 容器的隔离性 - 使用 Linux namespace 隔离容器的运行环境 (4)Docker 容器的隔

